Adenylosuccinate lyase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: <StructureSection load='1stp' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> == Function == '''Adenylosuccinate lyase''' (ADSL) is a bifunctional enzyme acting in...) |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | <StructureSection load='' size='450' side='right' caption='Adenylsuccinate lyase complex with AMP, oxalate, PEG 400 and Cl- ion (green) (PDB code [[2x75]])' scene='75/751814/Cv/1'> | |
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | |
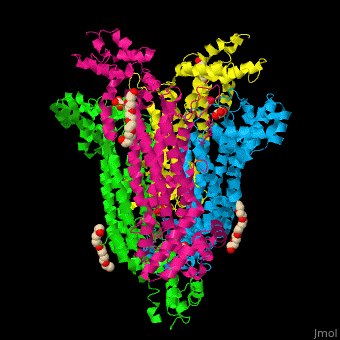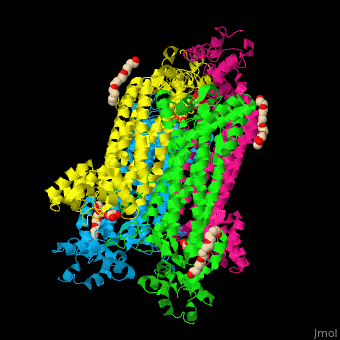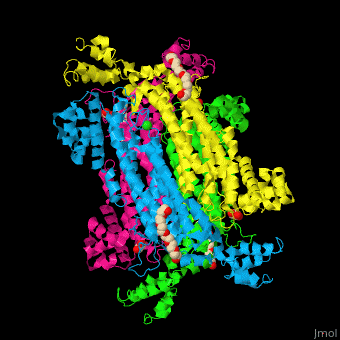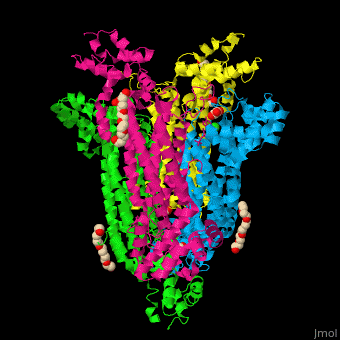
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''Adenylosuccinate lyase''' ( | + | '''Adenylosuccinate lyase''' (ASL) is a bifunctional enzyme acting in purine synthesis and purine nucleotide recycling<ref>PMID:10888601</ref>. ASL caalyzes two reactions: the cleavage of adenylsuccinate to AMP and fumarate and the cleavage of phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide (SAICAR) into 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide (AICAR) and fumarate. |
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| - | Mutations in | + | Mutations in ASL cause autosomal recessive disorder which manifests itself by encephalopathy with epilepsy and marked psychomotor retardation<ref>PMID:20054783</ref>. |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| + | The ASL can be divided into 3 domains. The <scene name='75/751814/Cv/6'>active site</scene> is situated between the 3 domains and contains the product AMP and and oxalate<ref>PMID:20693687</ref>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. <scene name='75/751814/Cv/7'>Oxalate binding</scene>. | ||
| - | + | ==3D structures of adenylosuccinate lyase== | |
| + | [[Adenylosuccinate lyase 3D structures]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Kmoch S, Hartmannova H, Stiburkova B, Krijt J, Zikanova M, Sebesta I. Human adenylosuccinate lyase (ADSL), cloning and characterization of full-length cDNA and its isoform, gene structure and molecular basis for ADSL deficiency in six patients. Hum Mol Genet. 2000 Jun 12;9(10):1501-13. PMID:10888601
- ↑ Mierzewska H, Schmidt-Sidor B, Jurkiewicz E, Bogdanska A, Kusmierska K, Stepien T. Severe encephalopathy with brain atrophy and hypomyelination due to adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency--MRI, clinical, biochemical and neuropathological findings of Polish patients. Folia Neuropathol. 2009;47(4):314-20. PMID:20054783
- ↑ Fyfe PK, Dawson A, Hutchison MT, Cameron S, Hunter WN. Structure of Staphylococcus aureus adenylosuccinate lyase (PurB) and assessment of its potential as a target for structure-based inhibitor discovery. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2010 Aug;66(Pt 8):881-8. Epub 2010, Jul 9. PMID:20693687 doi:10.1107/S0907444910020081