We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Plasminogen
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (22 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
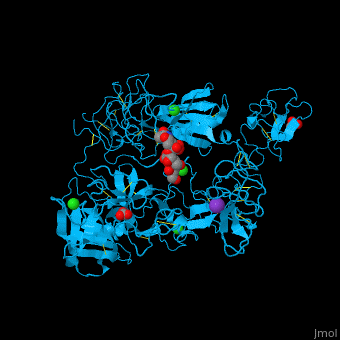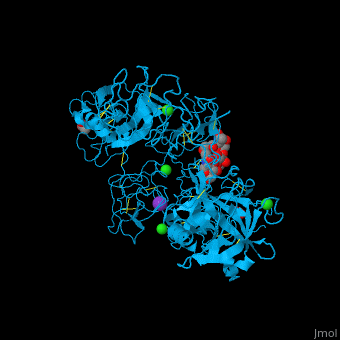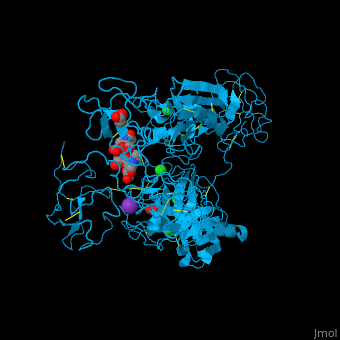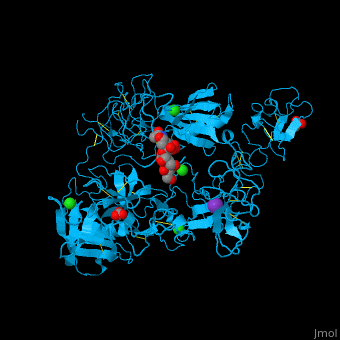
| - | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Human glycosylated plasminogen complex with acetate, bicarbonate, K+ (purple) and Cl- (green) ions (PDB entry [[4dur]])' scene='46/465445/Cv/1'> | |
| + | == Function == | ||
| + | '''Plasmin''' (PLN) is a serine protease which is involved in degradation of fibrin clots. PLN is released as the zymogen '''plasminogen''' (PLG) which is converted to the active PLN by a variety of enzymes. PLN cleavage produces angiostatin. | ||
| - | ''' | + | *'''Microplasmin''' induces posterior vitreous detachment from the retina (PVD)<ref>PMID:21099453</ref>. |
| - | + | == Disease == | |
| + | PLN mutations are associated with ligneous conjunctivitis and other disorders which lead to development of pseudo membranes on mucosal surfaces<ref>PMID:19141167</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Structural highlights == | ||
| + | <scene name='46/465445/Cv/11'>PLN contains 7 domains</scene> which are: N-terminal, C-terminal serine protease catalytic domain and 5 kringle domains of ca. 80 residues. The <scene name='46/465445/Cv/3'>kringle domain folds into a large loop containing 3 disulfide bonds</scene>, ''e.g.'' <scene name='46/465445/Cv/4'>Kringle 4</scene>. The kringle domain is important in protein-protein interaction with blood coagulation factors.<ref>PMID:22832192</ref>. | ||
| + | *<scene name='46/465445/Cv/12'>K ion coordination site</scene>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. | ||
| + | *<scene name='46/465445/Cv/13'>Cl ion coordination site I</scene>. | ||
| + | *<scene name='46/465445/Cv/14'>Cl ion coordination site II</scene>. | ||
| + | *<scene name='46/465445/Cv/15'>Cl ion coordination site III</scene>. | ||
| + | *<scene name='46/465445/Cv/16'>Cl ion coordination site IV</scene>. | ||
== 3D Structures of plasminogen == | == 3D Structures of plasminogen == | ||
| + | [[Plasminogen 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Goldenberg DT, Giblin FJ, Cheng M, Chintala SK, Trese MT, Drenser KA, Ruby AJ. Posterior vitreous detachment with microplasmin alters the retinal penetration of intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) in rabbit eyes. Retina. 2011 Feb;31(2):393-400. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e3181e586b2. PMID:21099453 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/IAE.0b013e3181e586b2
- ↑ Mehta R, Shapiro AD. Plasminogen deficiency. Haemophilia. 2008 Nov;14(6):1261-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2516.2008.01825.x. PMID:19141167 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2516.2008.01825.x
- ↑ Law RH, Caradoc-Davies T, Cowieson N, Horvath AJ, Quek AJ, Encarnacao JA, Steer D, Cowan A, Zhang Q, Lu BG, Pike RN, Smith AI, Coughlin PB, Whisstock JC. The X-ray crystal structure of full-length human plasminogen. Cell Rep. 2012 Mar 29;1(3):185-90. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.02.012. Epub 2012, Mar 8. PMID:22832192 doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2012.02.012