Monooxygenase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
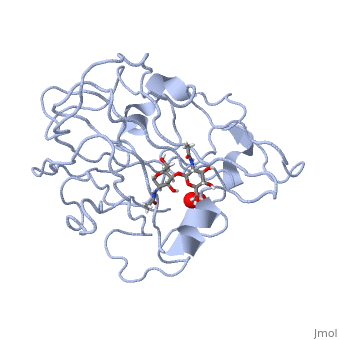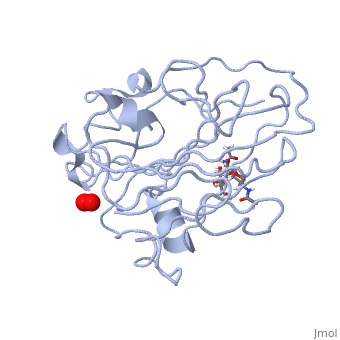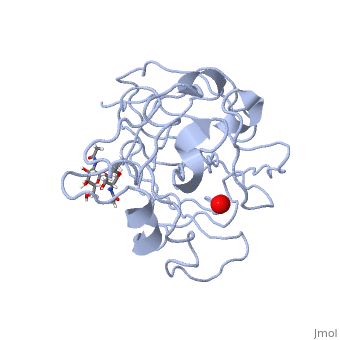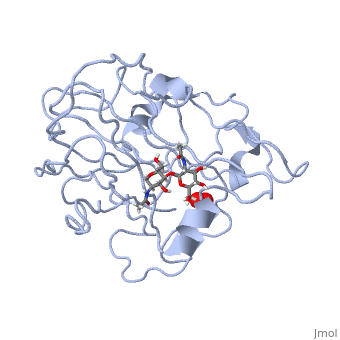
In recent years there has been a significant interest in describing the interactions of copper-containing enzymes with O<sub>2</sub>/H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>-derived species. The short-lived intermediates resulting from the activation of dioxygen are the key players in the mechanistic cycles in many metalloenzymes. In the enzyme <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/3'>peptidylglycine alpha-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM)</scene> various reduced Cu/oxygen species have been proposed to act as catalytically competent intermediates, yet their exact nature and their role in the enzymatic reaction is still unknown. | In recent years there has been a significant interest in describing the interactions of copper-containing enzymes with O<sub>2</sub>/H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>-derived species. The short-lived intermediates resulting from the activation of dioxygen are the key players in the mechanistic cycles in many metalloenzymes. In the enzyme <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/3'>peptidylglycine alpha-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM)</scene> various reduced Cu/oxygen species have been proposed to act as catalytically competent intermediates, yet their exact nature and their role in the enzymatic reaction is still unknown. | ||
Structural and other studies showed that peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM) contains <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/4'>two non-equivalent copper sites (CuH and CuM)</scene>. CuM serves as an oxygen binding and hydrogen abstraction site, CuH is involved in electron transfer. In the structure of Cu(II)-PHM complexed with hydrogen peroxide determined to 1.98 Å resolution, <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/7'>(hydro)peroxide binds exclusively to CuM in a slightly asymmetric side-on mode</scene>. The <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/8'>interatomic O-O distance of the copper-bound ligand is 1.5, characteristic of peroxide/hydroperoxide species, and the copper-oxygen distances are 2.0 and 2.1</scene> Å. This Cu(II)-bound <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/9'>peroxo moiety interacts closely with a molecule of water</scene>, forming <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/10'>hydrogen bonds that stabilize the structure</scene>. DFT and QM/MM calculations indicate that this species is a Cu-bound doubly deprotonated peroxidate and that its energy is similar to that of its isomer Cu(I)-bound superoxide. | Structural and other studies showed that peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM) contains <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/4'>two non-equivalent copper sites (CuH and CuM)</scene>. CuM serves as an oxygen binding and hydrogen abstraction site, CuH is involved in electron transfer. In the structure of