Introduction and Background
The cytoskeleton brings structure to the cell, is integral in cell division, and aids in migration. One of the constitutive parts of the cytoskeleton are microtubules. Microtubules are polymerized from tubulin subunits that incorporate into a hollow cylindrical structure linked together by lateral and vertical hydrogen bonds. Each tubulin subunit is made from a heterodimer of alpha and beta tubulin. Both alpha and beta tubulin are known to bind to GTP. However, only the beta subunit hydrolyzes GTP, which occurs once incorporated into microtubules. The beta tubulin hydrolysis of GTP to GDP is known to destabilize microtubules. Microtubules have polarity where one end of microtubule, called the plus end, has a greater affinity to add tubulin subunits than the other end, called the minus end. Microtubules are inherently dynamic, going through periods of depolymerization, known as catastrophe, and then return to polymerization, known as rescue. Microtubules can also go through a process called tread milling, where the length of the microtubule does not change but the rate of polymerization at the plus end equals the rate of depolymerization at the minus end. There are a number of microtubule associated proteins (MAPs) that are known to regulate the dynamics of microtubules. Some examples of this include MAPTau, MAP2 and stathmin. See beta tubulin, tau.
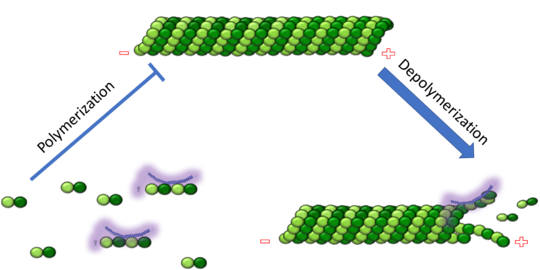
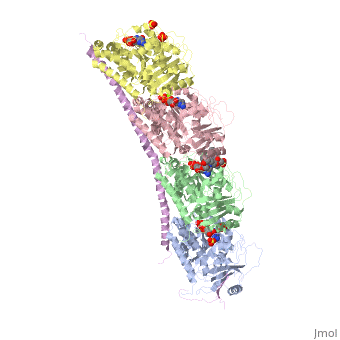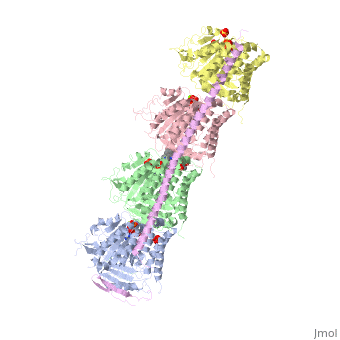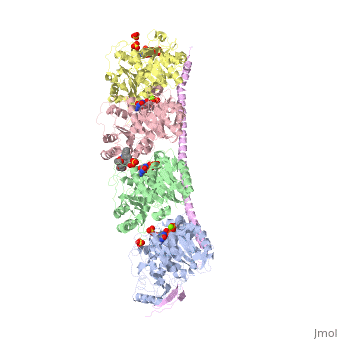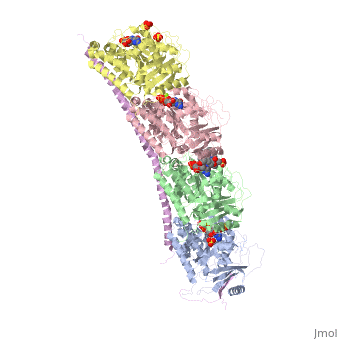
Figure XXX. Stathmin in purple can bind to tubulin dimers to prevent polymerization or to microtubules to increase catastrophe
Function
, also known as oncoprotein 18 or metablastin, is a 19kDa microtubule associated protein known to destabilize microtubules ( ). Stathmin is a cell cycle and developmentally regulated protein, known to play a role in proliferation, differentiation, and function of cells. ( ) Stathmin can bind to to inhibit polymerization or it can bind to the microtubule to enhance the rate of catastrophe.
Mitosis
Stathmin's role in the cell cycle progression is well characterized. During interphase, microtubules are relatively stable. However during the onset of mitosis, stathmin is upregulated to increase the rate of catastrophe of microtubules, causing them to become more dynamic (1). Stathmin has also been shown to bind and sequester two tubulin heterodimers, reducing the amount of available tubulin to polymerize microtubules (2). However, as mitosis progresses, microtubules must repolymerize to form the mitotic spindle. Stathmin is regulated during this process by phosphorylation ( ). There are four known , serine 16, serine 25, serine 38, and serine 63. Stathmin is the known target of cyclin-dependent kinases ( ). Stathmin overexpression prevents mitotic spindle formation where inhibition interferes with later stages in mitosis ( ).
Migration
The cytoskeleton is a vital part of cell migration. The leading edge is driven by actin polymerization ( ). However, microtubules are needed to retract from the trailing edge to move the cell forward. Stathmin is thought to have a role in migration, allowing to microtubules to depolymerize to aid in movement. Stathmin has been show to be a part of the integrin alpha5 beta1/FAK/ ERK pathway ( ).
Differentiation
Stathmin expression is regulated during stages of development. It is regulated in early and late embryogenesis. ( ) . It is also regulated in differentiating muscle cells, T lymphocytes, and oligodendryocytes (. ).
