Prion
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
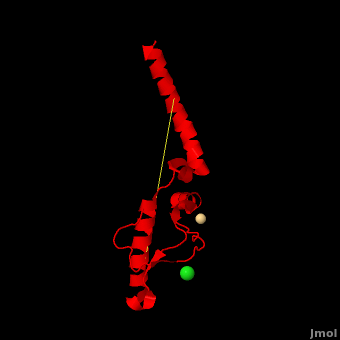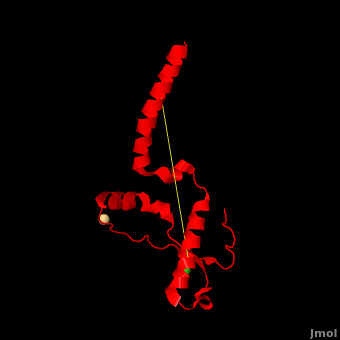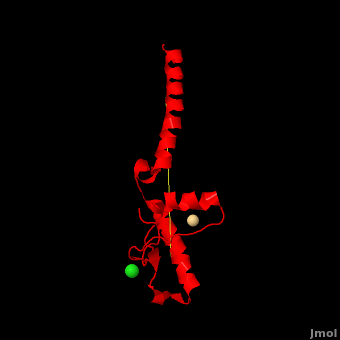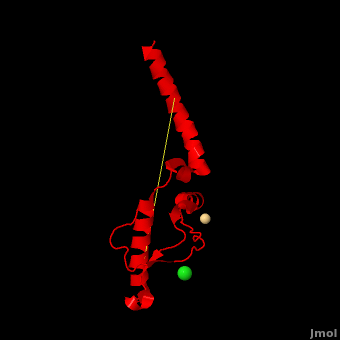
Here we use molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the structural determinants of the globular domain in engineered Mouse (Mo) PrP variants, in WT human (Hu) PrP (PDB: [[1hjn]]) and in WT MoPrP (PDB: [[1xyx]]). The Mo PrP variants investigated here contain one or two residues from ''Homo sapiens'' and are denoted “MoPrP chimeras”. <scene name='Journal:JBSD:4/Cv/3'>Some of them are resistant to PrP<sup>Sc</sup> infection</scene> <span style="color:yellow;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">(colored in yellow)</span> in ''in vivo'' or in ''in vitro'' cell-culture experiments, the <scene name='Journal:JBSD:4/Cv/7'>others are not</scene> <font color='darkmagenta'><b>(in darkmagenta)</b></font>. Our main results are the following: (i) The chimeras resistant to PrP<sup>Sc</sup> infection show <scene name='Journal:JBSD:4/Cv/8'>shorter intramolecular distances</scene> between the α1 helix and N-terminal of α3 helix than HuPrP, MoPrP and the non-resistant chimeras (<scene name='Journal:JBSD:4/Cv/12'>click here to see morph</scene>). This is due to stronger specific interactions between these two regions, mainly the <scene name='Journal:JBSD:4/Cv/9'>Y149-D202 and D202-Y157 (in Hu numbering and hereafter) hydrogen bonds</scene> and the <scene name='Journal:JBSD:4/Cv/10'>R156-E196 salt bridge</scene>. (ii) The β2-α2 <scene name='Journal:JBSD:4/Cv1/2'>loop (residues 167-171)</scene> of PrP<sup>C</sup> is known to differ in its conformation across different species and is suggested to be responsible for the species barrier of PrP<sup>Sc</sup> propagation. Our simulations detect exchanges between different conformations in this loop which can be categorized into two distinct patterns: some chimeras experience a 3<sub>10</sub>-helix/turn pattern like in MoPrP and others show a bend/turn pattern like in HuPrP. In the <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">Mo-like pattern (colored in green)</span>, 3<sub>10</sub>-helix conformation is stabilized by the <scene name='Journal:JBSD:4/Cv1/3'>Q168-P165 and Y169-V166 hydrogen bonds</scene>. In the <font color='darkred'><b>Hu-like pattern (colored in darkred)</b></font>, a <scene name='Journal:JBSD:4/Cv1/4'>D167-S170 hydrogen bond</scene> stabilizes the bend conformation. Interestingly, the dominant-negative effect of MoPrP chimeras over WT MoPrP occurs if the chimera not only resists PrP<sup>Sc</sup> infection but also adopts the Mo-like pattern of exchanges between conformations in the β2-α2 loop. This suggests that the compatible loop conformation allows these dominant-negative chimeras to interfere with the conversion of MoPrP to PrP<sup>Sc</sup>. | Here we use molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the structural determinants of the globular domain in engineered Mouse (Mo) PrP variants, in WT human (Hu) PrP (PDB: [[1hjn]]) and in WT MoPrP (PDB: [[1xyx]]). The Mo PrP variants investigated here contain one or two residues from ''Homo sapiens'' and are denoted “MoPrP chimeras”. <scene name='Journal:JBSD:4/Cv/3'>Some of them are resistant to PrP<sup>Sc</sup> infection</scene> <span style="color:yellow;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">(colored in yellow)</span> in ''in vivo'' or in ''in vitro'' cell-culture experiments, the <scene name='Journal:JBSD:4/Cv/7'>others