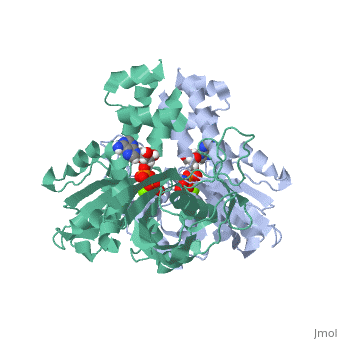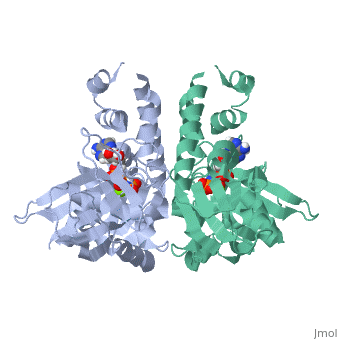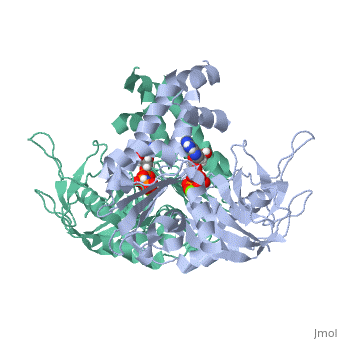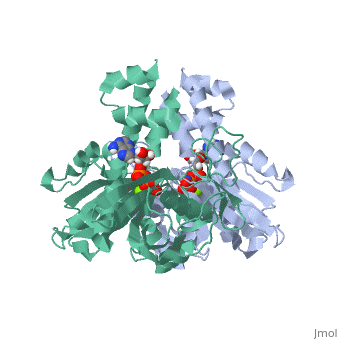Plasmid segregation protein ParM
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='4a61' size='340' side='right' caption='plasmid segregation protein ParM complex with AMPPNP and Mg+2 ion (PDB code [[4a61]])' scene=''> | + | <StructureSection load='4a61' size='340' side='right' caption='plasmid segregation protein ParM complex with AMPPNP (stick model) and Mg+2 ion (green) (PDB code [[4a61]])' scene=''> |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | + | '''Plasmid segregation protein''' (ParM) is required for plasmid partition and accurate segregation of low-copy-number plasmid R1<ref>PMID:20844556</ref>. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | + | ParM polymerizes into double helical protofilaments with repeats similar to F-actin. | |
Revision as of 09:11, 4 July 2016
| |||||||||||
3D structures of plasmid segregation protein ParM
Updated on 04-July-2016
1mwk – ParM – Escherichias coli
1mwm – ParM + ADP
2zgy – ParM + GDP
2zgz – ParM + GMPPNP
4a61 – ParM + AMPPNP
5aey – ParM + AMPPNP - CryoEM
4a62 – ParM + ParR C terminus
2qu4, 2ghc, 3iku, 3iky, 4a6j, 5ai7 – ParM – CryoEM
References
- ↑ Salje J, Gayathri P, Lowe J. The ParMRC system: molecular mechanisms of plasmid segregation by actin-like filaments. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010 Oct;8(10):683-92. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2425. PMID:20844556 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2425