Structural highlights
How does the structure relate to it's function?
consistis of a coiled coil alpha helix, that binds across two tubulin heterodimers, and a mostly disordered N-terminal region that also has some beta strand properties. These different regions of the protein are known to have different functions.
The is known to increase tubulin catastrophe. This region helps destabilize the ends of the microtubule filaments by curving the tubulin dimers at the end, and disrupting lateral hydrogen bonds. The N-terminal region is known as the regulatory domain of the protein, because it is subject to most of the post-translational modifications, as shown in Figure XXX. This region binds and caps alpha tubulin to accomplish this task. ( ) 4.
The, also known as the interaction domain, is known to sequester tubulin heterodimers. This region is comprised of a . This region of stathmin is . Helix 10 of alpha tubulin is thought to be important for incorporation into microtubules ( ) .
The structure of stathmin, in 4eb6, is bound to two tubulin heterodimers. The tubulin dimers are bound to outside ligands. is a chemotherapeutic that binds to tubulin to prevent microtubule polymerization ( ). The tubulin subunits are bound to from The beta subunits of tubulin are bound to GDP and each of the alpha subunits are bound to GTP and a Magnesium ion. There are also to the stathmin in this structure. The mutations at position 11 from an cysteine to an alanine and position 16 from a Phenylalanine to a Tryptophan.
Disease relevance
Multiple Schlerosis: Stathmin expression is has been linked to multiple sclerosis (MS) , a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by lack of motor control and numbness. MS is caused by loss of myelination on axons in the nervous system. Myelination of axons is performed by cells called oligodendrocytes. Stathmin is regulated in oligodendrocyte lineage, with progenitor cells containing larger amounts than differentiated oligodendrocytes. Brain tissue samples from people suffering from multiple sclerosis found that stathmin is up regulated later in the lineage of oligodendrocytes. The up-regulation of stathmin showed a more globular morphology of the cells. Oligodendrocyte ability to myelinate axons in the central nervous system was greatly reduced in these patients (Reference). (REFERENCE).
Cancer: Due to stathmin's role in mitosis and cell migration, it is not surprising that is has been implicated in many cancers and is an active target of cancer therapeutics. Stathmin is defined as an oncoprotein. Overexpression of stathmin has been shown to increase metastasis, worse prognosis, and increased chemoresistance ( ). Stathmin levels are known to be increasesd in a number of cancers. Stathmin was seen to be upregulated in breast cancer tissue comparative with normal breast tissue ( ). Another study was done to show stathmin upregulation in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas ( ). Studies using a non-phosphorylatable stathmin mutant shows that cells arrest during mitosis (Marklund, Larson)
Evolutionary conservation
Stathmin belongs to a gene family that have a characteristic stathmin-like domain. There are four isoforms of stathmin which are alternatively spliced from a single gene. This family includes Stathmin-1, SCG10/stathmin-2, SCILP/stathmin-3, and RB3/stathmin-4. SCG10 and SCLIP, are exclusively neuronal proteins, while RB3 is expressed mostly in the brain but some in the adrenal glands. Unlike the neuronal proteins, stathmin-1 is ubiquitously expressed in all cell types. All members of this family contain the C-terminal coiled coil domain. However, the binding affinity to tubulin of the protein family members differ (. ). Interestingly, the neuronal isoforms are known to contain an additional N-terminal domain to affect their localization ( ).
Links to available structures
References
1. Belmont LD, Mitchison TJ. 1996. Identification of a proteinthat interacts with tubulin dimers and increases thecatastrophe rate of microtubules. Cell 84:623–631
2. Jourdain L, Curmi P, Sobel A, Pantaloni D, Carlier M-F.1997. Stathmin: A tubulin-sequestering protein whichforms a ternary T2S complex with two tubulin molecules.Biochemistry 36:10817–10821.
3. Howell B, Larsson N, Gullberg M, Cassimeris L. 1999.Dissociation of the tubulin-sequestering and microtubulecatastrophe-promoting activities of oncoprotein 18/stath-min. Mol Biol Cell 10:105–118.
Tournebize, R., Andersen, S. S., Verde, F., Dore ́e, M., Karsenti, E., andHyman, A. A. (1997) EMBO J. 16, 5537–5549
L arssonN,MelanderH,MarklundU,Osterman0andGullbergM (1995)G2/M transition requires multisite phosphorylation of oncoprotein 18 by two distinct protein kinase systems. J Biol Chem 270: 14175-14183
LarssonN,MarklundU,GradinHM,BrattsandGandGullbergM (1997)Controlof microtubule dynamics by oncoprotein 18: dissection of the regulatory role of multisite phosphorylation during mitosis. Mol Cell Biol 17: 553(-5539
Lawler S, Gavet 0, Rich T and Sobel A (1998) Stathmin overexpression in 293 cells affectssignaltransductionandthecelcycle.FEBS Lett421:55-60
StrahlerJR,LambBJ,UngarDR,FoxDA andHanashSM (1992)Cellcycle progressionisassociatedwithdistinctpatternsofphosphorylationofOp18. BiochemBiophvsResCommun 185:197-203
http://www.jbc.org/content/268/22/16420.full.pdf