We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Aconitase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
== Cytosolic aconitase and its other function == | == Cytosolic aconitase and its other function == | ||
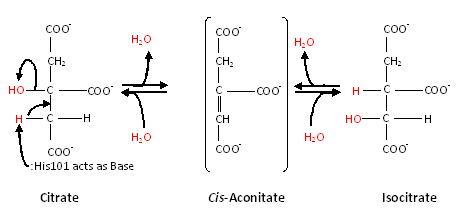
| - | A specialty of cAc is that in mammals it has developed a <scene name=' | + | A specialty of cAc is that in mammals it has developed a <scene name='33/338089/Cv/2'>second function</scene> as inhibitor of <scene name='33/338089/Cv/3'>those mRNA</scene> that carry an <scene name='33/338089/Cv/4'>iron-responsive element (IRE)</scene>. Therefore, the cytosolic cAc is named IREBP for IRE-binding protein when this function is talked about. Only one of the two functions is active, depending on whether <scene name='Aconitase/2b3x-cluster/1'>the (4Fe-4S) cofactor</scene> is present in the molecule: it's essential for <scene name='Aconitase/2b3x-total/1'>the ACO function</scene>. You can see, by <scene name='Aconitase/Morph/2'>looking at the morph</scene>, how much the enzyme structure differs between those two functions. |
Along with serving as a catalyst, aconitase is a member of the iron regulatory protien-1 (IRP-1) family. These enzymes have been found to play a role in regulatory RNA-binding proteins. This suggests a novel role for Fe-S clusters as post-translational regulatory switches.<ref name="Frishman" /> | Along with serving as a catalyst, aconitase is a member of the iron regulatory protien-1 (IRP-1) family. These enzymes have been found to play a role in regulatory RNA-binding proteins. This suggests a novel role for Fe-S clusters as post-translational regulatory switches.<ref name="Frishman" /> | ||
Revision as of 11:19, 8 January 2018
| |||||||||||
3D structures of Aconitase
Updated on 08-January-2018
Literature
- M. Claire Kennedy and Helmut Beinert: IX.4. Aconitase. in Ivano Bertini, Harry B. Gray, Edward I. Stiefel, Joan Selverstone Valentine (eds.): Biological Inorganic Chemistry: Structure and Reactivity. University Science Books, Herndon 2006. ISBN 1891389432 pp.209--
Additional Resources
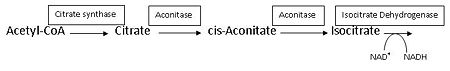
For additional information, see: Carbohydrate Metabolism; Krebs cycle step 2.
References
- ↑ Zheng L, Kennedy MC, Beinert H, Zalkin H. Mutational analysis of active site residues in pig heart aconitase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7895-903. PMID:1313811
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Frishman D, Hentze MW. Conservation of aconitase residues revealed by multiple sequence analysis. Implications for structure/function relationships. Eur J Biochem. 1996 Jul 1;239(1):197-200. PMID:8706708
- ↑ Dupuy J, Volbeda A, Carpentier P, Darnault C, Moulis JM, Fontecilla-Camps JC. Crystal structure of human iron regulatory protein 1 as cytosolic aconitase. Structure. 2006 Jan;14(1):129-39. PMID:16407072 doi:10.1016/j.str.2005.09.009
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Beinert, H., Kennedy, M. C., Stout, C.D. “Aconitase as Iron−Sulfur Protein, Enzyme, and Iron-Regulatory Protein.” Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 2335−2373.
- ↑ Lauble H, Kennedy MC, Beinert H, Stout CD. Crystal structures of aconitase with trans-aconitate and nitrocitrate bound. J Mol Biol. 1994 Apr 8;237(4):437-51. PMID:8151704 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1994.1246
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Voet, Donald, Judith G. Voet, and Charlotte W. Pratt. Fundamentals of Biochemistry Life at the Molecular Level. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2008. p. 578-579. Print.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Flint, DH., and Allen, RM. "Iron-sulfur protein with nonredox functions.” Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 2315−2334.
External links
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Ralf Stephan, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky, Anthony Noles, Angel Herraez, Eran Hodis