|
|
| (91 intermediate revisions not shown.) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| - | ----
| + | ==Rat Calcineurin== |
| - | ==Structure Rat Calcineurin== | + | <StructureSection load='4il1' size='340' side='right' caption='' scene=''> |
| - | <StructureSection load='4il1' size='340' side='right' caption='Rat calcineurin monomer, each of the four chains of the monomer is shown in a different color.' scene=''> | + | == Function == |
| - | <scene name='75/750223/Picture_intro/1'> Calcineurin </scene> is a serine/threonine phosphatase that is activated by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calmodulin calmodulin] in a calcium-dependant manner. Calcineurin is the only known calmodulin-activated protein phosphatase. Calcineurin is responsible mainly for dephosphorylating several member of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NFAT NFAT] transcription factor family (including NFATc1 through NFATc4). | + | <scene name='75/750223/Picture_intro/1'> Calcineurin </scene> is a serine/threonine [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphatase phosphatase] that is activated by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calmodulin calmodulin](CaM) in a calcium-dependant manner. |
| | + | Also known as Serine threonine phosphatase 2B, it plays an important role in multiple pathways. |
| | | | |
| - | ''' Localisation and expression''':
| + | Calcineurin can modulate the immune response, act on the muscle formation and remodeling as well as on the neuronal plasticity and the cell death. |
| - | | + | It is able to desphosphorylate numerous ion channels and thus modulate the basal excitability of neurons. Calcineurin has also an effect on the synaptic transmission since it affects the release of several neurotransmitters<ref>PMID: 9149541</ref><ref>PMID:PMID: 14623302</ref>. |
| - | Calcineurin is a cytoplasmic protein. The catalytic subunit calcineurin A, posses two major isoforms called calcineurin Aα and Aβ. Calcineurin Aα is widely expressed among tissues especially in the Central Nervous System (CNS). Calcineurin Aβ is rather found in the lymphoid cells.Calcineurin Aβ is therefore involved in the mediation of the immune response (PMID:16888030). | + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | == Function ==
| + | |
| | | | |
| | + | Calcineurin is responsible mainly for dephosphorylating several members of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NFAT NFAT] transcription factor family (including NFATc1 through NFATc4). |
| | == General structure == | | == General structure == |
| | | | |
| | <scene name='75/750223/Jw_caln_sec_strcutur/1'>Calcineurin</scene> is a heterodimeric Protein that consits of two subunits. They are called catalytic and regulatory subunit. Four molecules of Calcineurin form an asymmetric complex which leads to a total molecular weight of 370 kDa. | | <scene name='75/750223/Jw_caln_sec_strcutur/1'>Calcineurin</scene> is a heterodimeric Protein that consits of two subunits. They are called catalytic and regulatory subunit. Four molecules of Calcineurin form an asymmetric complex which leads to a total molecular weight of 370 kDa. |
| | | | |
| - | The structure presented in this article is the catalytic subunit isoform of the serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2B in [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/UniGene/UGOrg.cgi?TAXID=10116 rattus norvegicus (rat)]. It consists of 521 (http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P63329) aminoacids and has a molecular weight of 57 kDa (http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P63329). | + | The structure presented in this article is the catalytic subunit isoform of the serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2B in [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/UniGene/UGOrg.cgi?TAXID=10116 rattus norvegicus (rat)]. It consists of 521 [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P63329] aminoacids and has a molecular weight of 57 kDa [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P63329]. |
| - | The calatytic subunit is subdivided into functional domains which are a <scene name='75/750223/Catalytique_domain_of_chain_a/1'>catalytic domain (here chain A is shown)</scene>, a <scene name='75/750223/Interact_dom_ca/1'>binding domain for the regulary subunit</scene>, a <scene name='75/750223/Calm_bind_dom_ca/1'>calmodulin binding domain </scene> and an <scene name='75/750223/Auto_inh_dom_ca/1'>autoinhibitory domain</scene>. | + | The calatytic subunit is subdivided into functional domains which are a <scene name='75/750223/Catalytique_domain_of_chain_a/1'>catalytic domain (here chain A is shown)</scene>, a <scene name='75/750223/Interact_dom_ca/1'>binding domain for the regulary subunit</scene>, a <scene name='75/750223/Calm_bind_dom_ca/1'>calmodulin binding domain </scene> and an <scene name='75/750223/Auto_inh_dom_ca/1'>autoinhibitory domain</scene>. |