Cu(II)-PHM complexed with hydrogen peroxide determined to 1.98 Å resolution, <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/7'>(hydro)peroxide binds exclusively to CuM in a slightly asymmetric side-on mode</scene>. The <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/8'>interatomic O-O distance of the copper-bound ligand is 1.5, characteristic of peroxide/hydroperoxide species, and the copper-oxygen distances are 2.0 and 2.1</scene> Å. This Cu(II)-bound <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/9'>peroxo moiety interacts closely with a molecule of water</scene>, forming <scene name='Journal:JBIC:17/Cv/10'>hydrogen bonds that stabilize the structure</scene>. DFT and QM/MM calculations indicate that this species is a Cu-bound doubly deprotonated peroxidate and that its energy is similar to that of its isomer Cu(I)-bound superoxide. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==3D structures of monooxygenase== | ||
| + | [[Monooxygenase 3D structures]] | ||
| + | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 56: | Line 60: | ||
*'''Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase (KMO)''' | *'''Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase (KMO)''' | ||
| + | **[[5x68]] – hKMO + FAD - human<br /> | ||
**[[4j2w]], [[4j31]], [[4j33]], [[4j34]] – yKMO + FAD – yeast<br /> | **[[4j2w]], [[4j31]], [[4j33]], [[4j34]] – yKMO + FAD – yeast<br /> | ||
**[[4j36]], [[5x64]] – yKMO + FAD + inhibitor<br /> | **[[4j36]], [[5x64]] – yKMO + FAD + inhibitor<br /> | ||
**[[5x6q]] – yKMO (mutant) + FAD + inhibitor<br /> | **[[5x6q]] – yKMO (mutant) + FAD + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5x68]] – hKMO + FAD - human<br /> | ||
**[[5na5]], [[5x6p]] – PfKMO (mutant) + FAD – ''Pseudomonas fluorescens''<br /> | **[[5na5]], [[5x6p]] – PfKMO (mutant) + FAD – ''Pseudomonas fluorescens''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5y7a]], [[5y77]] – PfKMO + FAD + kynurenine <br /> | + | **[[5y7a]], [[5y77]], [[6fox]] – PfKMO + FAD + kynurenine <br /> |
**[[5nak]] – PfKMO (mutant) + FAD + kynurenine <br /> | **[[5nak]] – PfKMO (mutant) + FAD + kynurenine <br /> | ||
**[[5y66]] – PfKMO + FAD + kynurenine + inhibitor<br /> | **[[5y66]] – PfKMO + FAD + kynurenine + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6fph]], [[6fp1]], [[6fp0]], [[6foz]], [[6foy]] – PfKMO + FAD + inhibitor<br /> | ||
**[[5nah]], [[5nag]], [[5nae]], [[5nab]], [[5n7t]], [[5mzk]], [[5mzi]], [[5mzc]], [[5fn0]] – PfKMO (mutant) + FAD + inhibitor<br /> | **[[5nah]], [[5nag]], [[5nae]], [[5nab]], [[5n7t]], [[5mzk]], [[5mzi]], [[5mzc]], [[5fn0]] – PfKMO (mutant) + FAD + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| Line 74: | Line 79: | ||
**[[5pah]], [[6pah]] – hFMO catalytic domain + inhibitor <br /> | **[[5pah]], [[6pah]] – hFMO catalytic domain + inhibitor <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Phenylalanine 4-monooxygenase or phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase | ||
| + | |||
| + | See [[Hydroxylase]] | ||
*'''ActVA-Orf6 monooxygenase (AOMO)''' | *'''ActVA-Orf6 monooxygenase (AOMO)''' | ||
| Line 81: | Line 90: | ||
