2-isopropylmalate synthase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
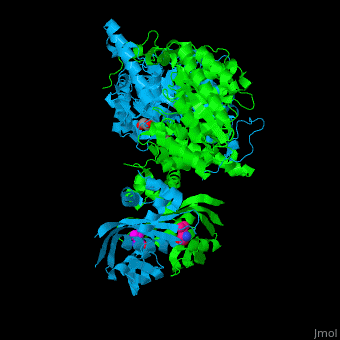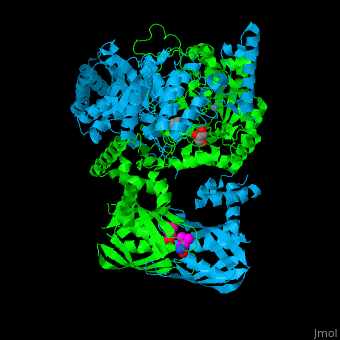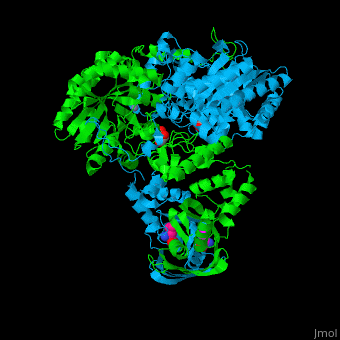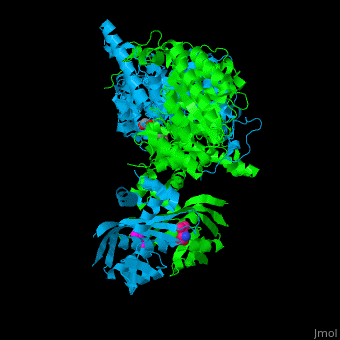
| - | <scene name='74/748866/Cv/ | + | <scene name='74/748866/Cv/5'>Domain organization of LeuA</scene>. LeuA structure is composed of 2 major domains - the catalytic N-terminal which shows a TIM barrel conformation and the regulatory C-terminal. The 2 domains are separated by subdomains I and II and a short flexible hinge region between the 2 subdomains. The catalytic domain binds the substrate and the <scene name='74/748866/Cv/6'>Zn+2 ion</scene><ref>PMID:15159544</ref>. <scene name='74/748866/Cv/7'>Leucine binding site</scene>. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of 2-isopropylmalate synthase== | ==3D structures of 2-isopropylmalate synthase== | ||
Revision as of 11:22, 16 December 2018
| |||||||||||
3D structures of 2-isopropylmalate synthase
Updated on 16-December-2018
References
- ↑ de Carvalho LP, Blanchard JS. Kinetic and chemical mechanism of alpha-isopropylmalate synthase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochemistry. 2006 Jul 25;45(29):8988-99. PMID:16846242 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi0606602
- ↑ Koon N, Squire CJ, Baker EN. Crystal structure of LeuA from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a key enzyme in leucine biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jun 1;101(22):8295-300. Epub 2004 May 24. PMID:15159544 doi:10.1073/pnas.0400820101