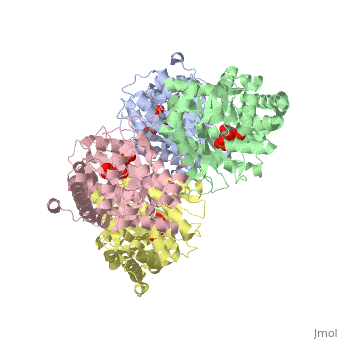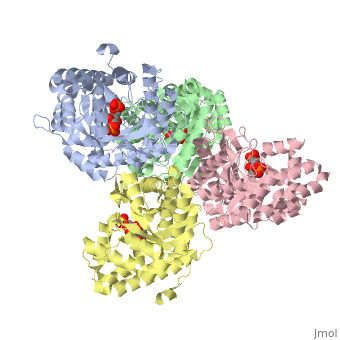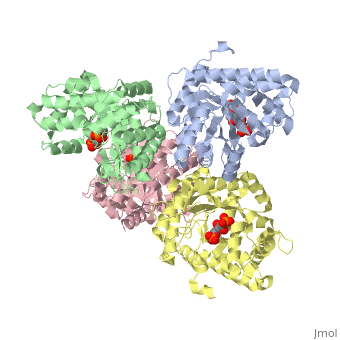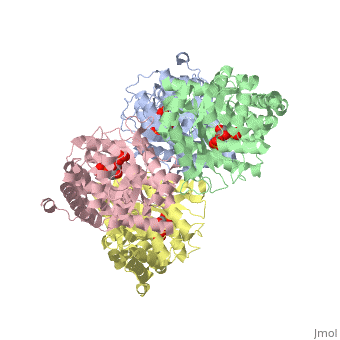
Aldolase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
**[[3q94]] – BaFBPA – ''Bacullus anthracis''<br /> | **[[3q94]] – BaFBPA – ''Bacullus anthracis''<br /> | ||
**[[3c4u]] – HpFBPA – ''Helicobacter pylori''<br /> | **[[3c4u]] – HpFBPA – ''Helicobacter pylori''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1zah]], [[1fdj]], [[1ewd]], [[1ewe]], [[1ex5]], [[1ado]] - rFBPA – rabbit<br /> | + | **[[1zah]], [[1fdj]], [[1ewd]], [[1ewe]], [[1ex5]], [[1ado]], [[5vy5]] - rFBPA – rabbit<br /> |
**[[3dfn]], [[3dfp]], [[3dfq]], [[3dft]], [[2bv4]], [[3b8d]], [[3bv4]], [[5f4x]] – rFBPA (mutant)<br /> | **[[3dfn]], [[3dfp]], [[3dfq]], [[3dft]], [[2bv4]], [[3b8d]], [[3bv4]], [[5f4x]] – rFBPA (mutant)<br /> | ||
**[[3kx6]] – FBPA – ''Babesia bovis''<br /> | **[[3kx6]] – FBPA – ''Babesia bovis''<br /> | ||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
**[[2iqt]] – FBPA – ''Porphyromonas gingivalis''<br /> | **[[2iqt]] – FBPA – ''Porphyromonas gingivalis''<br /> | ||
**[[2fjk]] – FBPA – ''Thermus caldophilus''<br /> | **[[2fjk]] – FBPA – ''Thermus caldophilus''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1xfb]], [[1qo5]], [[2ald]], [[1ald]] – hFBPA – human<br /> | + | **[[1xfb]], [[1qo5]], [[2ald]], [[1ald]], [[5ky6]] – hFBPA – human<br /> |
**[[1xdl]], [[1xdm]] – hFBPA (mutant)<br /> | **[[1xdl]], [[1xdm]] – hFBPA (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[1l6w]] – EcFBPA I - ''Escherichia coli''<br /> |
| + | **[[1gyn]], [[1dos]], [[1zen]], [[5gk3]], [[5gk4]], [[5gk5]], [[5gk6]], [[5gk7]], [[5gk8]] – EcFBPA II <br /> | ||
**[[1f2j]] – FBPA – ''Trypanosoma brucei''<br /> | **[[1f2j]] – FBPA – ''Trypanosoma brucei''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5o0w]] - FBPA – ''Trypanosoma congolense''<br /> | ||
**[[1fba]] – FBPA – ''Drosophila melanogaster''<br /> | **[[1fba]] – FBPA – ''Drosophila melanogaster''<br /> | ||
**[[3t2b]] – TnFBPA – ''Thermoproteus neutrophilus''<br /> | **[[3t2b]] – TnFBPA – ''Thermoproteus neutrophilus''<br /> | ||
**[[4moz]] – FBPA – ''Slackia heliotrinireducens''<br /> | **[[4moz]] – FBPA – ''Slackia heliotrinireducens''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4d2j]], [[4tu1]] – TgFBPA – ''Toxoplasma gondii''<br /> | + | **[[4d2j]], [[4tu1]], [[5tjs]] – TgFBPA – ''Toxoplasma gondii''<br /> |
| - | *FBPA | + | *FBPA complex |
**[[2yce]], [[1ok4]] – TptFBPA + reaction intermediate<br /> | **[[2yce]], [[1ok4]] – TptFBPA + reaction intermediate<br /> | ||
| Line 97: | Line 99: | ||
**[[1j4e]] - rFBPA (mutant) + substrate<br /> | **[[1j4e]] - rFBPA (mutant) + substrate<br /> | ||
**[[2ot0]] – rFBPA + Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein C-terminal<br /> | **[[2ot0]] – rFBPA + Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein C-terminal<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2ot1]], [[1zaj]], [[1zal]], [[3tu9]] – rFBPA + inhibitor<br /> | + | **[[2ot1]], [[1zaj]], [[1zal]], [[3tu9]], [[5tle]], [[5tlh]], [[5tlw]], [[5tlz]] – rFBPA + inhibitor<br /> |
**[[3lge]] – rFBPA + Sorting Nexin-9<br /> | **[[3lge]] – rFBPA + Sorting Nexin-9<br /> | ||
**[[3gay]] – GiFBPA + inhibitor<br /> | **[[3gay]] – GiFBPA + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| Line 117: | Line 119: | ||
**[[3t2d]] – TnFBPA + FBP<br /> | **[[3t2d]] – TnFBPA + FBP<br /> | ||
**[[3t2e]] – TnFBPA + F6P<br /> | **[[3t2e]] – TnFBPA + F6P<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3t2f]] – TnFBPA + EDTA + dihydroxyacetonephosphate | + | **[[3t2f]] – TnFBPA + EDTA + dihydroxyacetonephosphate<br /> |
| + | **[[5tk3]], [[5tkc]] – TgFBPA + G3P + dihydroxyacetonephosphate <br /> | ||
| + | **[[5tkn]], [[5tkp]] – TgFBPA + P6F <br /> | ||
| + | **[[5tkl]] – TgFBPA + P6F + dihydroxyacetonephosphate <br /> | ||
*Fructose–6-phosphate aldolase | *Fructose–6-phosphate aldolase | ||
| Line 321: | Line 326: | ||
**[[3nxf]], [[3o6y]], [[3ud6]], [[4pek]], [[4pej]], [[4pa8]] – RA – artificial gene<br /> | **[[3nxf]], [[3o6y]], [[3ud6]], [[4pek]], [[4pej]], [[4pa8]] – RA – artificial gene<br /> | ||
**[[4ou1]] – SsRA<br /> | **[[4ou1]] – SsRA<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *17-alpha-hydroxyprogesterone aldolase (steroid 17-alpha-hydroxylase /17,20 lyase) see [[Cytochrome P450]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
=Additional Resources= | =Additional Resources= | ||
Revision as of 09:16, 12 March 2018
| |||||||||||
3D structures of Aldolase
Updated on 12-March-2018
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Carbohydrate Metabolism
References
- ↑ Schurmann M, Sprenger GA. Fructose-6-phosphate aldolase is a novel class I aldolase from Escherichia coli and is related to a novel group of bacterial transaldolases. J Biol Chem. 2001 Apr 6;276(14):11055-61. Epub 2000 Dec 18. PMID:11120740 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M008061200
- ↑ Salleron L, Magistrelli G, Mary C, Fischer N, Bairoch A, Lane L. DERA is the human deoxyribose phosphate aldolase and is involved in stress response. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Dec;1843(12):2913-25. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.09.007. Epub 2014 Sep 16. PMID:25229427 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.09.007
- ↑ Goyer A, Illarionova V, Roje S, Fischer M, Bacher A, Hanson AD. Folate biosynthesis in higher plants. cDNA cloning, heterologous expression, and characterization of dihydroneopterin aldolases. Plant Physiol. 2004 May;135(1):103-11. Epub 2004 Apr 23. PMID:15107504 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.038430
- ↑ Smith BJ, Lawrence MC, Barbosa JA. Substrate-Assisted Catalysis in Sialic Acid Aldolase. J Org Chem. 1999 Feb 5;64(3):945-949. PMID:11674166
- ↑ Wang W, Mazurkewich S, Kimber MS, Seah SY. Structural and kinetic characterization of 4-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-oxoglutarate (HMG)/4-carboxy-4-hydroxy-2-oxoadipate (CHA) aldolase: a protocatechuate degradation enzyme evolutionarily convergent with the HpaI and DmpG pyruvate aldolases. J Biol Chem. 2010 Sep 15. PMID:20843800 doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.159509
- ↑ Powlowski J, Sahlman L, Shingler V. Purification and properties of the physically associated meta-cleavage pathway enzymes 4-hydroxy-2-ketovalerate aldolase and aldehyde dehydrogenase (acylating) from Pseudomonas sp. strain CF600. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(2):377-85. PMID:8419288