are not</scene> <font color='darkmagenta'><b>(in darkmagenta)</b></font>. Our main results are the following: (i) The chimeras resistant to PrP<sup>Sc</sup> infection show <scene name='Journal:JBSD:4/Cv/8'>shorter intramolecular distances</scene> between the α1 helix and N-terminal of α3 helix than HuPrP, MoPrP and the non-resistant chimeras (<scene name='Journal:JBSD:4/Cv/12'>click here to see morph</scene>). This is due to stronger specific interactions between these two regions, mainly the <scene name='Journal:JBSD:4/Cv/9'>Y149-D202 and D202-Y157 (in Hu numbering and hereafter) hydrogen bonds</scene> and the <scene name='Journal:JBSD:4/Cv/10'>R156-E196 salt bridge</scene>. (ii) The β2-α2 <scene name='Journal:JBSD:4/Cv1/2'>loop (residues 167-171)</scene> of PrP<sup>C</sup> is known to differ in its conformation across different species and is suggested to be responsible for the species barrier of PrP<sup>Sc</sup> propagation. Our simulations detect exchanges between different conformations in this loop which can be categorized into two distinct patterns: some chimeras experience a 3<sub>10</sub>-helix/turn pattern like in MoPrP and others show a bend/turn pattern like in HuPrP. In the <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">Mo-like pattern (colored in green)</span>, 3<sub>10</sub>-helix conformation is stabilized by the <scene name='Journal:JBSD:4/Cv1/3'>Q168-P165 and Y169-V166 hydrogen bonds</scene>. In the <font color='darkred'><b>Hu-like pattern (colored in darkred)</b></font>, a <scene name='Journal:JBSD:4/Cv1/4'>D167-S170 hydrogen bond</scene> stabilizes the bend conformation. Interestingly, the dominant-negative effect of MoPrP chimeras over WT MoPrP occurs if the chimera not only resists PrP<sup>Sc</sup> infection but also adopts the Mo-like pattern of exchanges between conformations in the β2-α2 loop. This suggests that the compatible loop conformation allows these dominant-negative chimeras to interfere with the conversion of MoPrP to PrP<sup>Sc</sup>. | ||
The structural features presented here indicate that stronger interactions between α1 helix and N-terminal of α3 helix are related to the resistance to PrP<sup>C</sup> → PrP<sup>Sc</sup> conversion, while the β2-α2 loop conformation may play an important role in the dominant-negative effect. | The structural features presented here indicate that stronger interactions between α1 helix and N-terminal of α3 helix are related to the resistance to PrP<sup>C</sup> → PrP<sup>Sc</sup> conversion, while the β2-α2 loop conformation may play an important role in the dominant-negative effect. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==3D structures of prion== | ||
| + | [[Prion 3D structures ]] | ||
| + | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 22: | Line 26: | ||
*Prion short polypeptides | *Prion short polypeptides | ||
| - | **[[3nve]] – ShPrP residues 138 -143 – Syrian hamster<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2kkg]] - GhPrP residues 23 -106 – Golden hamster - NMR<br /> | ||
**[[3nvf]] – hPrP residues 138 -143 – human<br /> | **[[3nvf]] – hPrP residues 138 -143 – human<br /> | ||
**[[2ol9]] - hPrP residues 170 – 175<br /> | **[[2ol9]] - hPrP residues 170 – 175<br /> | ||
| Line 34: | Line 36: | ||
