Single-stranded DNA-binding protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
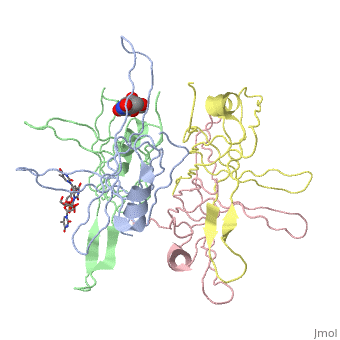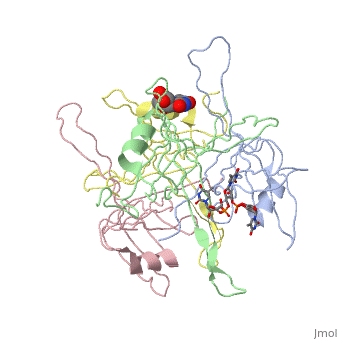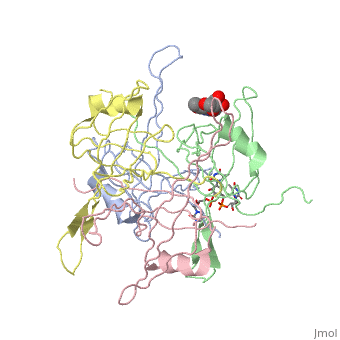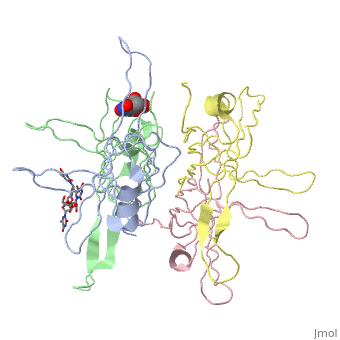
| - | <StructureSection load='1eqq' size='450' side='right' scene='' caption='E. coli SSB complex with ssDNA and UMP [[1eqq]]'> | + | <StructureSection load='1eqq' size='450' side='right' scene='' caption='E. coli SSB complex with ssDNA (stick model) and UMP [[1eqq]]'> |
'''Single-stranded DNA-binding protein''' (SSB) binds to single-stranded regions of DNA (ssDNA) to protect it from annealing, prevention of secondary structure formation and digestion. SSB binds to DNA in a sequence-independent manner. The binding of SSB enables processes like replication, DNA repair and recombination to occur. SSB can form complexes with specific genome maintenance proteins helping their activities<ref>PMID:22976174</ref>.<br /> | '''Single-stranded DNA-binding protein''' (SSB) binds to single-stranded regions of DNA (ssDNA) to protect it from annealing, prevention of secondary structure formation and digestion. SSB binds to DNA in a sequence-independent manner. The binding of SSB enables processes like replication, DNA repair and recombination to occur. SSB can form complexes with specific genome maintenance proteins helping their activities<ref>PMID:22976174</ref>.<br /> | ||
* '''Viral SSB proteins''' are monomeric.<br /> | * '''Viral SSB proteins''' are monomeric.<br /> | ||
Revision as of 08:05, 26 October 2017
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of single-stranded DNA-binding protein
Updated on 26-October-2017
References
- ↑ Marceau AH. Functions of single-strand DNA-binding proteins in DNA replication, recombination, and repair. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;922:1-21. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-032-8_1. PMID:22976174 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-032-8_1