TAL effector
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
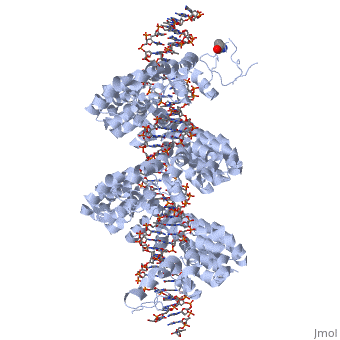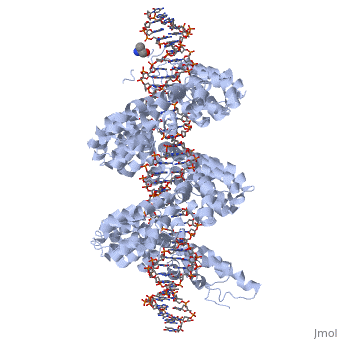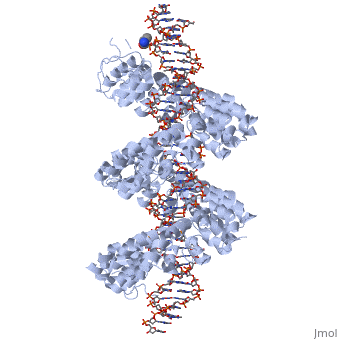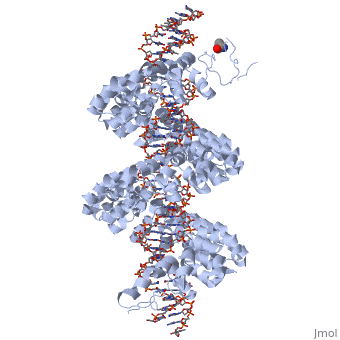
<StructureSection load='3ugm' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of TAL effector PthXo1 bound to its target DNA [[3ugm]]' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='3ugm' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of TAL effector PthXo1 bound to its target DNA [[3ugm]]' scene=''> | ||
| - | '''Transcription activator-like effector PthXo1''' (TALE PthXo1) TALEs are proteins originally derived from the plant pathogene Xanthomonas spp. The gene encoding for the effector are Pthxo1 and Pxo_00227. Originally they were detected in [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2432079/ Xanthomonas Oryzae] but the TALE PthXo1 genes were transformed into [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3100984/ Escherichia Coli] to express the DNA-binding protein. | + | ==Function== |
| + | '''Transcription activator-like effector PthXo1''' (TALE PthXo1) TALEs are proteins originally derived from the plant pathogene ''Xanthomonas'' spp. The gene encoding for the effector are Pthxo1 and Pxo_00227. Originally they were detected in [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2432079/ Xanthomonas Oryzae] but the TALE PthXo1 genes were transformed into [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3100984/ Escherichia Coli] to express the DNA-binding protein. | ||
{{ABSTRACT_PUBMED_022223736}} <ref> PMID:022223736 </ref> | {{ABSTRACT_PUBMED_022223736}} <ref> PMID:022223736 </ref> | ||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
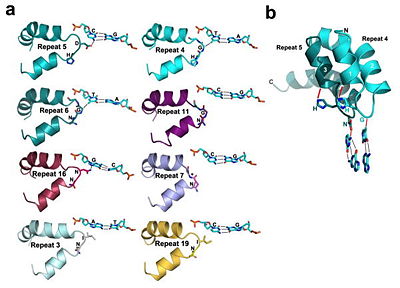
<br>[[Image:overview.jpg|left|300px|thumb|Fig.1 Structure of the PthXo1 DNA binding region in complex with its target site. The coloring of individual repeats matches the schematic in XXX]]<br> | <br>[[Image:overview.jpg|left|300px|thumb|Fig.1 Structure of the PthXo1 DNA binding region in complex with its target site. The coloring of individual repeats matches the schematic in XXX]]<br> | ||
| - | + | ==DNA binding module with marked RVD== | |
<br>[[Image:sanjana.png|left|400px|thumb|Fig.2]]<br> | <br>[[Image:sanjana.png|left|400px|thumb|Fig.2]]<br> | ||
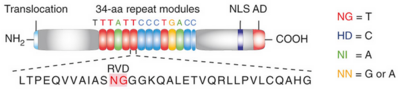
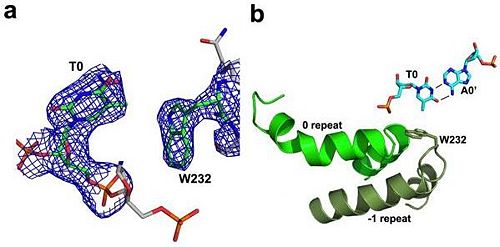
'''Figure 2''': Natural structure of TALEs derived from Xanthomonas sp. Each DNA-binding module consists of 34 amino acids, where the RVDs in the 12th and 13th amino acid positions of each repeat specify the DNA base being targeted according to the cipher NG = <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_701/T_blau/1'>T</scene>, HD = <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_701/C_schwarz/1'>C</scene>, NI = <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_701/A_gruen/1'>A</scene>, and NN = <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_701/G_gelb/1'>G</scene> or <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_701/A_gruen/1'>A</scene>. The DNA-binding modules are flanked by nonrepetitive N and C termini, which carry the translocation, nuclear localization (NLS) and transcription activation (AD) domains. A cryptic signal within the N terminus specifies a thymine as the first base of the target site.