6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase (DEBS)
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
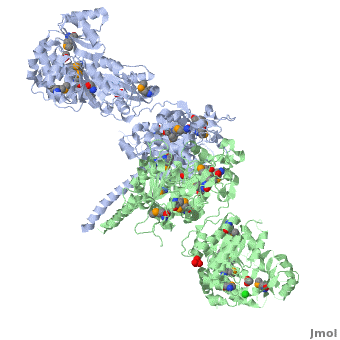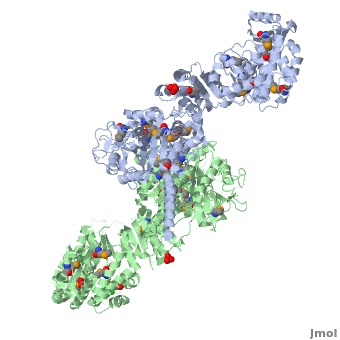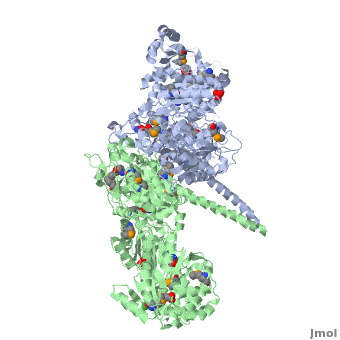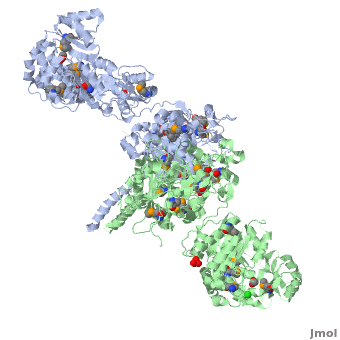
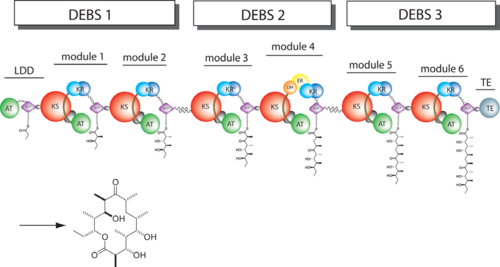
The 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase (DEBS), which catalyzes the formation of 6-dEB, consists of three large subunits, DEBS1, DEBS2 and DEBS3, each containing two modules and above 300 kD in size. There are 2 domains in the N-terminal loading module, responsible for priming the synthase with a proprionate starter unit, and 26 domains in the six extender modules, Each extender module contains at least three essential domains: a ketosynthase (KS), an acyl transferase (AT) and an acyl carrier protein (ACP). In detail, the AT domain selects the appropriate carbon extender unit and transfers the units from acyl-CoA onto the phosphopantetheine arm of ACP. The KSdomain accepts the polyketide chain from the previous module and catalyzes chain elongation reaction by adding an ACP-bound extender unit through decarboxylative condensation. | The 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase (DEBS), which catalyzes the formation of 6-dEB, consists of three large subunits, DEBS1, DEBS2 and DEBS3, each containing two modules and above 300 kD in size. There are 2 domains in the N-terminal loading module, responsible for priming the synthase with a proprionate starter unit, and 26 domains in the six extender modules, Each extender module contains at least three essential domains: a ketosynthase (KS), an acyl transferase (AT) and an acyl carrier protein (ACP). In detail, the AT domain selects the appropriate carbon extender unit and transfers the units from acyl-CoA onto the phosphopantetheine arm of ACP. The KSdomain accepts the polyketide chain from the previous module and catalyzes chain elongation reaction by adding an ACP-bound extender unit through decarboxylative condensation. | ||
| - | After the extender unit is added, it can be further processed by optional tailoring domains, including ketoreductases (KRs), dehydratases (DHs), and enoyl reductases (ERs), to yield a hydroxyl, enoyl, or methylene group at the beta-position. Finally, the thioesterase (TE) domain that located at the C-terminus of DEBS module 6 promotes the macrocyclization event which releases the final product, 6-dEB. | + | After the extender unit is added, it can be further processed by optional tailoring domains, including ketoreductases (KRs), dehydratases (DHs), and enoyl reductases (ERs), to yield a hydroxyl, enoyl, or methylene group at the beta-position. Finally, the thioesterase (TE) domain that located at the C-terminus of DEBS module 6 promotes the macrocyclization event which releases the final product, 6-dEB. <ref>PMID:17328673</ref> |
===Ketosynthase-acyltransferase (KS-AT)=== | ===Ketosynthase-acyltransferase (KS-AT)=== | ||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
}} | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
==Additional Resources== | ==Additional Resources== | ||
For additional information, see: [[Cancer]] | For additional information, see: [[Cancer]] | ||
Revision as of 10:25, 3 December 2015
| |||||||||||
3D structures of 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase
Updated on 03-December-2015
References
- ↑ Khosla C, Tang Y, Chen AY, Schnarr NA, Cane DE. Structure and mechanism of the 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase. Annu Rev Biochem. 2007;76:195-221. PMID:17328673 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.053105.093515
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Cancer
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Tsung-Yi Lin, Alexander Berchansky, Lawrence Sheringham Borketey, Joel L. Sussman, Jon Amoroso, David Canner, Jaime Prilusky