From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
proteopedia linkproteopedia link
|
|
| Line 41: |
Line 41: |
| | | | |
| | 3. Dablon et al. The catalytic mechanism of f3-lactamases: NMR titration of an active-site lysine residue of the TEM-1 enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1996, 74: 1747-1752. | | 3. Dablon et al. The catalytic mechanism of f3-lactamases: NMR titration of an active-site lysine residue of the TEM-1 enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1996, 74: 1747-1752. |
| | + | |
| | + | 4. Fonze, E.; Charlier, P.; To'th, Y.; Vermeire, M.; Raquet, X.; Dubus, A.; Frere, J. M. TEM1 beta-lactamase structure solved by molecular replacement and refined structure of the S235A mutant. |
| | + | Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1995, 51, 682-694. |
| | + | |
| | + | 5. Lenfant, F.; Labia, R.; Masson, J. -. Replacement of lysine 234 affects transition state stabilization in the active site of ß-lactamase TEM1. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 17187-17194. |
Revision as of 10:21, 14 April 2016
|
Structural highlights
1xpb is a 1 chain structure with sequence from Escherichia coli. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA. For a guided tour on the structure components use FirstGlance.
| | Ligands: | |
| Activity: | Beta-lactamase, with EC number 3.5.2.6 |
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBe, RCSB, PDBsum |
| Related: | 1axb, 1bt5, 1btl, 1ck3, 1erm, 1ero, 1erq, 1esu, 1fqg, 1jtd, 1jtg, 1jvj, 1jwp, 1jwv, 1jwz, 1lhy, 1li0, 1li9, 1m40, 1nxy, 1ny0, 1nym, 1nyy, 1pzo, 1pzp, 1s0w, 1tem, 1xxm, 1yt4, 1zg4, 1zg6, 2v1z |
Background and History
Antibiotics have long been the primary line of defense against many infections. The advent of penicillin in the 1930s brought an end to an era of uncertainty: diseases once considered fatal became treatable. Unfortunately, natural selection stops for no species. Resistance to some form of antibiotic now has become standard for many infections.[A] Moreover, their liberal usage have resulted in “superbugs”, which are resistant to multiple antibiotics.[B] These strains are capable of secreting enzymes capable of deactivating the antibiotic or modifying their cell walls to render the antibiotic ineffective.
Many antibiotics such as penicillin, their derivatives (penams), and cephalosporins (cephams) possess a β-lactam ring (Figure 1).
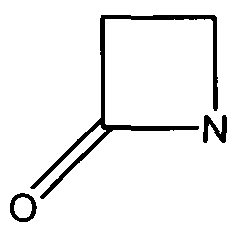
Figure 1. The beta-lactam ring is highlighted in red. Beta-lactamases function in hydrolyzing the amide bond within the ring, rendering the antibiotic ineffective. (Image Credit: Wikipedia)
β-Lactamases function by hydrolyzing the β-lactam ring within the antibiotic (Figure 2). This prevents the interaction between the cell wall and the antibiotic.
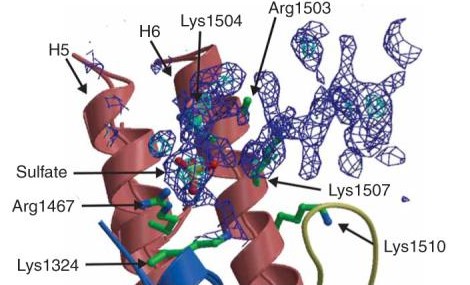
Figure 2. Bacteria are capable of becoming antibiotic resistant by catalyzing the hydrolysis of the β-lactam ring.
The TEM-1 subclass is one of the most common of all β-Lactamases.[3] Their prevalence began when bacteria started exhibiting penicillin resistance on a mass scale. Since the TEM-1 subclass has been prevalent for many years, many inhibitors have either been discovered or synthesized to prevent their catalytic function.
Function
Disease
Relevance
Structural highlights
This TEM1 CLass Antibiotic Resistant protein is similar in structure to other Beta Lactamases in its secondary structure. The protein consists of 236 amino acid residues, which are arranged into a particular structure to provide the function it was designed for. The structure itself consists of two main domains, forming a cleft in between them as the active site for the binding of a sulfate anion ligand. The first domain consists of five beta sheets, with three alpha helices overlaying the side facing the solvent, and another alpha helix flanking the sheets on the adjacent side. The other domain is characterized by its high concentration of alpha helices throughout the secondary structure of this domain. The protein in solution is solvated by 135 water molecules per asymmetric unit. In terms of overall structure, 42.2% consists of alpha helices, 17.5% participate in beta sheets, and 37.2% are turns and coils. Lysine 234, which is present on the wall of the active site as a constituent of one of the beta sheets, has been elucidated as an active binding agent towards substrates, as its amine group is involved in the electrostatic interaction towards penicillins.
|
References
1. Davies, J.; Davies, G. Origins and Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2010, Sep; 74(3): 417–433.
2. National Institute of Health. Stop the Spread of Superbugs Help Fight Drug-Resistant Bacteria. https://newsinhealth.nih.gov/issue/feb2014/feature1. (Last accessed: April 11, 2016).
3. Dablon et al. The catalytic mechanism of f3-lactamases: NMR titration of an active-site lysine residue of the TEM-1 enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1996, 74: 1747-1752.
4. Fonze, E.; Charlier, P.; To'th, Y.; Vermeire, M.; Raquet, X.; Dubus, A.; Frere, J. M. TEM1 beta-lactamase structure solved by molecular replacement and refined structure of the S235A mutant.
Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1995, 51, 682-694.
5. Lenfant, F.; Labia, R.; Masson, J. -. Replacement of lysine 234 affects transition state stabilization in the active site of ß-lactamase TEM1. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 17187-17194.