**[[1n5s]], [[1n5t]] – ScAOMO + acetyl dithranol<br /> | **[[1n5s]], [[1n5t]] – ScAOMO + acetyl dithranol<br /> | ||
**[[1n5v]] – ScAOMO + nanaomycine <br /> | **[[1n5v]] – ScAOMO + nanaomycine <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenase (BVMO) | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[6jdk]] – BVMO – ''Parvibaculum lavamentivorans''<br /> | ||
*'''Flavin-containing monooxygenase''' | *'''Flavin-containing monooxygenase''' | ||
| Line 88: | Line 101: | ||
**[[4a9w]] – SmMO + FAD – ''Stenotrophomonas maltophilia''<br /> | **[[4a9w]] – SmMO + FAD – ''Stenotrophomonas maltophilia''<br /> | ||
**[[4c5o]] – SmMO (mutant) + FAD <br /> | **[[4c5o]] – SmMO (mutant) + FAD <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5wan]] – | + | **[[5wan]] – EcMO + FMN + uracil – Escherichia coli<br /> |
**[[5iq4]], [[5iq1]], [[5ipy]] – RnMO (mutant) + FAD + NAP – ''Roseovarius nubinhibens'' <br /> | **[[5iq4]], [[5iq1]], [[5ipy]] – RnMO (mutant) + FAD + NAP – ''Roseovarius nubinhibens'' <br /> | ||
**[[5gsn]] – RnMO (mutant) + FAD + NAP + methimazole <br /> | **[[5gsn]] – RnMO (mutant) + FAD + NAP + methimazole <br /> | ||
| Line 153: | Line 166: | ||
**[[4q4k]] – PaMO + FMN <br /> | **[[4q4k]] – PaMO + FMN <br /> | ||
| + | **[[6e2a]] – PaMO + FMN + NAD<br /> | ||
**[[5lsm]] – MO + FMN – ''Shewanella oneidensis''<br /> | **[[5lsm]] – MO + FMN – ''Shewanella oneidensis''<br /> | ||
**[[6bka]] – MO + FMN – ''Cyberlyndnera mrakii''<br /> | **[[6bka]] – MO + FMN – ''Cyberlyndnera mrakii''<br /> | ||
| Line 165: | Line 179: | ||
*4-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-monooxygenase | *4-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-monooxygenase | ||
| - | **[[4ira]] – BmMO + FAD – Brucella melitensis<br /> | + | **[[4ira]] – BmMO + FAD – ''Brucella melitensis''<br /> |
**[[3cb0]] – BmMO + FMN<br /> | **[[3cb0]] – BmMO + FMN<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6eb0]] – EcMO oxygenase subunit<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6b1b]] – EcMO oxygenase subunit (mutant)<br /> | ||
*Ornithine N(5)-monooxygenase | *Ornithine N(5)-monooxygenase | ||
| Line 186: | Line 202: | ||
*Cyclohexanone monooxygenase | *Cyclohexanone monooxygenase | ||
| - | **[[5m10]] – TmMO + FAD + NAP + nicotinamide – ''Thermocripsum municipale | + | **[[5m10]] – TmMO + FAD + NAP + nicotinamide – ''Thermocripsum municipale''<br /> |
**[[5m0z]] – TmMO + FAD + NADP derivative <br /> | **[[5m0z]] – TmMO + FAD + NADP derivative <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4rg4]], [[4rg3]], [[3gwf]], [[3gwd]] – RhMO + FAD + NAP + caprolactone | + | **[[6gqi]] – TmMO + FAD + NADP + hexanic acid <br /> |
| + | **[[6era]], [[6er9]] – RhMO + FAD + NADP – ''Rhodococcus''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4rg4]], [[4rg3]], [[3gwf]], [[3gwd]] – RhMO + FAD + NAP + caprolactone <br /> | ||
**[[3ucl]] – RhMO + FAD + NADP + cyclohexanone <br /> | **[[3ucl]] – RhMO + FAD + NADP + cyclohexanone <br /> | ||
| Line 228: | Line 246: | ||
**[[5mw0]], [[5wkw]] – rMO <br /> | **[[5mw0]], [[5wkw]] – rMO <br /> | ||
| + | **[[1yjl]] – rMO (mutant)<br /> | ||
