Sandbox Reserved 1502
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
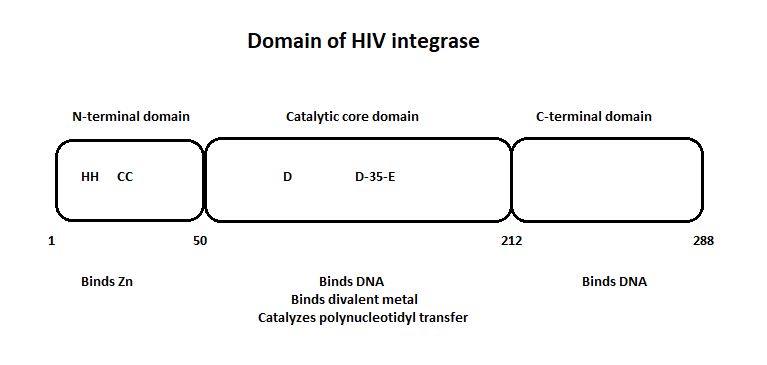
HIV-1 integrase is composed of three domains: the N-terminal (residues 1-49), the core domain (residues 50-212) and the C-terminal domain (residues 213-288). The core domain is responsible for the catalytic activity of the enzyme. It contains three acidic residues, the D,D-35-E motif which plays a key role in catalysis. The N-terminal domain includes the conserved HHCC motif, which binds zinc. The C-terminal domain is less well conserved. [http://www.jbc.org/content/276/26/23213/F2.expansion.html] | HIV-1 integrase is composed of three domains: the N-terminal (residues 1-49), the core domain (residues 50-212) and the C-terminal domain (residues 213-288). The core domain is responsible for the catalytic activity of the enzyme. It contains three acidic residues, the D,D-35-E motif which plays a key role in catalysis. The N-terminal domain includes the conserved HHCC motif, which binds zinc. The C-terminal domain is less well conserved. [http://www.jbc.org/content/276/26/23213/F2.expansion.html] | ||
| - | + | '''Representation of the three domain of the HIV integrase'''' | |
[[Image:Domain_HIV_Integrase.jpg]] | [[Image:Domain_HIV_Integrase.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
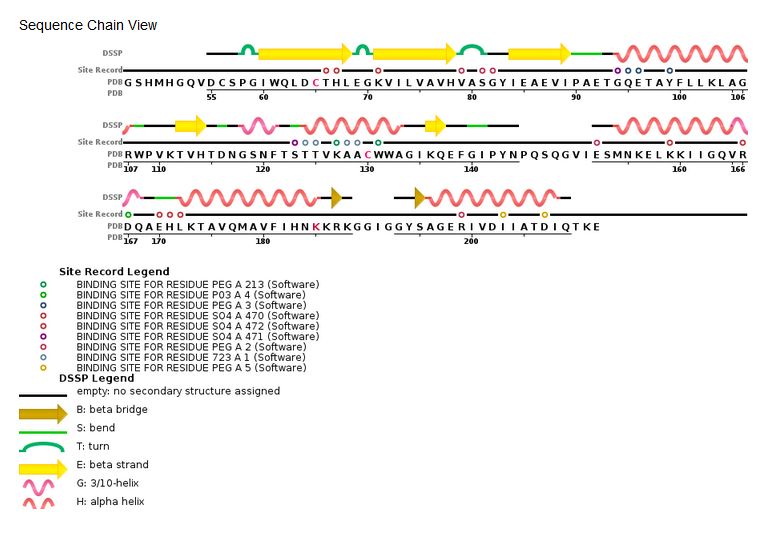
| + | '''HIV integrase sequence''' | ||
| + | [[Image:HIV_Integrase_Sequence.jpg]] | ||
[[Image:HIV Integrase sequence.jpg]] | [[Image:HIV Integrase sequence.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Structure and role of the core domain in the integration==== | ||
Revision as of 16:51, 10 January 2019
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
3lpt - HIV integrase
| |||||||||||