| - | | + | The catalytic side includes a residue (green) at position 151 that acts as proton donor and metal binding sites. <Scene name='75/750223/Zink/1'>Zinc</scene> (shown in brown) binds at the position 118, 150, 199 and 281. Four residues are modified with a serine or a tyrosine. At position 2, a N-acetylserine has been found by similarity, as well as a nitrated tyrosine at position 224, and phosphoserine at position 469 and 492. |
| - | The catalytic side includes a residue (green) at position 151 that acts as proton donor and metal binding sites. <Scene name='75/750223/Zink/1'>Zinc</scene> (shown in brown) binds at the position 118, 150, 199 and 281. Iron (blue) interacts at the positions 90, 92 and 118. | + | Calcineurin is a cytoplasmic protein. It is widely expressed among tissues especially in the central nervous system (CNS) qnd in lymphoid cells qnd therefore involved in the mediation of the immune response <ref>PMID:16888030</ref>. |
| - | | + | |
| - | <scene name='75/750223/Modified_residues/1'>Four residues</scene> are modified with a serine or a tyrosine. At position 2, a N-acetylserine has been found by similarity, as well as a nitrated tyrosine at position 224, and phosphoserine at position 469 and 492.
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| | | | |
| | '''Discovery of the structure:''' | | '''Discovery of the structure:''' |
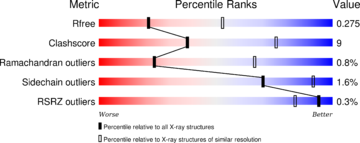
| | [[Image:4il1 multipercentile validation.png|thumb|upright=2|left]] | | [[Image:4il1 multipercentile validation.png|thumb|upright=2|left]] |
| - | The structure have been [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24018048 published in the year 2013 by Qilu Ye et al.] (PMID:24018048) in [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/journal/08986568 ''Cellular Signaling'']. For their experiments they used [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X-ray_crystallography#X-ray_diffraction x-ray diffraction]. The [http://www.wwpdb.org/validation/2016/XrayValidationReportHelp PDB validation] obtained a Resolutionof 3.0 Å, a free R-value of 0.273 and a work R-value of 0.241 (http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=4IL1). | + | The structure have been [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24018048 published in the year 2013 by Qilu Ye et al.] <ref>PMID:24018048</ref> in [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/journal/08986568 ''Cellular Signaling'']. For their experiments they used [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X-ray_crystallography#X-ray_diffraction x-ray diffraction]. The [http://www.wwpdb.org/validation/2016/XrayValidationReportHelp PDB validation] obtained a Resolutionof 3.0 Å, a free R-value of 0.273 and a work R-value of 0.241 [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=4IL1]. |
| | | | |
| | <br style="clear:both" /> | | <br style="clear:both" /> |
| - | | + | '''Secondary structure:''' |
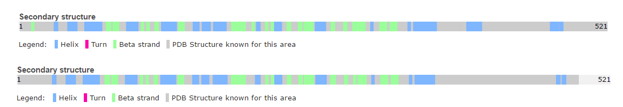
| - | '''secondary structure:''' | + | [[Image:170106 Uniprot SecundaryStructure.png|thumb|upright=4|The secondary structure mostly includes helical structures [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P63100 Uniprot]]] |
| - | | + | |
| - | [[Image:170106 Uniprot SecundaryStructure.png|thumb|upright=4|The secondary structure mostly includes helical structures]] | + | |
| - | | + | |
| | Besides, there are six turns reported in the structure of one chain. | | Besides, there are six turns reported in the structure of one chain. |
| - | | + | <br style="clear:both" /> |
| | + | The Ramachandran blot of Calcineurin [[Image:Ramachandran 4il1.jpg|thumb|left|Ramachandran Plot of 4il1]] has been obtained by [http://mordred.bioc.cam.ac.uk/~rapper/rampage2.php MolProbity of the DUke University]. It plots the torsional angles phi (φ) and psi (ψ) of the molecule and thereby represents the secondary structure. Further information about the Interpretation of this plot can be found at [[Ramachandran Plot]]. |
| | <br style="clear:both" /> | | <br style="clear:both" /> |
| | | | |
| - | The Ramachandran blot of Calcineurin [[Image:Ramachandran 4il1.jpg|thumb|left|Ramachandran Plot of 4il1]] has been obtained by [http://mordred.bioc.cam.ac.uk/~rapper/rampage2.php MolProbity of the DUke University]. It plots the torsional angles phi (φ)and psi (ψ)of the molecule and thereby represents the secondary structure. Further information about the Interpretation of this plot can be found at [[Ramachandran Plot]].
