User:Alisa Cario
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
'''Mitosis''' | '''Mitosis''' | ||
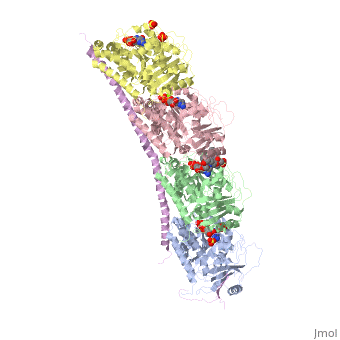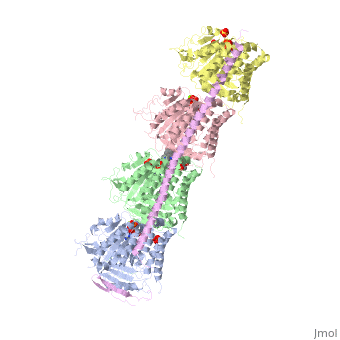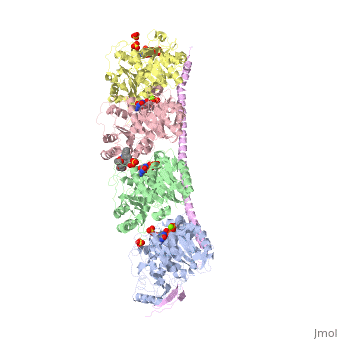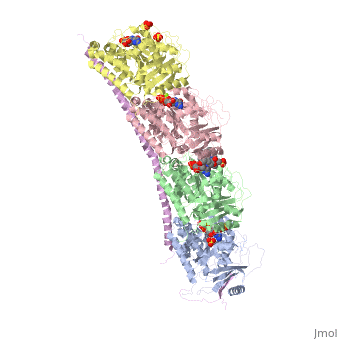
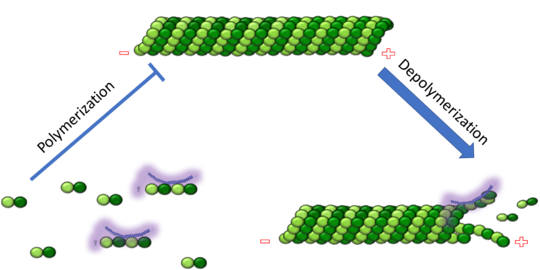
| - | Stathmin's role in the cell cycle progression is well characterized. During interphase, microtubules are relatively stable. However during the onset of mitosis, stathmin is upregulated to increase the rate of catastrophe of microtubules, causing them to become more dynamic (1). Stathmin has also been shown to bind and sequester two tubulin heterodimers, reducing the amount of available tubulin to polymerize microtubules (2). However, as mitosis progresses, microtubules must repolymerize to form the mitotic spindle. Stathmin is regulated during this process by phosphorylation ( ). There are four known phosphorylation sites of stathmin, serine 16, serine 25, serine 38, and serine 63. Stathmin is the known target of cyclin-dependent kinases ( ). Stathmin overexpression prevents mitotic spindle formation where inhibition interferes with later stages in mitosis ( ). | + | Stathmin's role in the cell cycle progression is well characterized. During interphase, microtubules are relatively stable. However during the onset of mitosis, stathmin is upregulated to increase the rate of catastrophe of microtubules, causing them to become more dynamic (1). Stathmin has also been shown to bind and sequester two tubulin heterodimers, reducing the amount of available tubulin to polymerize microtubules (2). However, as mitosis progresses, microtubules must repolymerize to form the mitotic spindle. Stathmin is regulated during this process by phosphorylation ( ). There are four known <scene name='77/778894/Stathmin_phospho/1'>phosphorylation sites of stathmin</scene>, serine 16, serine 25, serine 38, and serine 63. Stathmin is the known target of cyclin-dependent kinases ( ). Stathmin overexpression prevents mitotic spindle formation where inhibition interferes with later stages in mitosis ( ). |
[[Image:Stathmin_phosphorylation.png|center|thumb| upright=3| Figure XXX. ]] | [[Image:Stathmin_phosphorylation.png|center|thumb| upright=3| Figure XXX. ]] | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
== '''Disease relevance''' == | == '''Disease relevance''' == | ||
| - | '''Multiple Schlerosis''': Stathmin expression is has been linked to multiple sclerosis (MS) , a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by lack of motor control and numbness. MS is caused by loss of myelination on axons in the nervous system. Myelination of axons is performed by cells called oligodendrocytes. Stathmin is regulated in oligodendrocyte lineage, with progenitor cells containing larger amounts than differentiated oligodendrocytes. Brain tissue samples from people suffering from multiple sclerosis found that stathmin is up regulated later in the