Calcium uptake protein 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Structure of MICU1== | ==Structure of MICU1== | ||
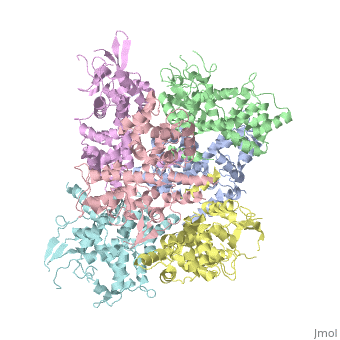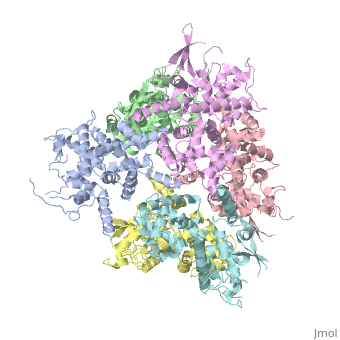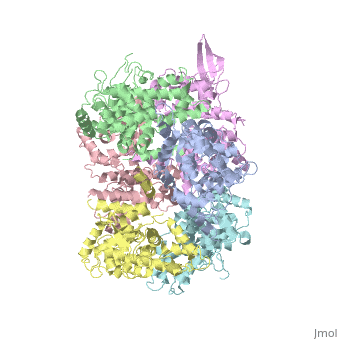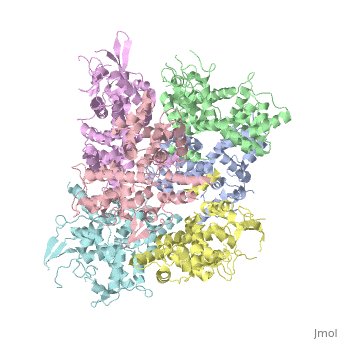
<StructureSection load='4NSC' size='340' side='left' caption='Human mitochondrial calcium uptake protein 1 (PDB code [[4nsc]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='4NSC' size='340' side='left' caption='Human mitochondrial calcium uptake protein 1 (PDB code [[4nsc]])' scene=''> | ||
| - | MICU 1 (Mitochondrial Calcium Uptake 1) is a key regulator of mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) required to increase calcium uptake by MCU when cytoplasmic calcium is high. | + | '''MICU 1''' ('''Mitochondrial Calcium Uptake Protein 1''') is a key regulator of mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) required to increase calcium uptake by MCU when cytoplasmic calcium is high. |
It also regulates glucose-dependent insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cells by regulating mitochondrial calcium uptake. | It also regulates glucose-dependent insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cells by regulating mitochondrial calcium uptake. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
If MICU1 gene is modified, Ca2+ can be load in higher concentration in the mitochondry resulting Myopathy with extrapyramidal signs (MPXPS). This is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by early-onset proximal muscle weakness with a static course and moderately to grossly elevated serum creatine kinase levels accompanied by learning difficulties. Most patients develop subtle extrapyramidal motor signs that progress to a debilitating disorder of involuntary movement with variable features, including chorea, tremor, dystonic posturing and orofacial dyskinesia. Additional variable features include ataxia, microcephaly, ophthalmoplegia, ptosis, optic atrophy and axonal peripheral neuropathy. | If MICU1 gene is modified, Ca2+ can be load in higher concentration in the mitochondry resulting Myopathy with extrapyramidal signs (MPXPS). This is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by early-onset proximal muscle weakness with a static course and moderately to grossly elevated serum creatine kinase levels accompanied by learning difficulties. Most patients develop subtle extrapyramidal motor signs that progress to a debilitating disorder of involuntary movement with variable features, including chorea, tremor, dystonic posturing and orofacial dyskinesia. Additional variable features include ataxia, microcephaly, ophthalmoplegia, ptosis, optic atrophy and axonal peripheral neuropathy. | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == 3D Structures of calcium uptake protein 1 == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[4nsc]] – hCBARA1 - human <BR /> | ||
| + | [[4nsd]] – hCBARA1 + Ca <BR /> | ||
| + | [[2a8n]] – AtCDA – ''Agrobacterium tumefaciens'' <BR /> | ||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
Revision as of 09:35, 1 January 2018
Contents |
Structure of MICU1
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of calcium uptake protein 1
Updated on 01-January-2018
4nsc – hCBARA1 - human
4nsd – hCBARA1 + Ca
2a8n – AtCDA – Agrobacterium tumefaciens
See Also
References
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260152737_Structural_and_mechanistic_insights_into_MICU1_regulation_of_mitochondrial_calcium_uptake
- http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/gene/MICU1
- http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/home/home.do
- http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9BPX6