| + | == Principle of action == |
| | + | [[Image:Genes Dev. 2003 Sep 17(18) 2205-32, Figure 1.jpg|thumb|upright=2|Schematic view of the NFAT activation cycle <ref>PMID:12975316</ref>]] |
| | + | As a response of receptor tyrosine kinase [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_tyrosine_kinase(RTK)] activation as well as G protein-coupled receptor [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein%E2%80%93coupled_receptor (GCPR)] activation the [[Phospholipase C]] [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phospholipase_C (PLC)] catalyse the hydrolysis of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphatidylinositol_4,5-bisphosphate PIP2] to [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inositol_trisphosphate IP3] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diglyceride DAG]. IP3 activates the [[Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptor]] and therby leads to an increasing amount of the second Messenger Ca<sup>2+</sup> in the cytoplasma. |
| | | | |
| | + | Calcineurin is activated by [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/potm/2003_3/Page_1.htm Calmodulin], a calcium-binding protein. Calmodulin interacts with the calmodulin-binding/regulatory region of Calcineurin. That binding leads to a conformational change in the autoinhibitory domain and remove it from the active site <ref>PMID:22100452</ref>. |
| | | | |
| | + | It has been reported that Calcineurin activates the transcription factor [https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/NF-AT NFAT] by forming a complex and dephosporylation <ref>PMID:17502104</ref>. Following, the factor enters the nucleus and activates the expression of Interleukin-2. |
| | <br style="clear:both" /> | | <br style="clear:both" /> |
| | + | == Binding Partners == |
| | + | The main partners of interaction are [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calmodulin Calmodulin], NFATc1, NFATc2 and NFATc3. |
| | + | Many of the calcineurin substrates contain a PxIxIT motif. Among them, beside the phosphorylated forms of NFAT we can also mention cAMP response element binding protein (CREB), PP1, microtubule-associated protein tau and glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK- 3)<ref>PMID: 17666045</ref><ref>PMID: 22676853</ref><ref>PMID:14701880</ref><ref>PMID: 7515479</ref>. |
| | + | <scene name='75/750223/Can_fk506/1'>Calcineurin, here shown in complex with FK506 and FKPB (in pink on the model)</scene> is inhibited by the immunosuppressive drugs tacrolismus (<scene name='75/750223/Tacrolimus/1'>FK506</scene>) or cyclosporine A (CsA). CsA and conduct their therapeutic role thought binding to the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immunophilins immunophilins] cyclophilin and FK506 binding protein (FK506BP) respectively. The complexes CsA-cyclophilin and FK506-FK506BP bind then to calcineurin in a calcium-dependent manner thus inhibiting its phosphatase activity. Therefore the addition of these drugs to lymphocytes T prevent NFAT translocation to the nucleus and the subsequent activation its target gene.That's why FK506 and CsA are use in the treatment of various immune-mediated diseases. However since calcineurin is is widely expressed in non-haemopoietic tissues like the kidney and the hearth, both drugs present a long term toxicity and can lead to deleterious effect to these Organs <ref>PMID: 8811062</ref><ref>http://www.uptodate.com/contents/pharmacology-of-cyclosporine-and-tacrolimus</ref>. |
| | | | |
| | + | '''Cofactors''': |
| | | | |
| - | == Principle of action ==
| + | Calcineurin belong to the family of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metalloprotein metalloprotein]. To conduct its activity it requires the presence of exposing Fe<sup>3+</sup> and exposing Zn<sup>2+</sup> ions in the active site (one per subunit). Superoxide dismutase has been shown to protect calcineurin from inactivation by preventing Fe<sup>3+</sup> from oxidation. Thus after activation of calcineurin by calmodulin, the AID is displaced from the <scene name='75/750223/Catalytic_core/1'> catalytic core,with phosphate and Fe and Zn ions bound </scene> exposing Fe<sup>3+</sup> to oxidation <ref>PMID: 8837775</ref><ref>Calmodulin and Signal Transduction (p184), Linda J. Van Eldik,D. Martin Watterson (1998)</ref>. |
| - | [[Image:Genes Dev. 2003 Sep 17(18) 2205-32, Figure 1.jpg|thumb|upright=2|Schematic view of the NFAT activation cycle (PMID:12975316)]]
| + | |
| - | As a response of receptor tyrosine kinase [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_tyrosine_kinase(RTK)] activation as well as G protein-coupled receptor [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein%E2%80%93coupled_receptor (GCPR)] activation the [[Phospholipase C]] [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phospholipase_C (PLC)] catalyse the hydrolysis of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphatidylinositol_4,5-bisphosphate PIP2] to [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inositol_trisphosphate IP3] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diglyceride DAG]. IP3 activates the [[Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptor]] and therby leads to an increasing amount of the second Messenger Ca2+ in the cytoplasma.
