User:Alisa Cario
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
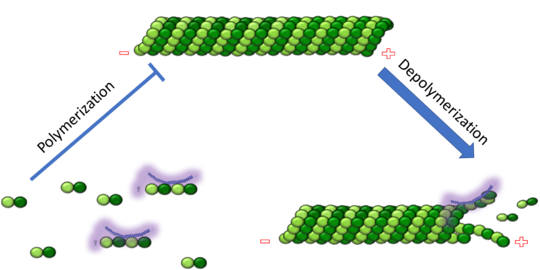
| - | '''Mitosis''' Stathmin's role in the cell cycle progression is well characterized. During interphase, microtubules are relatively stable. However during the onset of mitosis, stathmin is upregulated to increase the rate of catastrophe of microtubules, causing them to become more dynamic (1). Stathmin has also been shown to bind and sequester two tubulin heterodimers, reducing the amount of available tubulin to polymerize microtubules (2). However, as mitosis progresses, microtubules must repolymerize to form the mitotic spindle. Stathmin is regulated during this process by phosphorylation ( ). | + | '''Mitosis''' Stathmin's role in the cell cycle progression is well characterized. During interphase, microtubules are relatively stable. However during the onset of mitosis, stathmin is upregulated to increase the rate of catastrophe of microtubules, causing them to become more dynamic (1). Stathmin has also been shown to bind and sequester two tubulin heterodimers, reducing the amount of available tubulin to polymerize microtubules (2). However, as mitosis progresses, microtubules must repolymerize to form the mitotic spindle. Stathmin is regulated during this process by phosphorylation ( ). There are four known phosphorylation sites of stathmin, serine 16, serine 25, serine 38, and serine 63. Stathmin is the known target of cyclin-dependent kinases ( ). Stathmin overexpression prevents mitotic spindle formation where inhibition interferes with later stages in mitosis. |
[[Image:Stathmin_phosphorylation.png|center|thumb| upright=3| Figure XXX. ]] | [[Image:Stathmin_phosphorylation.png|center|thumb| upright=3| Figure XXX. ]] | ||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
====How does the structure relate to it's function?==== | ====How does the structure relate to it's function?==== | ||
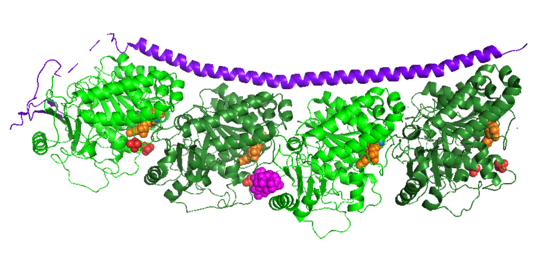
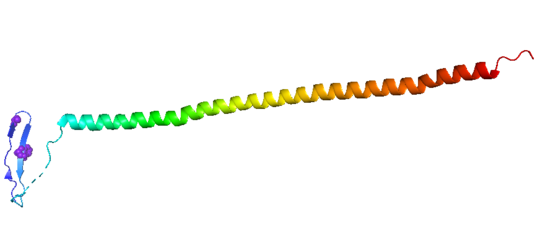
| - | Stathmin is not A structurally complicated the protein, consisting of a single alpha helix, that binds across two tubulin heterodimers, and a mostly disordered N-terminal region that also has some beta strand properties. These different regions of the protein are known to have different functions | + | Stathmin is not A structurally complicated the protein, consisting of a single alpha helix, that binds across two tubulin heterodimers, and a mostly disordered N-terminal region that also has some beta strand properties. These different regions of the protein are known to have different functions. |
