We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
PE/PPE Protein Complex
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: <StructureSection load="2g38" size="400" color="" frame="true" spin="on" Scene='2g38/Pe_ppe_longitudinal/1' align="right" caption= > 200px<br /> ===A PE/PPE ...) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load="2g38" size="400" color="" frame="true" spin="on" Scene='2g38/Pe_ppe_longitudinal/1' | + | <StructureSection load="2g38" size="400" color="" frame="true" spin="on" Scene='2g38/Pe_ppe_longitudinal/1' side="right" caption="[[2g38]]" > |
[[Image:2g38.png|left|200px]]<br /> | [[Image:2g38.png|left|200px]]<br /> | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
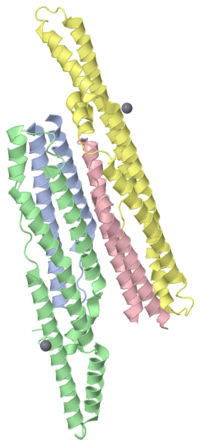
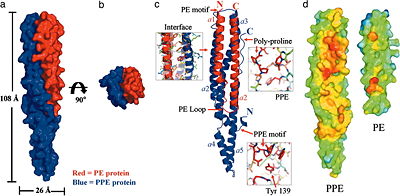
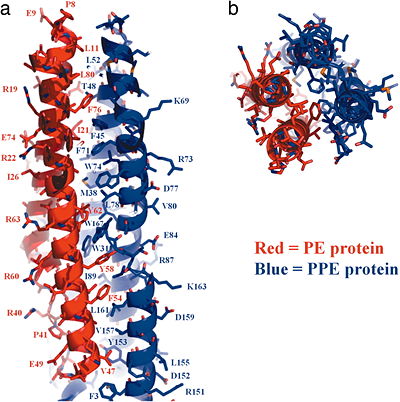
The heterodimeric <scene name='2g38/Pe_ppe_longitudinal/1'>PE/PPE protein complex</scene> from ''M. tuberculosis'' is composed of a 99 amino acid <scene name='2g38/Pe_ppe_pe/3'>PE protein</scene> protein (Rv2431c, shown in RED) and a 194 amino acid <scene name='2g38/Pe_ppe_ppe/1'>PPE protein</scene> (Rv2430c, shown in BLUE), that are encoded next to each other on the M. tuberculosis genome (suggestive of a potential operon). These proteins represent two of the largest protein families in the M. tuberculosis genome. The PE and PPE proteins form an <scene name='2g38/Pe_ppe_longitudinal/1'>elongated helical structure</scene>, reminiscent of a four-helix bundle, which can be best viewed down the <scene name='2g38/Pe_ppe_axis/2'>axis</scene>. The protein interaction <scene name='2g38/Pe_ppe_interface/1'>interface</scene> between the two proteins is lined with hydrophobic residues, contributing to the stability of the protein complex. Click here to view a <scene name='2g38/Pe_ppe_space_fill/2'>SpaceFill</scene> representation. | The heterodimeric <scene name='2g38/Pe_ppe_longitudinal/1'>PE/PPE protein complex</scene> from ''M. tuberculosis'' is composed of a 99 amino acid <scene name='2g38/Pe_ppe_pe/3'>PE protein</scene> protein (Rv2431c, shown in RED) and a 194 amino acid <scene name='2g38/Pe_ppe_ppe/1'>PPE protein</scene> (Rv2430c, shown in BLUE), that are encoded next to each other on the M. tuberculosis genome (suggestive of a potential operon). These proteins represent two of the largest protein families in the M. tuberculosis genome. The PE and PPE proteins form an <scene name='2g38/Pe_ppe_longitudinal/1'>elongated helical structure</scene>, reminiscent of a four-helix bundle, which can be best viewed down the <scene name='2g38/Pe_ppe_axis/2'>axis</scene>. The protein interaction <scene name='2g38/Pe_ppe_interface/1'>interface</scene> between the two proteins is lined with hydrophobic residues, contributing to the stability of the protein complex. Click here to view a <scene name='2g38/Pe_ppe_space_fill/2'>SpaceFill</scene> representation. | ||
| - | <!-- | ||
| - | The line below this paragraph, {{ABSTRACT_PUBMED_16690741}}, adds the Publication Abstract to the page | ||
| - | (as it appears on PubMed at http://www.pubmed.gov), where 16690741 is the PubMed ID number. | ||
| - | --> | ||
{{ABSTRACT_PUBMED_16690741}} | {{ABSTRACT_PUBMED_16690741}} | ||
| Line 46: | Line 42: | ||
[[Category: Tb structural genomics consortium]] | [[Category: Tb structural genomics consortium]] | ||
[[Category: Tbsgc]] | [[Category: Tbsgc]] | ||
| - | Created with the participation of [[User:Michael Strong|Michael Strong]], [[User:Eran Hodis|Eran Hodis]]. | + | <br /> |
| + | *Created with the participation of [[User:Michael Strong|Michael Strong]], [[User:Eran Hodis|Eran Hodis]]. | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
Reference
Toward the structural genomics of complexes: crystal structure of a PE/PPE protein complex from Mycobacterium tuberculosis., Strong M, Sawaya MR, Wang S, Phillips M, Cascio D, Eisenberg D, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 May 23;103(21):8060-5. Epub 2006 May 11. PMID:16690741
- Created with the participation of Michael Strong, Eran Hodis.