| + | |
| | | | |
| - | Calcineurin is activated by [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/potm/2003_3/Page_1.htm Calmodulin], a calcium-binding protein. Calmodulin interacts with the calmodulin-binding/regulatory region of Calcineurin. That binding leads to a conformational change in the autoinhibitory domain and remove it from the active site (doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2011.11.008). | + | == Related health defects == |
| | + | Calcineurin hyperactivation thought dysregulation of the Ca<sup>2+</sup> dynamic have been show to play a critical role in several diseases like Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Schizophrenia ,Diabetes, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus as well as Alzheimer diseases (AD) <ref>http://www.uptodate.com/contents/pharmacology-of-cyclosporine-and-tacrolimus)</ref><ref>PMID: 12851457</ref><ref>PMID: 16988714</ref><ref>PMID:20421909</ref>. |
| | + | Taking the example of AD which is a age-related memory dysfunction, it it know that in older organism the brain is less plastic due to a dysregulation of Ca<sup>2+</sup> dynamic. This in addition to the presence of oligomeric Aß is sufficient to explain an enhancement of CaN activity leading to severals symptoms like decreased neurotransmission, synaptic loss and neuroinflammation<ref>PMID:22654726</ref>. Therefore calmodulin inhibitors are potential alternatives against Alzheimer diseases. |
| | | | |
| - | It has been reported that Calcineurin activates the transcription factor [https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/NF-AT NFAT] by forming a complex and dephosporylation (PMID:17502104). Following, the factor enters the nucleus and activates the expression of Interleukin-2.
| + | == Human/Rat calcineurin comparison == |
| | + | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q08209 Human] and [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P63329 Rat] calcineurin have the same function and global structure [[Image:Human rat comparison.PNG|thumb|upright=4|left| Structure of rat calcineurin and human calcineurin]]. |
| | | | |
| | + | The size (521 amino acids) and subunits of the linear structure are the same, as well as the 3D structure. |
| | <br style="clear:both" /> | | <br style="clear:both" /> |
| | + | [[Image:Proteopedia.PNG|thumb|upright=4|right| Structure of human calcineurin (up) and rat calcineurin (down) ]] |
| | + | <br style="clear:both" /> |
| | + | However, there are a few differences, such as the secondary structures. |
| | + | For instance, Human Calcineurin has one Beta strand at <scene name='75/750223/Residues_11-13_beta_strand/1'>residues 11-13</scene> whereas Rat Calcineurin has not. |
| | | | |
| - | == Binding Partners == | + | <br style="clear:both" /> |
| - | The main partners of interaction are [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calmodulin Calmodulin],NFATc1, NFATc2 and NFATc3.
| + | Indeed, Calcineurin is a highly conserved protein from yeast to mammals. |
| - | Many of the calcineurin substrates’ contain a PxIxIT motif. Among them, beside the phosphorylated forms of NFAT we can also mentioned; cAMP response element binding protein (CREB), PP1, microtubule-associated protein tau and glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK- 3)(PMID: 17666045)(PMID: 22676853)(PMID: 14701880)(PMID: 7515479).