- ↑ Bell BJ, Watanabe L, Rios-Steiner JL, Tulinsky A, Lebioda L, Arni RK. Structure of 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate (KDPG) aldolase from Pseudomonas putida. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2003 Aug;59(Pt 8):1454-8. Epub 2003, Jul 23. PMID:12876349
- ↑ Hall DR, Bond CS, Leonard GA, Watt CI, Berry A, Hunter WN. Structure of tagatose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase. Insight into chiral discrimination, mechanism, and specificity of class II aldolases. J Biol Chem. 2002 Jun 14;277(24):22018-24. Epub 2002 Apr 8. PMID:11940603 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M202464200
- ↑ Joerger AC, Gosse C, Fessner WD, Schulz GE. Catalytic action of fuculose 1-phosphate aldolase (class II) as derived from structure-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry. 2000 May 23;39(20):6033-41. PMID:10821675
- ↑ Rea D, Fulop V, Bugg TD, Roper DI. Structure and mechanism of HpcH: a metal ion dependent class II aldolase from the homoprotocatechuate degradation pathway of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 2007 Nov 2;373(4):866-76. Epub 2007 Jun 26. PMID:17881002 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.06.048
- ↑ Riedel TJ, Johnson LC, Knight J, Hantgan RR, Holmes RP, Lowther WT. Structural and Biochemical Studies of Human 4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutarate Aldolase: Implications for Hydroxyproline Metabolism in Primary Hyperoxaluria. PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26021. Epub 2011 Oct 6. PMID:21998747 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026021
- ↑ KARASEK MA, GREENBERG DM. Studies on the properties of threonine aldolases. J Biol Chem. 1957 Jul;227(1):191-205. PMID:13449064
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 Voet, D, Voet, J, & Pratt, C. (2008). Fundamentals of biochemistry, third edition. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- ↑ Protein: fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase from human (homo sapiens), muscle isozyme. (2009). Retrieved from http://scop.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Gefflaut, T., B. Casimir, J. Perie, and M. Willson. "Class I Aldolases: Substrate Specificity, Mechanism, Inhibitors and Structural Aspects." Prog. Biophys. molec. Biol.. 63. (1995): 301-340.
- ↑ Dalby A, Dauter Z, Littlechild JA. Crystal structure of human muscle aldolase complexed with fructose 1,6-bisphosphate: mechanistic implications. Protein Sci. 1999 Feb;8(2):291-7. PMID:10048322
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Sygusch, J., and Beaudry, D. "Allosteric communication in mammalian muscle aldolase." Biochem. J.. 327. (1997): 717-720.
- ↑ Paolella, G, Buono, P, Mancini, F P, Izzo, P, and Salvatore, F. "Structure and expression of mouse aldolase genes." Eur. J. Biochem.. 156. (1986): 229-235.
- ↑ Buono, P, Cassano, S, Alfieri, A, Mancini, A, and Salvatore, F. "Human aldolase C gene expression is regulated by adenosine 30,50-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) in PC12 cells." Gene. 291. (2002): 115-121.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Sophie Mullinix, Jaime Prilusky, Austin Drake, David Canner