<ref> PMID:022223736 </ref> | '''Figure 2''': Natural structure of TALEs derived from Xanthomonas sp. Each DNA-binding module consists of 34 amino acids, where the RVDs in the 12th and 13th amino acid positions of each repeat specify the DNA base being targeted according to the cipher NG = <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_701/T_blau/1'>T</scene>, HD = <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_701/C_schwarz/1'>C</scene>, NI = <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_701/A_gruen/1'>A</scene>, and NN = <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_701/G_gelb/1'>G</scene> or <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_701/A_gruen/1'>A</scene>. The DNA-binding modules are flanked by nonrepetitive N and C termini, which carry the translocation, nuclear localization (NLS) and transcription activation (AD) domains. A cryptic signal within the N terminus specifies a thymine as the first base of the target site.<ref> PMID:022223736 </ref> | ||
| - | + | ==Tertiary structure of the RVD== | |
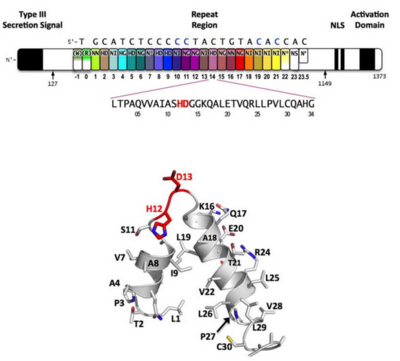
<br>[[Image:Mak_An.png|right|400px|thumb|Fig.3]]<br> | <br>[[Image:Mak_An.png|right|400px|thumb|Fig.3]]<br> | ||
| Line 23: | Line 24: | ||
Sequence-specific contacts of PthXo1 to the DNA are made exclusively by the second residue in each RVD to the corresponding base on the sense strand. In contrast, the side chain at the first position of each RVD contacts the backbone carbonyl oxygen of position 8 in each repeat, constraining the RVD-containing loop (Figure 3). Additional, nonspecific contacts to the DNA are made by a lysine and glutamine found at positions 16 and 17. | Sequence-specific contacts of PthXo1 to the DNA are made exclusively by the second residue in each RVD to the corresponding base on the sense strand. In contrast, the side chain at the first position of each RVD contacts the backbone carbonyl oxygen of position 8 in each repeat, constraining the RVD-containing loop (Figure 3). Additional, nonspecific contacts to the DNA are made by a lysine and glutamine found at positions 16 and 17. | ||
| - | + | ==Interaction between RVDs and DNA== | |
‘HD’ RVDs: | ‘HD’ RVDs: | ||
Revision as of 09:19, 6 September 2016
| |||||||||||
3D structures of TAL effectors
3ugm - XoTAL pthxo1 + DNA - Xanthomonas oryzae
3v6p - XoTAL dHax3
4gg4 – XoTAL dHax3 + DNA + RNA
3v6t – XoTAL dHax3 + DNA
4gjr, 4gjp – XoTAL dHax3 (mutant) + DNA
Reference
- Mak AN, Bradley P, Cernadas RA, Bogdanove AJ, Stoddard BL. The Crystal Structure of TAL Effector PthXo1 Bound to Its DNA Target. Science. 2012 Jan 5. PMID:22223736 doi:10.1126/science.1216211
- Sanjana NE, Cong L, Zhou Y, Cunniff MM, Feng G, Zhang F. A transcription activator-like effector toolbox for genome engineering. Nat Protoc. 2012 Jan 5;7(1):171-92. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2011.431. PMID:22222791 doi:10.1038/nprot.2011.431
- Barberousse V, Sacco D, Dellacherie E. Chromatographic evaluation of the binding of haemoglobin to polyanionic polymers. J Chromatogr. 1986 Nov 7;369(1):244-7. PMID:2432079
Contributors
Fabian Stritt, Philipp Warmer
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Philipp Warmer, Michal Harel, Jaime Prilusky, OCA, Alexander Berchansky