| + | <br style="clear:both" /> |
| - | Calcineurin is inhibited by the immunosuppressive drugs tacrolismus (FK506) or cyclosporine A (CsA). CsA and FK506 conduct their therapeutic role thought binding to the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immunophilins immunophilins] cyclophilin and FK506 binding protein (FK506BP) respectively. The complexes CsA-cyclophilin and FK506-FK506BP bind then to calcineurin in a calcium-dependent manner thus inhibiting its phosphatase activity. Therefore the addition of these drugs to lymphocytes T prevent NFAT translocation to the nucleus and the subsequent activation its target gene.That's why FK506 and CsA are use in the treatment of various immune-mediated diseases. However since calcineurin is is widely expressed in non-haemopoietic tissues like the kidney and the hearth, both drugs present a long term toxicity and can lead to deleterious effect to these Organs (PMID: 8811062), (http://www.uptodate.com/contents/pharmacology-of-cyclosporine-and-tacrolimus). | + | |
| | | | |
| | + | == Evolutionary conservation == |
| | + | [[Image:Ih.jpg|thumb|upright=2|right|size=4| Evolutionary conservation of Calcineurin B within eukaryotes ]] |
| | | | |
| | + | '''Calcineurin A''' |
| | | | |
| - | '''Cofactors''':
| + | This catalytic subunit is highly conserved. Nevertheless it can be up to 20 % larger in lower eukaryotic species. |
| - | Calcineurin belong to the family of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metalloprotein metalloprotein]. To conduct its activity it requires the presence of Fe3+ and Zn2+ ions in the active site (one per subunit).Superoxide dismutase has been shown to protect calcineurin from inactivation by preventing Fe3+ from oxidation. Thus after activation of calcineurin by calmodulin, the AID is displaced from the catalytic core exposing Fe3+ to oxidation (PMID: 8837775)(Calmodulin and Signal Transduction (p184), Linda J. Van Eldik,D. Martin Watterson (1998)).
| + | In addition, the NH<sub>2</sub> and COOH terminals are variable among species, as well as between calcineurin A genes within the same organism. |
| | + | The function of these variable domains is unknown.<ref name="paper">PMID: 11015619</ref> |
| | | | |
| | + | '''Calcineurin B''' |
| | | | |
| | + | This regulatory subunit is also highly conserved throughout evolution. For instance, the sequence of the rat calcineurin B brain isoform is exactly the same as the human calcineurin B. |
| | + | This high degree of conservation allows functional interchange of calcineurin B subunits between eukaryotic species. <ref name="paper" /> |
| | + | <br style="clear:both" /> |
| | | | |
| | + | == Calcineurin history == |
| | + | Calcineurin was first detected by Wang and Desai in 1976 as a column fraction that inhibited the calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. |
| | | | |
| | + | Klee and Krinks did the first purification of calcineurin in 1978 and hypothesized that it might be a regulatory subunit of phosphodiesterase since it was demonstrated to inhibit phosphodiesterase activity. |
| | | | |
| - | == Related health defects ==
| + | Klee et al. named it “calcineurin” on the basis of its Ca<sup>2+</sup>-binding properties (calci) and localization to neuronal tissue (neurin). |
| | | | |
| - | Calcineurin hyperactivation thought dysregulation of the Ca2+ dynamic have been show to play a critical role in several diseases like Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Schizophrenia ,Diabetes, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus as well as Alzheimer diseases (http://www.uptodate.com/contents/pharmacology-of-cyclosporine-and-tacrolimus)(PMID: 12851457)(PMID: 16988714)(PMID: 20421909)(PMID: 22654726).In order to fight those health defects calmodulin inhibitors can be administrated. | + | From this time, functions and structure of Calcineurin have been discovered as well as medical applications (e.g. calcineurin inhibitors). <ref name="paper" /> |
| | + | == References == |
| | + | <references/> |
|
Function
is a serine/threonine phosphatase that is activated by calmodulin(CaM) in a calcium-dependant manner.
Also known as Serine threonine phosphatase 2B, it plays an important role in multiple pathways.
