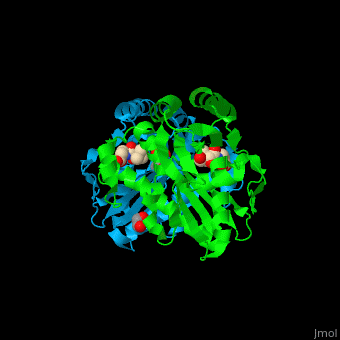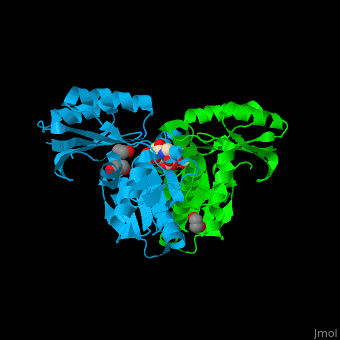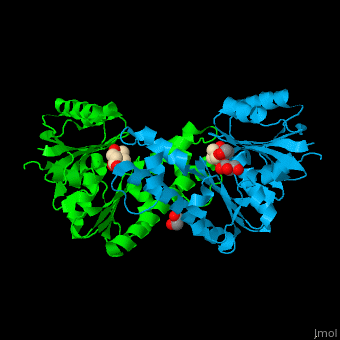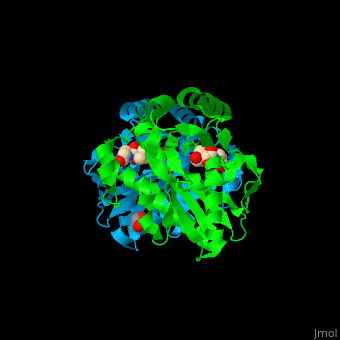
Pantothenate kinase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (17 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Pantothenate kinase III dimer complex with pantothenate, glycerol and ethane diol, [[2f9w]]' scene='52/525168/Cv/1' pspeed='8'> | |
| - | '''Pantothenate kinase''' (PanK) phosphorylates pantothenate (vitamin B5) (PAU) to form 4’-phosphopantothenate (PPT) using ATP as phosphate source. This is the first step in coenzyme A biosynthesis. PanK is regulated by feedback inhibition by CoA and its thioesters. | + | == Function == |
| + | '''Pantothenate kinase''' (PanK) phosphorylates pantothenate (vitamin B5) (PAU) to form 4’-phosphopantothenate (PPT) using ATP as phosphate source. This is the first step in coenzyme A biosynthesis<ref>. PanK is regulated by feedback inhibition by CoA and its thioesters.PMID:9890959</ref>.<br /> | ||
| - | + | Three types of PanK are known.<br > | |
| + | * '''PanK I''' found in bacteria<br /> | ||
| + | * '''PanK II''' found mostly in eukaryotes<br /> | ||
| + | * '''PanK III''' found in bacteria and known as CoaX. | ||
| - | + | == Disease == | |
| + | Mutations in PanK II cause the autosomal-recessive disorder Pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration<ref>PMID:15911822</ref>. | ||
| - | + | == Structural highlights == | |
| - | + | <scene name='52/525168/Cv/5'>Pantothenate binds in a buried pocket at the PanK dimer interface</scene><ref>PMID:16905099</ref>. | |
| - | + | *<scene name='52/525168/Cv/6'>Buried pocket at the PanK dimer interface</scene>. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | == | + | ==3D structures of pantothenate kinase== |
| - | + | [[Pantothenate kinase 3D structures]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | == | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ . PanK is regulated by feedback inhibition by CoA and its thioesters.PMID:9890959
- ↑ Pellecchia MT, Valente EM, Cif L, Salvi S, Albanese A, Scarano V, Bonuccelli U, Bentivoglio AR, D'Amico A, Marelli C, Di Giorgio A, Coubes P, Barone P, Dallapiccola B. The diverse phenotype and genotype of pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration. Neurology. 2005 May 24;64(10):1810-2. PMID:15911822 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1212/01.WNL.0000161843.52641.EC
- ↑ Hong BS, Yun MK, Zhang YM, Chohnan S, Rock CO, White SW, Jackowski S, Park HW, Leonardi R. Prokaryotic type II and type III pantothenate kinases: The same monomer fold creates dimers with distinct catalytic properties. Structure. 2006 Aug;14(8):1251-61. PMID:16905099 doi:10.1016/j.str.2006.06.008