Sandbox Reserved 1502
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
== '''HIV''' == | == '''HIV''' == | ||
| - | |||
| - | HIV is a virus spread through certain body fluids that attacks the body’s immune system, specifically the CD4 cells, often called T cells. Over time, HIV can destroy so many of these cells that the body can’t fight off infections and disease. These special cells help the immune system fight off infections. Untreated, HIV reduces the number of CD4 cells (T cells) in the body. This damage to the immune system makes it harder and harder for the body to fight off infections and some other diseases. Opportunistic infections or cancers take advantage of a very weak immune system and signal that the person has AIDS. Learn more about the stages of HIV and how to know whether you’re infected. | ||
HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus. It is the virus that can lead to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, or AIDS, if not treated. Unlike some other viruses, the human body can’t get rid of HIV completely, even with treatment. So once you get HIV, you have it for life. | HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus. It is the virus that can lead to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, or AIDS, if not treated. Unlike some other viruses, the human body can’t get rid of HIV completely, even with treatment. So once you get HIV, you have it for life. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 22: | ||
=='''Disease : AIDS'''== | =='''Disease : AIDS'''== | ||
| - | AIDS is the most severe phase of HIV infection. People with AIDS have such badly damaged immune systems that they get an increasing number of severe illnesses, called opportunistic infections. | + | AIDS stands for Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. It is the most severe phase of HIV infection. People with AIDS have such badly damaged immune systems that they get an increasing number of severe illnesses, called opportunistic infections. |
This is the stage of HIV infection that occurs when your immune system is badly damaged and you become vulnerable to opportunistic infections. When the number of your CD4 cells falls below 200 cells per cubic millimeter of blood (200 cells/mm3), you are considered to have progressed to AIDS. (In someone with a healthy immune system, CD4 counts are between 500 and 1,600 cells/mm3.) You are also considered to have progressed to AIDS if you develop one or more opportunistic illnesses, regardless of your CD4 count. | This is the stage of HIV infection that occurs when your immune system is badly damaged and you become vulnerable to opportunistic infections. When the number of your CD4 cells falls below 200 cells per cubic millimeter of blood (200 cells/mm3), you are considered to have progressed to AIDS. (In someone with a healthy immune system, CD4 counts are between 500 and 1,600 cells/mm3.) You are also considered to have progressed to AIDS if you develop one or more opportunistic illnesses, regardless of your CD4 count. | ||
Revision as of 21:31, 9 January 2019
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
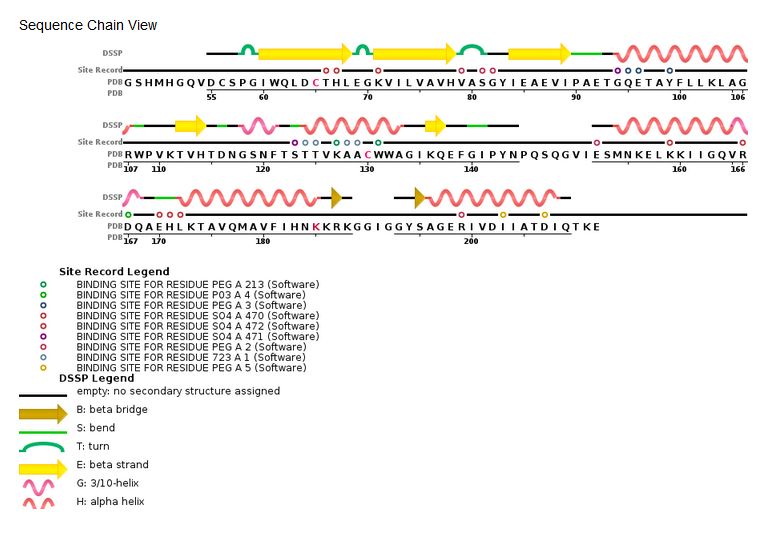
3lpt - HIV integrase
| |||||||||||