Calcineurin can modulate the immune response, act on the muscle formation and remodeling as well as on the neuronal plasticity and the cell death.
It is able to desphosphorylate numerous ion channels and thus modulate the basal excitability of neurons. Calcineurin has also an effect on the synaptic transmission since it affects the release of several neurotransmitters[1][2].
Calcineurin is responsible mainly for dephosphorylating several members of the NFAT transcription factor family (including NFATc1 through NFATc4).
General structure
is a heterodimeric Protein that consits of two subunits. They are called catalytic and regulatory subunit. Four molecules of Calcineurin form an asymmetric complex which leads to a total molecular weight of 370 kDa.
The structure presented in this article is the catalytic subunit isoform of the serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2B in rattus norvegicus (rat). It consists of 521 [1] aminoacids and has a molecular weight of 57 kDa [2].
The calatytic subunit is subdivided into functional domains which are a , a , a and an .
The catalytic side includes a residue (green) at position 151 that acts as proton donor and metal binding sites. (shown in brown) binds at the position 118, 150, 199 and 281. Four residues are modified with a serine or a tyrosine. At position 2, a N-acetylserine has been found by similarity, as well as a nitrated tyrosine at position 224, and phosphoserine at position 469 and 492.
Calcineurin is a cytoplasmic protein. It is widely expressed among tissues especially in the central nervous system (CNS) qnd in lymphoid cells qnd therefore involved in the mediation of the immune response [3].
Discovery of the structure:
The structure have been published in the year 2013 by Qilu Ye et al. [4] in Cellular Signaling. For their experiments they used x-ray diffraction. The PDB validation obtained a Resolutionof 3.0 Å, a free R-value of 0.273 and a work R-value of 0.241 [3].
Secondary structure:
 The secondary structure mostly includes helical structures UniprotBesides, there are six turns reported in the structure of one chain.
The Ramachandran blot of Calcineurin 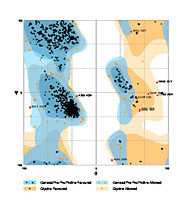 Ramachandran Plot of 4il1 has been obtained by MolProbity of the DUke University. It plots the torsional angles phi (φ) and psi (ψ) of the molecule and thereby represents the secondary structure. Further information about the Interpretation of this plot can be found at Ramachandran Plot.
Principle of action
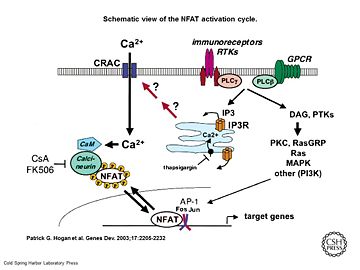 Schematic view of the NFAT activation cycle [5]As a response of receptor tyrosine kinase [4] activation as well as G protein-coupled receptor (GCPR) activation the Phospholipase C (PLC) catalyse the hydrolysis of PIP2 to IP3 and DAG. IP3 activates the Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptor and therby leads to an increasing amount of the second Messenger Ca2+ in the cytoplasma.
Calcineurin is activated by Calmodulin, a calcium-binding protein. Calmodulin interacts with the calmodulin-binding/regulatory region of Calcineurin. That binding leads to a conformational change in the autoinhibitory domain and remove it from the active site [6].
It has been reported that Calcineurin activates the transcription factor NFAT by forming a complex and dephosporylation [7]. Following, the factor enters the nucleus and activates the expression of Interleukin-2.
Binding Partners
The main partners of interaction are Calmodulin, NFATc1, NFATc2 and NFATc3.
Many of the calcineurin substrates contain a PxIxIT motif. Among them, beside the phosphorylated forms of NFAT we can also mention cAMP response element binding protein (CREB), PP1, microtubule-associated protein tau and glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK- 3)[8][9][10][11].
is inhibited by the immunosuppressive drugs tacrolismus () or cyclosporine A (CsA). CsA and conduct their therapeutic role thought binding to the immunophilins cyclophilin and FK506 binding protein (FK506BP) respectively. The complexes CsA-cyclophilin and FK506-FK506BP bind then to calcineurin in a calcium-dependent manner thus inhibiting its phosphatase activity. Therefore the addition of these drugs to lymphocytes T prevent NFAT translocation to the nucleus and the subsequent activation its target gene.That's why FK506 and CsA are use in the treatment of various immune-mediated diseases. However since calcineurin is is widely expressed in non-haemopoietic tissues like the kidney and the hearth, both drugs present a long term toxicity and can lead to deleterious effect to these Organs [12][13].
