We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Madeleine Wilson/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
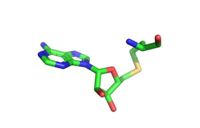
[[Image:Sinefugin.jpg|200px|left|thumb|Sinegungin]] | [[Image:Sinefugin.jpg|200px|left|thumb|Sinegungin]] | ||
Sinefungin is a potent methyltransferase inhibitor. It is a structural analog of S-adenosylmethionine that is more stable due to the ability to create two additional hydrogen bonds to its amine group in the active site. It has been used experimentally to inhibit the SET 7/9 protein on peritoneal fibrosis in mice and in human peritoneal mesothelial cells. Tamura et al. (2018) found that sinefungin suppressed the cell accumulation and thickening in methylglyoxal peritoneal fibrosis. | Sinefungin is a potent methyltransferase inhibitor. It is a structural analog of S-adenosylmethionine that is more stable due to the ability to create two additional hydrogen bonds to its amine group in the active site. It has been used experimentally to inhibit the SET 7/9 protein on peritoneal fibrosis in mice and in human peritoneal mesothelial cells. Tamura et al. (2018) found that sinefungin suppressed the cell accumulation and thickening in methylglyoxal peritoneal fibrosis. | ||
| - | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. DesJarlais, R.; Tummino, P.J. Role of Histone-Modifying Enzymes and Their Complexes in Regulation of Chromatin Biology. Biochemistry 2016, 55: 1584-1599. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. Lu, D. Epigenetic modification enzymes: catalytic mechanisms and inhibitors. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 2013, 3: 141-149. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. Dong, X.; Weng, Z. The correlation between histone modifications and gene expression. Epigenomics 2013, 5: 113-6. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4. Xiao, B.; Jing, C.; Wilson, J.; Walker, P.; Vasisht, N.; et al. Structure and catalytic mechanism of the human histone methyltranferase SET7/9. Letters to Nature 2003, 412: 652-655. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 5. Del Rizzo, P. A.; Trievel, R.C. Substrate and product specificities of SET domain methyltransferases. Epigenetics 2011, 6: 1059-1067 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 6. Mao, X.; Qiao, Z.; Fan, C.; Guo, A.; Yu, X.; Jin, F. Expression pattern and methylation of estrogen receptor α in breast intraductal proliferative lesions. Oncology Reports 2016, 36: 1868-1874. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 7. Tamura, R., Doi, S., Nakashima, A., Sasaki, K., Maeda, K., Ueno, T., & Masaki, T. (2018). Inhibition of the H3K4 methyltransferase SET7/9 ameliorates peritoneal fibrosis. PloS one, 13(5), e0196844. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0196844 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 8. Schluckebier et al. (1997), Differential binding of S-andeosylmethionine S-adenosylhomocysteine and Sinefungin to adenine-specific DNA methyltransferase M. TaqI; J. Mol. Biol., 265 56 | ||
Revision as of 00:53, 10 April 2019
Lysine Methyl Transferase, Homo Sapiens
| |||||||||||