| - | The | + | The N-terminal region is known to increase tubulin catastrophe. This region helps destabilize the ends of the microtubule filaments by curving the tubulin dimers at the end, and disrupting lateral hydrogen bonds. The N-terminal region is known as the regulatory domain of the protein, because it is subject to most of the post-translational modifications. This region binds and caps alpha tubulin to accomplish this task. ( ) 4. |
| + | |||
| + | The C-terminal region, also known as the interaction domain, is known to sequester tubulin heterodimers. This region is comprised of a coiled-coil single alpha helix. This region of stathmin is known to bind to helix 10 of alpha tubulin. Helix 10 of alpha tubulin is known to be important for incorporation into microtubules. | ||
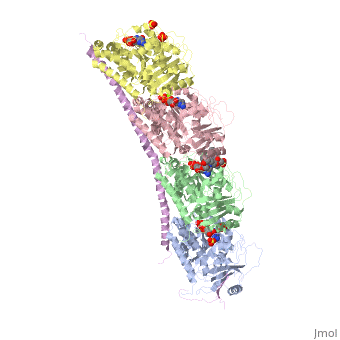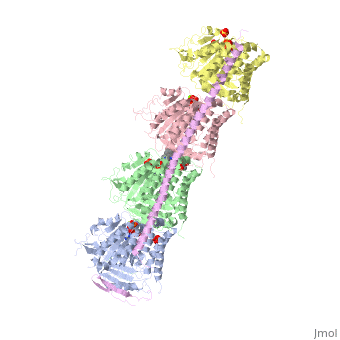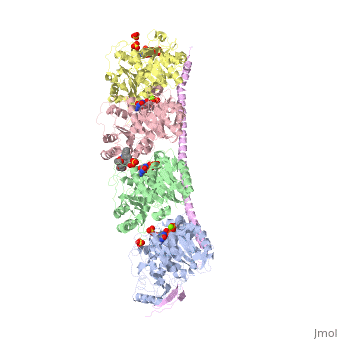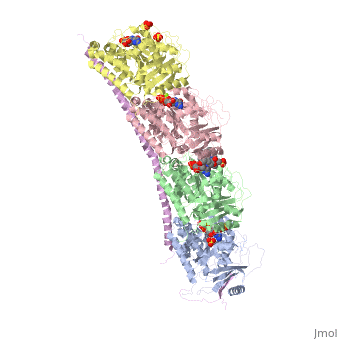
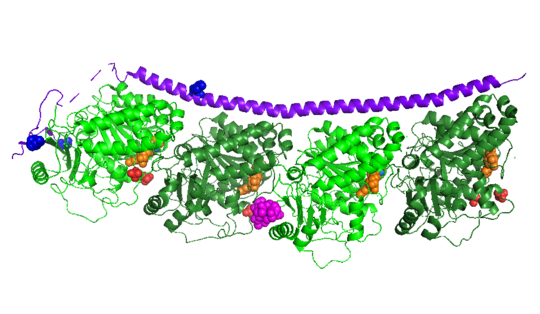
The structure of stathmin, in 4eb6, is stabilized by outside ligands. Vinblastine, is a _____. Also, there are two known mutations in the protein. | The structure of stathmin, in 4eb6, is stabilized by outside ligands. Vinblastine, is a _____. Also, there are two known mutations in the protein. | ||
| Line 69: | Line 71: | ||
== '''Evolutionary conservation''' == | == '''Evolutionary conservation''' == | ||
| - | Stathmin belongs to a gene family. This family includes SCG10 and SCILP, which are neuronal proteins. | + | Stathmin belongs to a gene family. This family includes SCG10 and SCILP, which are neuronal proteins. Other members of this family of proteins include XB3, which was discovered in Xenopus (34 from https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.t01-2-00794.x) |
| - | + | ||
'''Isoforms''' | '''Isoforms''' | ||
| - | There are four isoforms of stathmin. Stathmin 1-3 are expressed early in development | + | There are four isoforms of stathmin which are alternatively spliced from a single gene in . Stathmin 1-3 are expressed early in development |
DEVELOPMENTAL REGULATION | DEVELOPMENTAL REGULATION | ||
LOCATION OF ISOFORMS | LOCATION OF ISOFORMS | ||
Revision as of 12:50, 26 April 2018
- Full Real Name: Alisa Cario
- Position: Graduate Student
- Institution (NO ABBREVIATIONS): University of Vermont
- City, State/Province, Country: Burlington, VT USA
- Field of Expertise or Study: Creation of protopedia page for a class project. The class is Proteins 1 under Dr. Stephen Everse
Stathmin-4 bound to Tubulin stabilized with Vinblastin
4eb6
| |||||||||||