Cofactors:
Calcineurin belong to the family of metalloprotein. To conduct its activity it requires the presence of exposing Fe3+ and exposing Zn2+ ions in the active site (one per subunit). Superoxide dismutase has been shown to protect calcineurin from inactivation by preventing Fe3+ from oxidation. Thus after activation of calcineurin by calmodulin, the AID is displaced from the exposing Fe3+ to oxidation [14][15].
Related health defects
Calcineurin hyperactivation thought dysregulation of the Ca2+ dynamic have been show to play a critical role in several diseases like Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Schizophrenia ,Diabetes, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus as well as Alzheimer diseases (AD) [16][17][18][19].
Taking the example of AD which is a age-related memory dysfunction, it it know that in older organism the brain is less plastic due to a dysregulation of Ca2+ dynamic. This in addition to the presence of oligomeric Aß is sufficient to explain an enhancement of CaN activity leading to severals symptoms like decreased neurotransmission, synaptic loss and neuroinflammation[20]. Therefore calmodulin inhibitors are potential alternatives against Alzheimer diseases.
Human/Rat calcineurin comparison
Human and Rat calcineurin have the same function and global structure 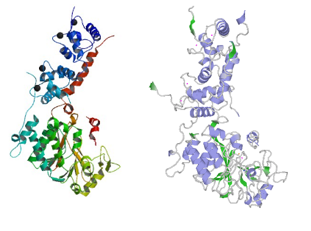 Structure of rat calcineurin and human calcineurin .
The size (521 amino acids) and subunits of the linear structure are the same, as well as the 3D structure.
 Structure of human calcineurin (up) and rat calcineurin (down)
However, there are a few differences, such as the secondary structures.
For instance, Human Calcineurin has one Beta strand at whereas Rat Calcineurin has not.
Indeed, Calcineurin is a highly conserved protein from yeast to mammals.
Evolutionary conservation
 Evolutionary conservation of Calcineurin B within eukaryotes Calcineurin A
This catalytic subunit is highly conserved. Nevertheless it can be up to 20 % larger in lower eukaryotic species.
In addition, the NH2 and COOH terminals are variable among species, as well as between calcineurin A genes within the same organism.
The function of these variable domains is unknown.[21]
Calcineurin B
This regulatory subunit is also highly conserved throughout evolution. For instance, the sequence of the rat calcineurin B brain isoform is exactly the same as the human calcineurin B.
This high degree of conservation allows functional interchange of calcineurin B subunits between eukaryotic species. [21]
Calcineurin history
Calcineurin was first detected by Wang and Desai in 1976 as a column fraction that inhibited the calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase.
Klee and Krinks did the first purification of calcineurin in 1978 and hypothesized that it might be a regulatory subunit of phosphodiesterase since it was demonstrated to inhibit phosphodiesterase activity.
Klee et al. named it “calcineurin” on the basis of its Ca2+-binding properties (calci) and localization to neuronal tissue (neurin).