**[[3mib]], [[3mic]], [[3mid]], [[3mie]], [[3mif]], [[3mig]], [[3mih]], [[3mlj]], [[3mlk]], [[3mll]], [[1opm]] – rMO + Cu + Ni <br /> | **[[3mib]], [[3mic]], [[3mid]], [[3mie]], [[3mif]], [[3mig]], [[3mih]], [[3mlj]], [[3mlk]], [[3mll]], [[1opm]] – rMO + Cu + Ni <br /> | ||
| + | **[[6ao6]], [[5wja]] – rMO (mutant) + Cu + Ni<br /> | ||
**[[1sdw]] – rMO + Cu + Ni + O2 + threonine derivative<br /> | **[[1sdw]] – rMO + Cu + Ni + O2 + threonine derivative<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1yjl]] – rMO (mutant)<br /> | ||
**[[1yjk]], [[1yip]], [[1phm]] – rMO + Cu<br /> | **[[1yjk]], [[1yip]], [[1phm]] – rMO + Cu<br /> | ||
**[[1yi9]], [[6ay0]], [[6an3]], [[6amp]], [[6alv]], [[6ala]] – rMO (mutant) + Cu<br /> | **[[1yi9]], [[6ay0]], [[6an3]], [[6amp]], [[6alv]], [[6ala]] – rMO (mutant) + Cu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[6ao6]], [[5wja]] – rMO (mutant) + Cu + Ni<br /> | ||
**[[3fw0]] – rMO + Hg<br /> | **[[3fw0]] – rMO + Hg<br /> | ||
**[[3fvz]] – rMO + Zn + Fe<br /> | **[[3fvz]] – rMO + Zn + Fe<br /> | ||
| Line 249: | Line 267: | ||
**[[5f5l]] – MiMO – ''Micromonospora'' <br /> | **[[5f5l]] – MiMO – ''Micromonospora'' <br /> | ||
**[[5f5n]] – MiMO + NAD + substrate <br /> | **[[5f5n]] – MiMO + NAD + substrate <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Monooxygenase TROPB | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[6nes]] – TsMO + FAD – ''Talaromyces stipitatus''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6nev]], [[6neu]] – TsMO (mutant) + FAD <br /> | ||
| + | **[[6net]] – TsMO + FAD + dihydroxy dimethylbenzaldehyde<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Lactate 2-monooxygenase or lactate oxydase | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[6dvi]] – MsLMO + FMN – ''Mycobacterium smegmatis''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6dvh]] – MsLMO (mutant) + FMN <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Squalene monooxygenase or squalene epoxidase | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[6c6r]], [[6c6p]], [[6c6n]] – hSMO + FAD + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Dimethyl-sulfide monooxygenase | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[6ak1]] – DMOA – ''Hyphomicrobium sulfonivorans''<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Salicylate 1-monooxygenase or salicylate hydroxylase | ||
| + | |||
| + | See [[Hydroxylase]] | ||
'''Methane monooxygenase''' See [[Methane monooxygenase]] | '''Methane monooxygenase''' See [[Methane monooxygenase]] | ||
Revision as of 11:10, 3 November 2019
| |||||||||||
3D structures of monooxygenase
Updated on 03-November-2019
See Hydroxylase
See Hydroxylase
Methane monooxygenase See Methane monooxygenase
Camphor 5-monooxygenase See Cytochrome P450
Luciferin 4-monooxygenase and Alkanal monooxygenase See Luciferase
References
- ↑ Rudzka K, Moreno DM, Eipper B, Mains R, Estrin DA, Amzel LM. Coordination of peroxide to the Cu(M) center of peptidylglycine alpha-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM): structural and computational study. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2012 Dec 18. PMID:23247335 doi:10.1007/s00775-012-0967-z
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Alexander Berchansky, Jaime Prilusky