Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='3uzt' size=' | + | <StructureSection load='3uzt' size='350' side='right' caption='Human BARK1 complex with RNA and Mg+2 ion (green) (PDB code [[3uzt]])' scene='70/705677/Cv/1'> |
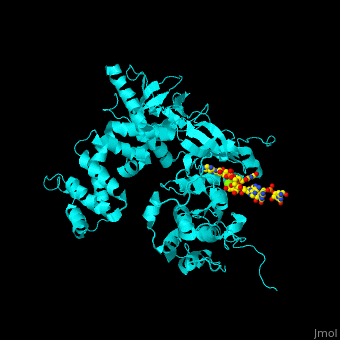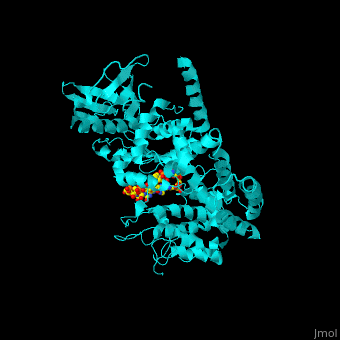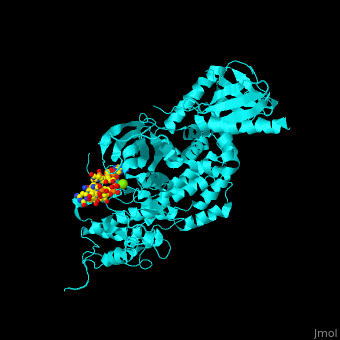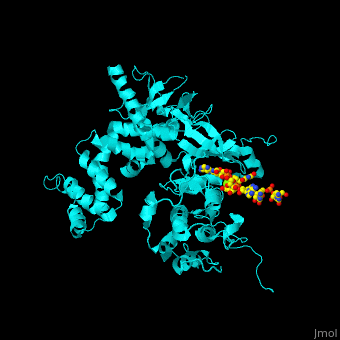
'''Beta adrenergic receptor kinase''' (BARK) is an intracellular serine/threonine kinase. BARK is activated by protein kinase A. BARK phosphorylates the β adregenic receptor (BAR) when it is occupied by the agonist thus causing its desensitization. BARK belongs to the family of G protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK). <ref>PMID:2871555</ref> <scene name='70/705677/Cv/2'>Human BARK1 complex with RNA and Mg+2 ion</scene> (PDB code [[3uzt]]).<ref>PMID:22727813</ref> | '''Beta adrenergic receptor kinase''' (BARK) is an intracellular serine/threonine kinase. BARK is activated by protein kinase A. BARK phosphorylates the β adregenic receptor (BAR) when it is occupied by the agonist thus causing its desensitization. BARK belongs to the family of G protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK). <ref>PMID:2871555</ref> <scene name='70/705677/Cv/2'>Human BARK1 complex with RNA and Mg+2 ion</scene> (PDB code [[3uzt]]).<ref>PMID:22727813</ref> | ||
Revision as of 10:13, 30 November 2015
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Benovic JL, Strasser RH, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ. Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: identification of a novel protein kinase that phosphorylates the agonist-occupied form of the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2797-801. PMID:2871555
- ↑ Tesmer VM, Lennarz S, Mayer G, Tesmer JJ. Molecular Mechanism for Inhibition of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 by a Selective RNA Aptamer. Structure. 2012 Jun 21. PMID:22727813 doi:10.1016/j.str.2012.05.002
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Cristina Murga, Joel L. Sussman