lineage of oligodendrocytes. The up-regulation of stathmin showed a more globular morphology of the cells. Oligodendrocyte ability to myelinate axons in the central nervous system was greatly reduced in these patients (Reference). | + | '''Multiple Schlerosis''': Stathmin expression is has been linked to multiple sclerosis (MS) , a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by lack of motor control and numbness. MS is caused by loss of myelination on axons in the nervous system. Myelination of axons is performed by cells called oligodendrocytes. Stathmin is regulated in oligodendrocyte lineage, with progenitor cells containing larger amounts than differentiated oligodendrocytes. Brain tissue samples from people suffering from multiple sclerosis found that stathmin is up regulated later in the lineage of oligodendrocytes. The up-regulation of stathmin showed a more globular morphology of the cells. Oligodendrocyte ability to myelinate axons in the central nervous system was greatly reduced in these patients (Reference). (REFERENCE). |
'''Cancer''': Due to stathmin's role in mitosis and cell migration, it is not surprising that is has been implicated in many cancers and is an active target of cancer therapeutics. Stathmin is defined as an oncoprotein. Overexpression of stathmin has been shown to increase metastasis, worse prognosis, and increased chemoresistance ( ). Stathmin levels are known to be increasesd in a number of cancers. Stathmin was seen to be upregulated in breast cancer tissue comparative with normal breast tissue ( ). Another study was done to show stathmin upregulation in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas ( ). Studies using a non-phosphorylatable stathmin mutant shows that cells arrest during mitosis (Marklund, Larson) | '''Cancer''': Due to stathmin's role in mitosis and cell migration, it is not surprising that is has been implicated in many cancers and is an active target of cancer therapeutics. Stathmin is defined as an oncoprotein. Overexpression of stathmin has been shown to increase metastasis, worse prognosis, and increased chemoresistance ( ). Stathmin levels are known to be increasesd in a number of cancers. Stathmin was seen to be upregulated in breast cancer tissue comparative with normal breast tissue ( ). Another study was done to show stathmin upregulation in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas ( ). Studies using a non-phosphorylatable stathmin mutant shows that cells arrest during mitosis (Marklund, Larson) | ||
Revision as of 19:23, 27 April 2018
* Full Real Name: Alisa Cario
- Position: Graduate Student
- Institution (NO ABBREVIATIONS): University of Vermont
- City, State/Province, Country: Burlington, VT USA
- Field of Expertise or Study: Creation of protopedia page for a class project. The class is Proteins 1 under Dr. Stephen Everse
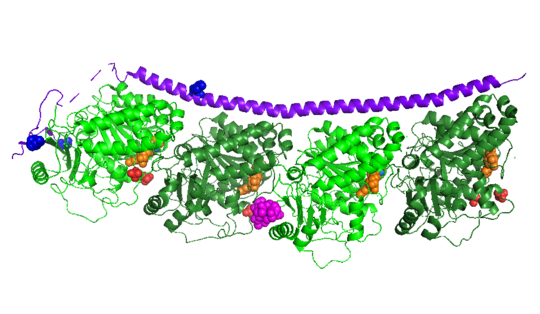
Stathmin-4 (RB3) bound to Tubulin stabilized with Vinblastin
4eb6
| |||||||||||