Purine repressor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
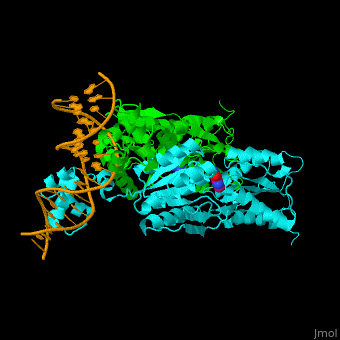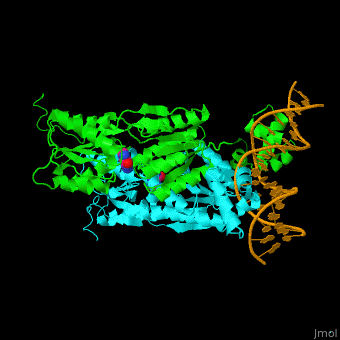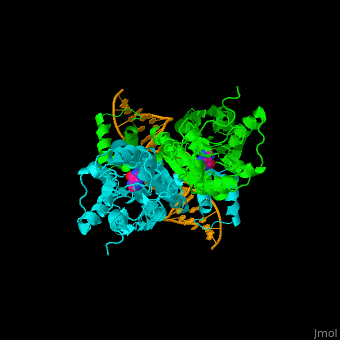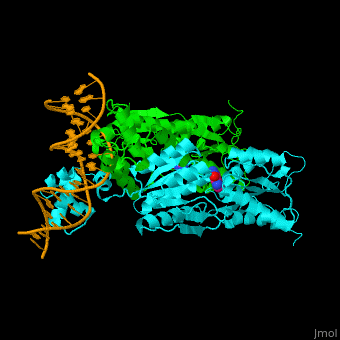
| - | The <scene name='55/554904/Cv/2'>PurP guanine co-repressor binding site includes stacking interactions as well as hydrogen bonded ones</scene>. Water molecules shown as red spheres. The DNA binding domain contains a helix-turn-helix-loop-helix motif which interacts with the DNA major groove and a hinge helix binding to to the DNA minor groove. Residue L53 interdigitates with the DNA central base pair<ref>PMID:9278422</ref>. | + | The <scene name='55/554904/Cv/2'>PurP guanine co-repressor binding site includes stacking interactions as well as hydrogen bonded ones</scene>. Water molecules shown as red spheres. The DNA binding domain contains a <scene name='55/554904/Cv/3'>helix-turn-helix-loop-helix motif which interacts with the DNA major groove and a hinge helix binding to to the DNA minor groove</scene>. <scene name='55/554904/Cv/4'>Residue L53 interdigitates with the DNA central base pair</scene><ref>PMID:9278422</ref>. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 11:49, 31 July 2016
| |||||||||||
3D structures of purine repressor
Updated on 31-July-2016
References
- ↑ Wilson HR, Turnbough CL Jr. Role of the purine repressor in the regulation of pyrimidine gene expression in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3208-13. PMID:1971621
- ↑ Schumacher MA, Glasfeld A, Zalkin H, Brennan RG. The X-ray structure of the PurR-guanine-purF operator complex reveals the contributions of complementary electrostatic surfaces and a water-mediated hydrogen bond to corepressor specificity and binding affinity. J Biol Chem. 1997 Sep 5;272(36):22648-53. PMID:9278422