From this time, functions and structure of Calcineurin have been discovered as well as medical applications (e.g. calcineurin inhibitors). [21]
References
- ↑ Yakel JL. Calcineurin regulation of synaptic function: from ion channels to transmitter release and gene transcription. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1997 Apr;18(4):124-34. PMID:9149541
- ↑ PMID:PMID: 14623302
- ↑ Yoo SA, Park BH, Park GS, Koh HS, Lee MS, Ryu SH, Miyazawa K, Park SH, Cho CS, Kim WU. Calcineurin is expressed and plays a critical role in inflammatory arthritis. J Immunol. 2006 Aug 15;177(4):2681-90. PMID:16888030
- ↑ Ye Q, Feng Y, Yin Y, Faucher F, Currie MA, Rahman MN, Jin J, Li S, Wei Q, Jia Z. Structural basis of calcineurin activation by calmodulin. Cell Signal. 2013 Sep 7;25(12):2661-2667. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.08.033. PMID:24018048 doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.08.033
- ↑ Hogan PG, Chen L, Nardone J, Rao A. Transcriptional regulation by calcium, calcineurin, and NFAT. Genes Dev. 2003 Sep 15;17(18):2205-32. PMID:12975316 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.1102703
- ↑ Rumi-Masante J, Rusinga FI, Lester TE, Dunlap TB, Williams TD, Dunker AK, Weis DD, Creamer TP. Structural basis for activation of calcineurin by calmodulin. J Mol Biol. 2012 Jan 13;415(2):307-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.11.008. Epub 2011 , Nov 12. PMID:22100452 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2011.11.008
- ↑ Takeuchi K, Roehrl MH, Sun ZY, Wagner G. Structure of the calcineurin-NFAT complex: defining a T cell activation switch using solution NMR and crystal coordinates. Structure. 2007 May;15(5):587-97. PMID:17502104 doi:10.1016/j.str.2007.03.015
- ↑ Kingsbury TJ, Bambrick LL, Roby CD, Krueger BK. Calcineurin activity is required for depolarization-induced, CREB-dependent gene transcription in cortical neurons. J Neurochem. 2007 Oct;103(2):761-70. Epub 2007 Jul 31. PMID:17666045 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04801.x
- ↑ Karch CM, Jeng AT, Goate AM. Calcium phosphatase calcineurin influences tau metabolism. Neurobiol Aging. 2013 Feb;34(2):374-86. doi:, 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.05.003. Epub 2012 Jun 6. PMID:22676853 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.05.003
- ↑ Hilioti Z, Gallagher DA, Low-Nam ST, Ramaswamy P, Gajer P, Kingsbury TJ, Birchwood CJ, Levchenko A, Cunningham KW. GSK-3 kinases enhance calcineurin signaling by phosphorylation of RCNs. Genes Dev. 2004 Jan 1;18(1):35-47. Epub 2003 Dec 30. PMID:14701880 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.1159204
- ↑ Mulkey RM, Endo S, Shenolikar S, Malenka RC. Involvement of a calcineurin/inhibitor-1 phosphatase cascade in hippocampal long-term depression. Nature. 1994 Jun 9;369(6480):486-8. PMID:7515479 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/369486a0
- ↑ Ho S, Clipstone N, Timmermann L, Northrop J, Graef I, Fiorentino D, Nourse J, Crabtree GR. The mechanism of action of cyclosporin A and FK506. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1996 Sep;80(3 Pt 2):S40-5. PMID:8811062
- ↑ http://www.uptodate.com/contents/pharmacology-of-cyclosporine-and-tacrolimus
- ↑ Wang X, Culotta VC, Klee CB. Superoxide dismutase protects calcineurin from inactivation. Nature. 1996 Oct 3;383(6599):434-7. PMID:8837775 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/383434a0
- ↑ Calmodulin and Signal Transduction (p184), Linda J. Van Eldik,D. Martin Watterson (1998)
- ↑ http://www.uptodate.com/contents/pharmacology-of-cyclosporine-and-tacrolimus)
- ↑ Miyakawa T, Leiter LM, Gerber DJ, Gainetdinov RR, Sotnikova TD, Zeng H, Caron MG, Tonegawa S. Conditional calcineurin knockout mice exhibit multiple abnormal behaviors related to schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Jul 22;100(15):8987-92. Epub 2003 Jul 8. PMID:12851457 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1432926100
- ↑ Heit JJ, Apelqvist AA, Gu X, Winslow MM, Neilson JR, Crabtree GR, Kim SK. Calcineurin/NFAT signalling regulates pancreatic beta-cell growth and function. Nature. 2006 Sep 21;443(7109):345-9. PMID:16988714 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature05097
- ↑ Lampropoulos CE, D'Cruz DP. Topical calcineurin inhibitors in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2010 Apr 15;6:95-101. PMID:20421909
- ↑ Reese LC, Taglialatela G. A role for calcineurin in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2011 Dec;9(4):685-92. doi: 10.2174/157015911798376316. PMID:22654726 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/157015911798376316
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 Rusnak F, Mertz P. Calcineurin: form and function. Physiol Rev. 2000 Oct;80(4):1483-521. PMID:11015619
|