1cbs
From Proteopedia
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
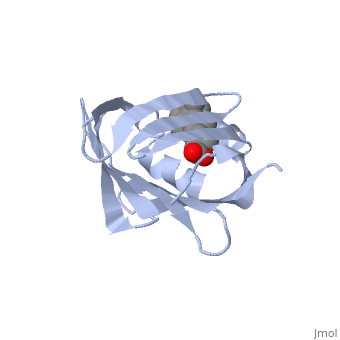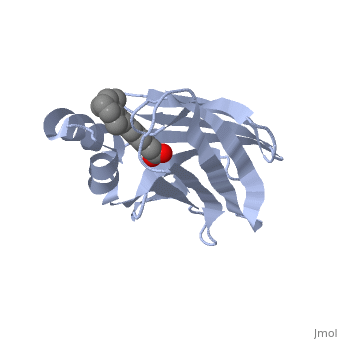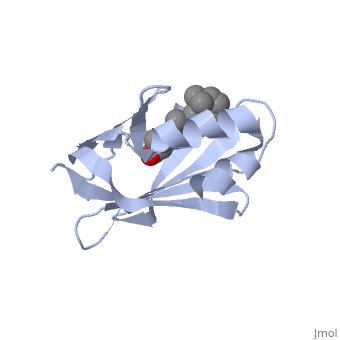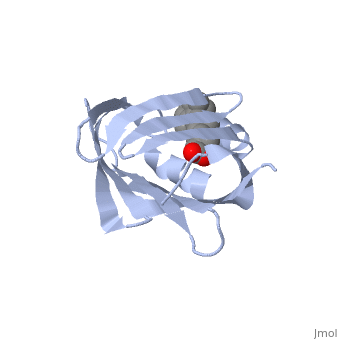
|PDB= 1cbs |SIZE=350|CAPTION= <scene name='initialview01'>1cbs</scene>, resolution 1.8Å | |PDB= 1cbs |SIZE=350|CAPTION= <scene name='initialview01'>1cbs</scene>, resolution 1.8Å | ||
|SITE= | |SITE= | ||
| - | |LIGAND= <scene name='pdbligand=REA:RETINOIC ACID'>REA</scene> | + | |LIGAND= <scene name='pdbligand=REA:RETINOIC+ACID'>REA</scene> |
|ACTIVITY= | |ACTIVITY= | ||
|GENE= HUMAN CRABP-II ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 Homo sapiens]) | |GENE= HUMAN CRABP-II ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 Homo sapiens]) | ||
| + | |DOMAIN= | ||
| + | |RELATEDENTRY= | ||
| + | |RESOURCES=<span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1cbs FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1cbs OCA], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1cbs PDBsum], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1cbs RCSB]</span> | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 25: | Line 28: | ||
[[Category: Jones, T A.]] | [[Category: Jones, T A.]] | ||
[[Category: Kleywegt, G J.]] | [[Category: Kleywegt, G J.]] | ||
| - | [[Category: REA]] | ||
[[Category: retinoic-acid transport]] | [[Category: retinoic-acid transport]] | ||
| - | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on | + | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Sun Mar 30 19:18:35 2008'' |
Revision as of 16:18, 30 March 2008
| |||||||
| , resolution 1.8Å | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | |||||||
| Gene: | HUMAN CRABP-II (Homo sapiens) | ||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBsum, RCSB | ||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF CELLULAR RETINOIC-ACID-BINDING PROTEINS I AND II IN COMPLEX WITH ALL-TRANS-RETINOIC ACID AND A SYNTHETIC RETINOID
Overview
BACKGROUND: Retinoic acid (RA) plays a fundamental role in diverse cellular activities. Cellular RA binding proteins (CRABPs) are thought to act by modulating the amount of RA available to nuclear RA receptors. CRABPs and cellular retinol-binding proteins (CRBPs) share a unique fold of two orthogonal beta-sheets that encapsulate their ligands. It has been suggested that a trio of residues are the prime determinants defining the high specificity of CRBPs and CRABPs for their physiological ligands. RESULTS: Bovine/murine CRABP I and human CRABP II have been crystallized in complex with their natural ligand, all-trans-RA. Human CRABP II has also been crystallized in complex with a synthetic retinoid, 'compound 19'. Their structures have been determined and refined at resolutions of 2.9 A, 1.8 A and 2.2 A, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: The retinoid-binding site in CRABPs differs significantly from that observed in CRBP. Structural changes in three juxtaposed areas of the protein create a new, displaced binding site for RA. The carboxylate of the ligand interacts with the expected trio of residues (Arg132, Tyr134 and Arg111; CRABP II numbering). The RA ligand is almost flat with the beta-ionone ring showing a significant deviation (-33 degrees) from a cis conformation relative to the isoprene tail. The edge atoms of the beta-ionone ring are accessible to solvent in a suitable orientation for presentation to metabolizing enzymes. The bulkier synthetic retinoid causes small conformational changes in the protein structure.
About this Structure
1CBS is a Single protein structure of sequence from Homo sapiens. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
Crystal structures of cellular retinoic acid binding proteins I and II in complex with all-trans-retinoic acid and a synthetic retinoid., Kleywegt GJ, Bergfors T, Senn H, Le Motte P, Gsell B, Shudo K, Jones TA, Structure. 1994 Dec 15;2(12):1241-58. PMID:7704533
Page seeded by OCA on Sun Mar 30 19:18:35 2008