Sandbox Reserved 1502
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
HIV integrase is an enzyme required for the integration of viral DNA into the host genome. The process of integration can be divided into two sequential reactions. In the first one, named 3'-processing, the enzyme removes di- or trinucleotides from viral DNA ends to expose 3′-hydroxyls attached to the invariant CA dinucleotides. The second step is the insertion of the processed 3′-viral DNA ends into the host chromosomal DNA by a trans-esterification reaction. This is the strand transfer. | HIV integrase is an enzyme required for the integration of viral DNA into the host genome. The process of integration can be divided into two sequential reactions. In the first one, named 3'-processing, the enzyme removes di- or trinucleotides from viral DNA ends to expose 3′-hydroxyls attached to the invariant CA dinucleotides. The second step is the insertion of the processed 3′-viral DNA ends into the host chromosomal DNA by a trans-esterification reaction. This is the strand transfer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Reserach on antiviral == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Research on HIV show that the integrase use a protein, the LEDGF/p75 cofactor, so as to the preintegration complex is ligated to the DNA. | ||
| + | Some recents experimental antiviral inhibe this interaction and unable the integrase to interact with the cofactor. Thus, the DNA wouldn’t be inserted into the genome of the cell. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| Line 21: | Line 29: | ||
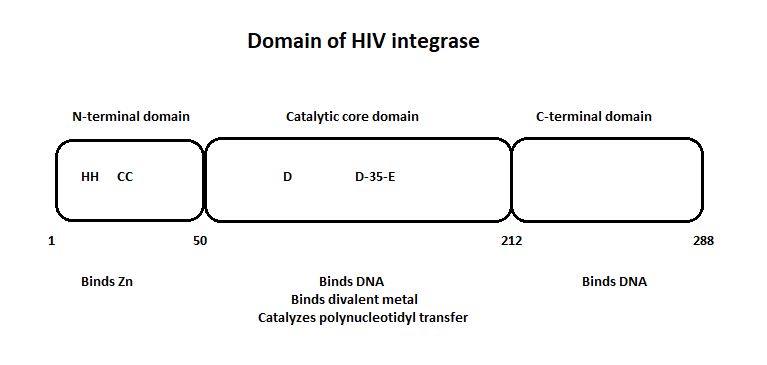
HIV-1 integrase is composed of three domains: the N-terminal (residues 1-49), the core domain (residues 50-212) and the C-terminal domain (residues 213-288). The core domain is responsible for the catalytic activity of the enzyme. It contains three acidic residues, the D,D-35-E motif which plays a key role in catalysis. The N-terminal domain includes the conserved HHCC motif, which binds zinc. The C-terminal domain is less well conserved. [http://www.jbc.org/content/276/26/23213/F2.expansion.html] | HIV-1 integrase is composed of three domains: the N-terminal (residues 1-49), the core domain (residues 50-212) and the C-terminal domain (residues 213-288). The core domain is responsible for the catalytic activity of the enzyme. It contains three acidic residues, the D,D-35-E motif which plays a key role in catalysis. The N-terminal domain includes the conserved HHCC motif, which binds zinc. The C-terminal domain is less well conserved. [http://www.jbc.org/content/276/26/23213/F2.expansion.html] | ||
| - | + | ====Structure and role of the core domain in the integration==== | |
[[Image:Domain_HIV_Integrase.jpg]] | [[Image:Domain_HIV_Integrase.jpg]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | '''HIV integrase sequence:''' | ||
| - | [[Image:HIV_Integrase_Sequence.jpg]] | ||
[[Image:HIV Integrase sequence.jpg]] | [[Image:HIV Integrase sequence.jpg]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | ====Structure and role of the core domain in the integration==== | ||
Revision as of 16:52, 10 January 2019
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
3lpt - HIV integrase
| |||||||||||