Calcium uptake protein 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
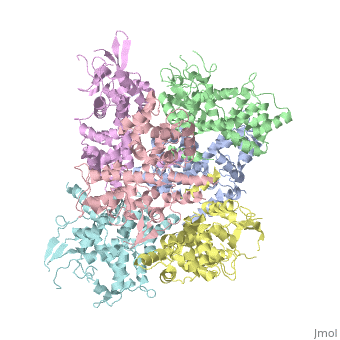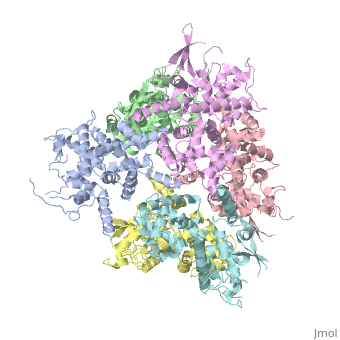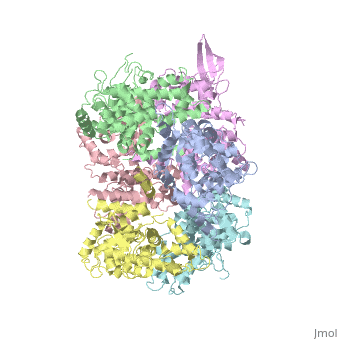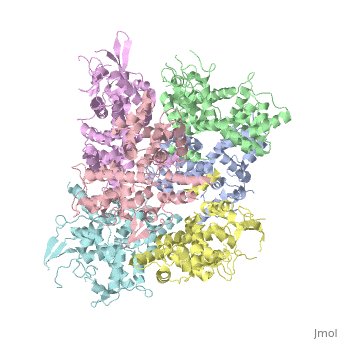
<StructureSection load='4NSC' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='4NSC' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | ||
| - | + | MICU 1 (Mitochondrial Calcium Uptake 1) is a key regulator of mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) required to increase calcium uptake by MCU when cytoplasmic calcium is high. | |
It also regulates glucose-dependent insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cells by regulating mitochondrial calcium uptake. | It also regulates glucose-dependent insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cells by regulating mitochondrial calcium uptake. | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| + | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9BPX6 Uniprot MICU1] | ||
| + | |||
MICU 1 is a regulator of Ca 2+ uptakes in mitochondria. To do this regulation, it can sense the concentration of calcium in the cytosol of the cell thanks to 2 EF-hand domains. It mainly acts on MCU which is a transmembrane uniporter channel located on the inner membrane of the mitochondria. To interact with MCU, MICU1 has to be linked to MICU2 (a paralogue protein). The entire complex of Ca2+ regulation is MICU1/MICU2/MCU/EMRE. EMRE is a protein which is required for the interaction of MCU with MICU1/MICU2. | MICU 1 is a regulator of Ca 2+ uptakes in mitochondria. To do this regulation, it can sense the concentration of calcium in the cytosol of the cell thanks to 2 EF-hand domains. It mainly acts on MCU which is a transmembrane uniporter channel located on the inner membrane of the mitochondria. To interact with MCU, MICU1 has to be linked to MICU2 (a paralogue protein). The entire complex of Ca2+ regulation is MICU1/MICU2/MCU/EMRE. EMRE is a protein which is required for the interaction of MCU with MICU1/MICU2. | ||
When it is not linked to Ca2+ it has an hexameric conformation. In this conformation MICU 1 silences the activity of MCU/EMRE and stop the Ca 2+ from entering the mitochondria by blocking the entrance of the channel. | When it is not linked to Ca2+ it has an hexameric conformation. In this conformation MICU 1 silences the activity of MCU/EMRE and stop the Ca 2+ from entering the mitochondria by blocking the entrance of the channel. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 14: | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
If MICU1 gene is modified, Ca2+ can be load in higher concentration in the mitochondry resulting Myopathy with extrapyramidal signs (MPXPS). This is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by early-onset proximal muscle weakness with a static course and moderately to grossly elevated serum creatine kinase levels accompanied by learning difficulties. Most patients develop subtle extrapyramidal motor signs that progress to a debilitating disorder of involuntary movement with variable features, including chorea, tremor, dystonic posturing and orofacial dyskinesia. Additional variable features include ataxia, microcephaly, ophthalmoplegia, ptosis, optic atrophy and axonal peripheral neuropathy. | If MICU1 gene is modified, Ca2+ can be load in higher concentration in the mitochondry resulting Myopathy with extrapyramidal signs (MPXPS). This is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by early-onset proximal muscle weakness with a static course and moderately to grossly elevated serum creatine kinase levels accompanied by learning difficulties. Most patients develop subtle extrapyramidal motor signs that progress to a debilitating disorder of involuntary movement with variable features, including chorea, tremor, dystonic posturing and orofacial dyskinesia. Additional variable features include ataxia, microcephaly, ophthalmoplegia, ptosis, optic atrophy and axonal peripheral neuropathy. | ||
| - | |||
| - | == Relevance == | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | + | In absence of Ca2+, MICU1 is an homohexamer with a <scene name='72/723172/Secondary_structure_of_micu_1/1'>secondary structure</scene> composed by several alpha helix, beta sheets and loops. When it <scene name='72/723172/Protein_dimer_when_ca_is_bound/3'>links to this ion</scene> , it becomes a homooligomer. | |
| - | + | MICU 1 is composed by differents domains : | |
| - | + | :- C helix region (or Coiled-coil domain) : this domain permits different interactions with other proteins (MCU/MICU2) and is required to assemble free Ca2+ with homohexamer. | |
| - | + | :- Polybasic region : it’s a domain which permits protein-protein interactions | |
| - | + | :- <scene name='72/723172/Ef_domains/1'>EF-hand domains</scene> There are 2 of them. They are the most important domains in MICU1 protein because they contain the Ca2+ binding region and detect the concentration of calcium in the cell for activation of signalling. An EF-hand domain is a calcium sensor. An EF-hand domain is a helix loop helix structural domain that means that it is 2 alpha helices linked by a short loop region. Ca2+ ions are coordinated in this space thanks to ligands within the loop : in EF-1 residues concerning are Asp231, Asn233, Asp235, Glu237 and Glu242 and in EF-2 they are Asp421, Asp423, Asn425, Glu427 and Glu432. When Ca2+ binds itself to this domain, the protein changes its conformation to expose a domain that can interact with other proteins. | |
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
| - | MCU : http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/gene/MCU | + | :MCU : http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/gene/MCU |
| - | MICU 2 : http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/gene/MICU2 | + | :MICU 2 : http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/gene/MICU2 |
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 15:14, 28 January 2016
Structure
| |||||||||||