UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
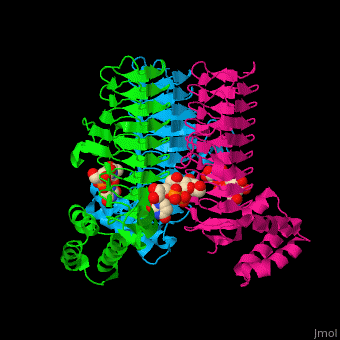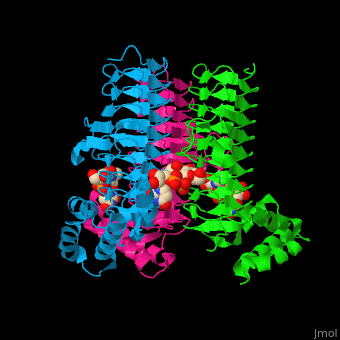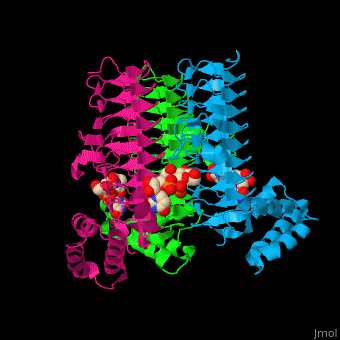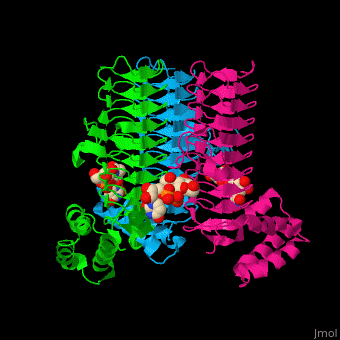
| - | The <scene name='74/749395/Cv/ | + | The <scene name='74/749395/Cv/6'>substrate-binding site</scene> of LpxA interacts with the substrate UDP moiety and the Glc-NAc moiety. It contains a <scene name='74/749395/Cv/7'>His-Asp catalytic dyad</scene> where the His acts as a general base and Asp helps to orient the His for participation in the catalysis<ref>PMID:17434525</ref>. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 12:04, 10 October 2019
| |||||||||||
3D structures of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase
Updated on 10-October-2019
References
- ↑ Wyckoff TJ, Raetz CR. The active site of Escherichia coli UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase. Chemical modification and site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1999 Sep 17;274(38):27047-55. PMID:10480918
- ↑ Ulaganathan V, Buetow L, Hunter WN. Nucleotide substrate recognition by UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase (LpxA) in the first step of lipid A biosynthesis. J Mol Biol. 2007 Jun 1;369(2):305-12. Epub 2007 Mar 21. PMID:17434525 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.03.039