Main Page
From Proteopedia
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
<tr style="font-size: 1.2em; text-align: center;"> | <tr style="font-size: 1.2em; text-align: center;"> | ||
| - | <td style="padding: 10px;>How to author pages and contribute to Proteopedia</td> | + | <td style="padding: 10px;>[[http://proteopedia.org/w/Help:Contents#For_authors:_contributing_content|How to author pages and contribute to Proteopedia]]</td> |
<td style="padding: 10px;></td> | <td style="padding: 10px;></td> | ||
<td style="padding: 10px;>How to get an Interactive 3D Complement for your paper</td> | <td style="padding: 10px;>How to get an Interactive 3D Complement for your paper</td> | ||
Revision as of 13:24, 18 October 2018
|
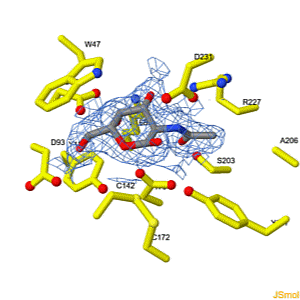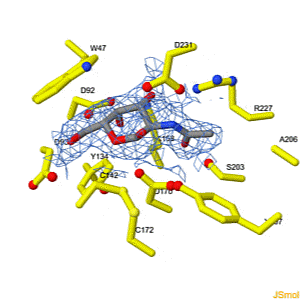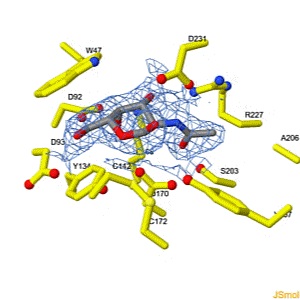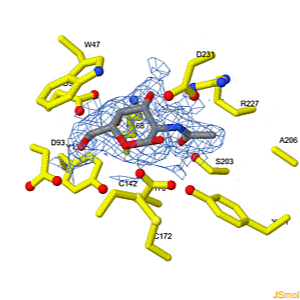
Because life has more than 2D, Proteopedia helps to understand relationships between structure and function. Proteopedia is a free, collaborative 3D-encyclopedia of proteins & other molecules. ISSN 2310-6301 | |||||||||||
| Selected Pages | Art on Science | Journals | Education | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
| Other Selected Pages | More Art on Science | Other Journals | More on Education | ||||||||
| [to author pages and contribute to Proteopedia] | How to get an Interactive 3D Complement for your paper | How to author pages and contribute to Proteopedia | |||||||||