Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
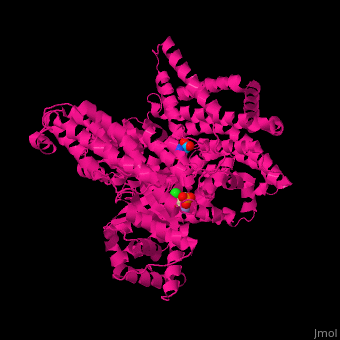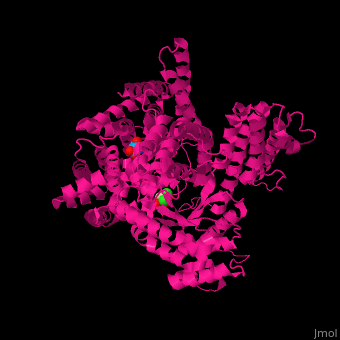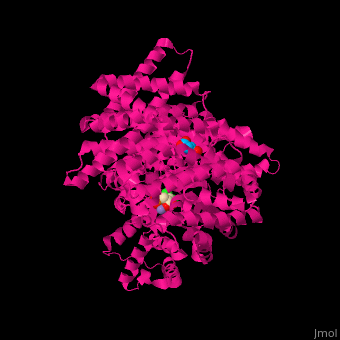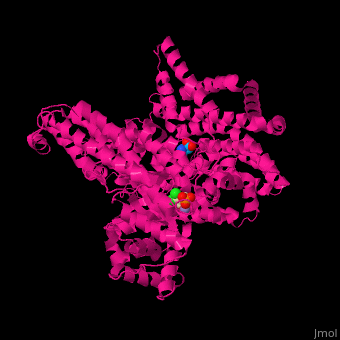
| - | Maze PEPC active site contains an Mn+2 ion<ref>PMID:12467579</ref>. | + | Maze PEPC <scene name='57/573979/Cv/2'>active site</scene> contains an <scene name='57/573979/Cv/3'>Mn+2 ion</scene><ref>PMID:12467579</ref>. <scene name='57/573979/Cv/4'>Aspartate binding site</scene>. Water molecules shown as red spheres. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase== | ==3D structures of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase== | ||
Revision as of 12:49, 29 August 2017
| |||||||||||
3D structures of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
Updated on 29-August-2017
3odm – PEPC + malonate – Clostridium perfringens
3zgb, 3zge – PEPC + aspartate – Flaveria pringlei
1fiy, 1qb4 – EcPEPC + aspartate – Escherichia coli
1jqn – EcPEPC + aspartate + PEP analog
1jqo – PEPC – corn
4bxc – FtPEPC + α-D-glucose-6-phosphate – Flaveria trinervia
4bxh – FtPEPC
References
- ↑ Rademacher T, Hausler RE, Hirsch HJ, Zhang L, Lipka V, Weier D, Kreuzaler F, Peterhansel C. An engineered phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase redirects carbon and nitrogen flow in transgenic potato plants. Plant J. 2002 Oct;32(1):25-39. PMID:12366798
- ↑ Matsumura H, Xie Y, Shirakata S, Inoue T, Yoshinaga T, Ueno Y, Izui K, Kai Y. Crystal structures of C4 form maize and quaternary complex of E. coli phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylases. Structure. 2002 Dec;10(12):1721-30. PMID:12467579
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Karsten Theis, Lucas Xavier da Cunha, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman