Phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
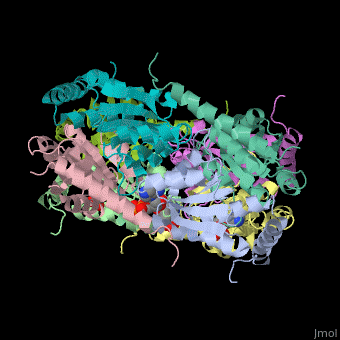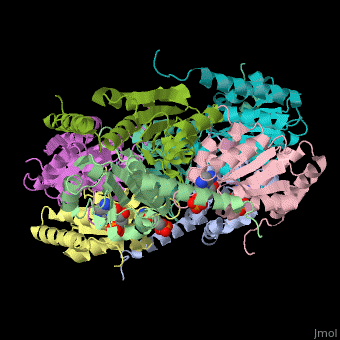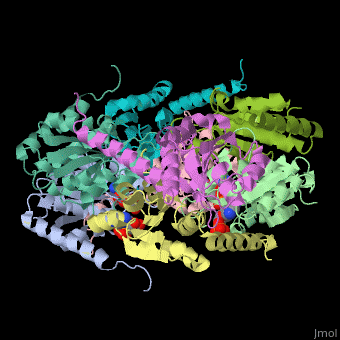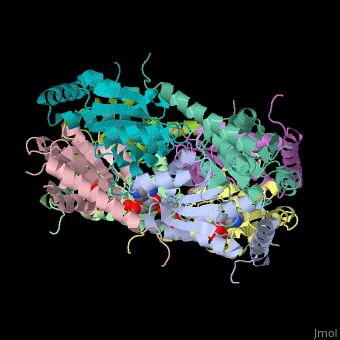
| - | The biological assembly of E. coli PurE is <scene name='57/571253/Cv/2'>octamer</scene>. PurE active site is located in a cleft between 3 subunits<ref>PMID:10574791</ref>. | + | The biological assembly of E. coli PurE is <scene name='57/571253/Cv/2'>octamer</scene>. PurE <scene name='57/571253/Cv/3'>active site</scene> is located in a <scene name='57/571253/Cv/4'>cleft between 3 subunits</scene><ref>PMID:10574791</ref>. Water molecule shown as red sphere. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 11:53, 24 August 2016
| |||||||||||
3D structures of PurE
Updated on 24-August-2016
References
- ↑ Meyer E, Leonard NJ, Bhat B, Stubbe J, Smith JM. Purification and characterization of the purE, purK, and purC gene products: identification of a previously unrecognized energy requirement in the purine biosynthetic pathway. Biochemistry. 1992 Jun 2;31(21):5022-32. PMID:1534690
- ↑ Mathews II, Kappock TJ, Stubbe J, Ealick SE. Crystal structure of Escherichia coli PurE, an unusual mutase in the purine biosynthetic pathway. Structure. 1999 Nov 15;7(11):1395-406. PMID:10574791
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky