Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
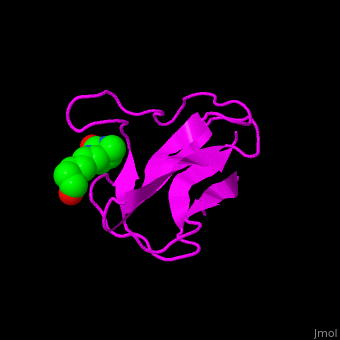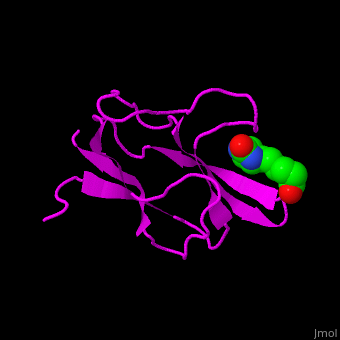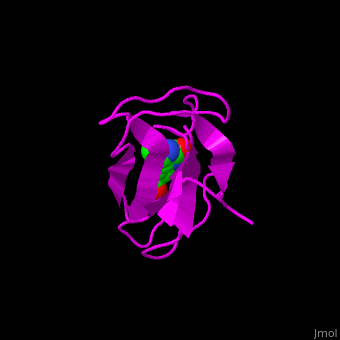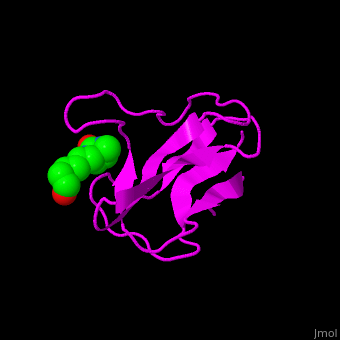
<StructureSection load='1bdo' size='350' side='right' scene='49/492046/Cv/1' caption='E. coli Acetyl-CoA carboxylase biotinyl domain complex with biotin (PDB code [[1bdo]]) '> | <StructureSection load='1bdo' size='350' side='right' scene='49/492046/Cv/1' caption='E. coli Acetyl-CoA carboxylase biotinyl domain complex with biotin (PDB code [[1bdo]]) '> | ||
| - | + | __TOC__ | |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Acetyl-CoA carboxylase''' (ACC) catalyzes the irreversible carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA. Malonyl-CoA is a building block in in the biosynthesis of fatty acids. ACC is biotin- and ATP-dependent enzyme. In mammals, 2 forms of ACC exist. ACC1 and ACC2 differ in their tissue distribution and function. | '''Acetyl-CoA carboxylase''' (ACC) catalyzes the irreversible carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA. Malonyl-CoA is a building block in in the biosynthesis of fatty acids. ACC is biotin- and ATP-dependent enzyme. In mammals, 2 forms of ACC exist. ACC1 and ACC2 differ in their tissue distribution and function. | ||
Revision as of 11:14, 30 November 2015
| |||||||||||
3D structures of acetyl-CoA carboxylase
Updated on 30-November-2015
References
- ↑ Athappilly FK, Hendrickson WA. Structure of the biotinyl domain of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase determined by MAD phasing. Structure. 1995 Dec 15;3(12):1407-19. PMID:8747466