User:Alisa Cario
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
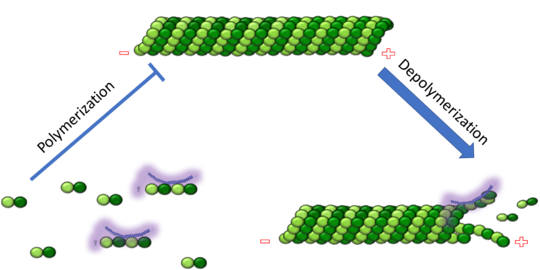
<scene name='77/778894/Stathmin/1'>Stathmin</scene>, also known as oncoprotein 18 or metablastin, is a 19kDa microtubule associated protein known to destabilize microtubules ( ). Stathmin is a cell cycle and developmentally regulated protein, known to play a role in proliferation, differentiation, and function of cells. ( ) Stathmin can bind to <scene name='77/778894/Highlight_of_tubulin/1'>tubulin dimers</scene> to inhibit polymerization or it can bind to the microtubule to enhance the rate of catastrophe. | <scene name='77/778894/Stathmin/1'>Stathmin</scene>, also known as oncoprotein 18 or metablastin, is a 19kDa microtubule associated protein known to destabilize microtubules ( ). Stathmin is a cell cycle and developmentally regulated protein, known to play a role in proliferation, differentiation, and function of cells. ( ) Stathmin can bind to <scene name='77/778894/Highlight_of_tubulin/1'>tubulin dimers</scene> to inhibit polymerization or it can bind to the microtubule to enhance the rate of catastrophe. | ||
| - | '''Mitosis''' | + | '''Mitosis''': Stathmin's role in the cell cycle progression is well characterized. During interphase, microtubules are relatively stable. However during the onset of mitosis, stathmin is upregulated to increase the rate of catastrophe of microtubules, causing them to become more dynamic (1). Stathmin has also been shown to bind and sequester two tubulin heterodimers, reducing the amount of available tubulin to polymerize microtubules (2). However, as mitosis progresses, microtubules must repolymerize to form the mitotic spindle. Stathmin is regulated during this process by phosphorylation ( ). There are four known <scene name='77/778894/Stathmin_phospho/1'>phosphorylation sites of stathmin</scene>, serine 16, serine 25, serine 38, and serine 63. Stathmin is the known target of cyclin-dependent kinases ( ). Stathmin overexpression prevents mitotic spindle formation where inhibition interferes with later stages in mitosis ( ). |
| - | Stathmin's role in the cell cycle progression is well characterized. During interphase, microtubules are relatively stable. However during the onset of mitosis, stathmin is upregulated to increase the rate of catastrophe of microtubules, causing them to become more dynamic (1). Stathmin has also been shown to bind and sequester two tubulin heterodimers, reducing the amount of available tubulin to polymerize microtubules (2). However, as mitosis progresses, microtubules must repolymerize to form the mitotic spindle. Stathmin is regulated during this process by phosphorylation ( ). There are four known <scene name='77/778894/Stathmin_phospho/1'>phosphorylation sites of stathmin</scene>, serine 16, serine 25, serine 38, and serine 63. Stathmin is the known target of cyclin-dependent kinases ( ). Stathmin overexpression prevents mitotic spindle formation where inhibition interferes with later stages in mitosis ( ). | ||
| + | '''Migration''': The cytoskeleton is a vital part of cell migration. The leading edge is driven by actin polymerization ( ). However, microtubules are needed to retract from the trailing edge to move the cell forward. Stathmin is thought to have a role in migration, allowing to microtubules to depolymerize to aid in movement. Stathmin has been show to be a part of the integrin alpha5 beta1/FAK/ ERK pathway ( ). | ||
| - | + | '''Differentiation''': Stathmin expression is regulated during stages of development. It is regulated in early and late embryogenesis. ( ) . It is also regulated in differentiating muscle cells, T lymphocytes, and oligodendryocytes (. ). | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | '''Differentiation''' | + | |
| - | Stathmin expression is regulated during stages of development. It is regulated in early and late embryogenesis. ( ) . It is also regulated in differentiating muscle cells, T lymphocytes, and oligodendryocytes (. ). | + | |
| - | + | ||
== '''Structural highlights''' == | == '''Structural highlights''' == | ||
Revision as of 19:29, 27 April 2018
* Full Real Name: Alisa Cario
- Position: Graduate Student
- Institution (NO ABBREVIATIONS): University of Vermont
- City, State/Province, Country: Burlington, VT USA
- Field of Expertise or Study: Creation of protopedia page for a class project. The class is Proteins 1 under Dr. Stephen Everse
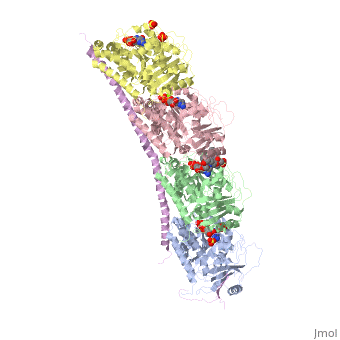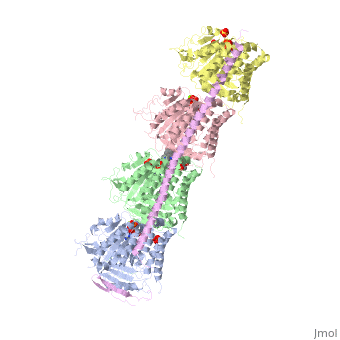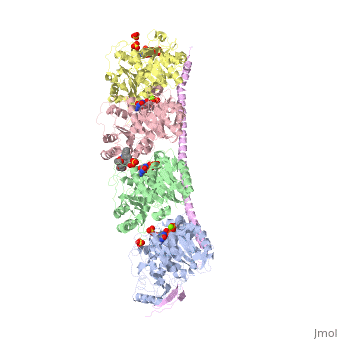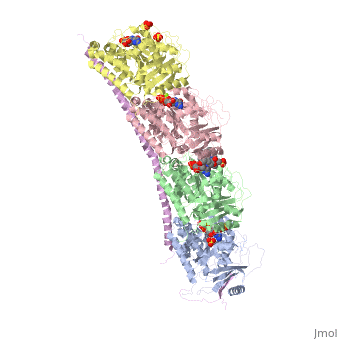
Stathmin-4 (RB3) bound to Tubulin stabilized with Vinblastin
4eb6
| |||||||||||