**[[2iv4]] - hPrP residues 180 -195 – NMR<br /> | **[[2iv4]] - hPrP residues 180 -195 – NMR<br /> | ||
**[[4e1h]], [[4e1i]] - hPrP residues 177 -182 + 211-216<br /> | **[[4e1h]], [[4e1i]] - hPrP residues 177 -182 + 211-216<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3nvg]], [[3nvh]] - mPrP residues 138 -143 – mouse<br /> | ||
**[[1skh]] - bPrP residues 1 – 30 - bovine<br /> | **[[1skh]] - bPrP residues 1 – 30 - bovine<br /> | ||
**[[3fva]] - ePrP residues 173 -178 – Elk<br /> | **[[3fva]] - ePrP residues 173 -178 – Elk<br /> | ||
| Line 42: | Line 43: | ||
**[[2rmv]], [[2rmw]] - sPrP residues 142 – 166 (mutant) – NMR<br /> | **[[2rmv]], [[2rmw]] - sPrP residues 142 – 166 (mutant) – NMR<br /> | ||
**[[6axz]], [[6btk]] - vPrP residues 168 - 176 – vole<br /> | **[[6axz]], [[6btk]] - vPrP residues 168 - 176 – vole<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3nve]] – ShPrP residues 138 -143 – Syrian hamster<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2kkg]] - GhPrP residues 23 -106 – Golden hamster - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3nvg]], [[3nvh]] - mPrP residues 138 -143 – mouse<br /> | ||
*Prion | *Prion | ||
| + | **[[3haf]], [[3hak]], [[3hj5]], [[1i4m]] - hPrP C-terminal<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1hjm]], [[1hjn]], [[2kun]], [[5l6r]], [[5yj5]] – hPrP C-terminal – NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1h0l]], [[1fkc]], [[2k1d]], [[1fo7]], [[1e1s]], [[1e1g]], [[1e1j]], [[1e1p]], [[1e1u]], [[1e1w]], [[1qlx]], [[1qlz]], [[1qm0]], [[1qm1]], [[1qm2]], [[1qm3]], [[1qlz]], [[1qm0]], [[1qm1]], [[2lej]], [[5yj4]] - hPrP C-terminal (mutant) - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3heq]], [[3her]], [[3hes]], [[3hjx]] - hPrP C-terminal (mutant)<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2lft]], [[2lsb]], [[2m8t]] - hPrP residues 90 -231 – NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2lv1]] - hPrP residues 90 -231 (mutant) – NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2lsb]] - hPrP residues 120 -230 + antibody<br /> | ||
**[[3o79]] – rPrP C-terminal – rabbit<br /> | **[[3o79]] – rPrP C-terminal – rabbit<br /> | ||
**[[4hls]], [[4hmm]], [[4hmr]]- rPrP C-terminal (mutant)<br /> | **[[4hls]], [[4hmm]], [[4hmr]]- rPrP C-terminal (mutant)<br /> | ||
**[[2fj3]] - rPrP C-terminal – NMR<br /> | **[[2fj3]] - rPrP C-terminal – NMR<br /> | ||
**[[2joh]], [[2jom]] - rPrP C-terminal (mutant) – NMR<br /> | **[[2joh]], [[2jom]] - rPrP C-terminal (mutant) – NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1xyw]] – ePrP C terminal - NMR<br /> | + | **[[1xyw]], [[3fva]] – ePrP C terminal - NMR<br /> |
**[[2ku4]] - PrP C-terminal – horse<br /> | **[[2ku4]] - PrP C-terminal – horse<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3fva]] - ePrP C-terminal – NMR<br /> | ||
**[[2kfl]] - PrP C-terminal – Wallaby – NMR<br /> | **[[2kfl]] - PrP C-terminal – Wallaby – NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2k56]] - PrP C-terminal – Vole – NMR<br /> | ||
**[[2ktm]] – sPrP residues 167-234 H2H3 domain (mutant) – NMR<br /> | **[[2ktm]] – sPrP residues 167-234 H2H3 domain (mutant) – NMR<br /> | ||
**[[1xyu]], [[1y2s]], [[2n53]] - sPrP C-terminal – NMR<br /> | **[[1xyu]], [[1y2s]], [[2n53]] - sPrP C-terminal – NMR<br /> | ||
**[[2mv8]], [[2mv9]] - sPrP C-terminal (mutant) – NMR<br /> | **[[2mv8]], [[2mv9]] - sPrP C-terminal (mutant) – NMR<br /> | ||
**[[1uw3]] - sPrP C-terminal<br /> | **[[1uw3]] - sPrP C-terminal<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3haf]], [[3hak]], [[3hj5]], [[1i4m]] - hPrP C-terminal<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1hjm]], [[1hjn]], [[2kun]], [[5l6r]], [[5yj5]] – hPrP C-terminal – NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1h0l]], [[1fkc]], [[2k1d]], [[1fo7]], [[1e1s]], [[1e1g]], [[1e1j]], [[1e1p]], [[1e1u]], [[1e1w]], [[1qlx]], [[1qlz]], [[1qm0]], [[1qm1]], [[1qm2]], [[1qm3]], [[1qlz]], [[1qm0]], [[1qm1]], [[2lej]], [[5yj4]] - hPrP C-terminal (mutant) - NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3heq]], [[3her]], [[3hes]], [[3hjx]] - hPrP C-terminal (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2lft]], [[2lsb]], [[2m8t]] - hPrP residues 90 -231 – NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2lv1]] - hPrP residues 90 -231 (mutant) – NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2lsb]] - hPrP residues 120 -230 + antibody<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2ku5]], [[2ku6]], [[2kfm]], [[2kfo]], [[2k5o]], [[1y16]], [[1y15]] - mPrP C-terminal (mutant) - NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1xyx]] - mPrP C-terminal - NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2l1k]], [[2l1d]], [[2l1e]], [[2l40]] - mPrP C terminal (mutant) – NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1ag2]], [[2l1h]], [[2l39]] - mPrP C terminal - NMR<br /> | ||
**[[1u3m]] – PrP C-terminal – chicken – NMR<br /> | **[[1u3m]] – PrP C-terminal – chicken – NMR<br /> | ||
**[[1u5l]] - PrP C-terminal – turtle – NMR<br /> | **[[1u5l]] - PrP C-terminal – turtle – NMR<br /> | ||
| Line 78: | Line 76: | ||
**[[1dwz]] - bPrP C-terminal (mutant) - NMR<br /> | **[[1dwz]] - bPrP C-terminal (mutant) - NMR<br /> | ||
**[[1b10]] - ShPrP C-terminal – NMR<br /> | **[[1b10]] - ShPrP C-terminal – NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2lh8]] - ShPrP C-terminal + thiamine – NMR | + | **[[2lh8]] - ShPrP C-terminal + thiamine – NMR<br /> |
| + | **[[2k56]] - PrP C-terminal – Vole – NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2ku5]], [[2ku6]], [[2kfm]], [[2kfo]], [[2k5o]], [[1y16]], [[1y15]] - mPrP C-terminal (mutant) - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1xyx]] - mPrP C-terminal - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2l1k]], [[2l1d]], [[2l1e]], [[2l40]] - mPrP C terminal (mutant) – NMR<br /> | ||
*Yeast prions | *Yeast prions | ||
| Line 91: | Line 93: | ||
**[[2w9e]], [[4h88]], [[2lsb]], [[4dgi]], [[6aq7]] - hPrP C-terminal + anti-PrP antibody<br /> | **[[2w9e]], [[4h88]], [[2lsb]], [[4dgi]], [[6aq7]] - hPrP C-terminal + anti-PrP antibody<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4j8r]] - mPrP residues 67-82 + antibody<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4ma7]], [[4ma8]] - mPrP residues 116 - 229 + antibody<br /> | ||
**[[4n9o]] - hPrP C terminal + nanobody<br /> | **[[4n9o]] - hPrP C terminal + nanobody<br /> | ||
**[[4kml]] - hPrP + nanobody<br /> | **[[4kml]] - hPrP + nanobody<br /> | ||
**[[2hh0]] - bPrP peptide epitope + anti-PrP antibody<br /> | **[[2hh0]] - bPrP peptide epitope + anti-PrP antibody<br /> | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[4yx2]] - bPrP + antibody<br /> |
**[[1tpx]], [[1tqb]], [[1tqc]] - sPrP C-terminal + anti-PrP antibody<br /> | **[[1tpx]], [[1tqb]], [[1tqc]] - sPrP C-terminal + anti-PrP antibody<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4yx2]] - bPrP + antibody<br /> | ||
**[[4yxh]] - PrP + antibody – mule deer<br /> | **[[4yxh]] - PrP + antibody – mule deer<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4yxk]] - | + | **[[4yxk]] - ePrP + antibody <br /> |
**[[4yxl]] - GhPrP + antibody<br /> | **[[4yxl]] - GhPrP + antibody<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4j8r]] - mPrP residues 67-82 + antibody<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4ma7]], [[4ma8]] - mPrP residues 116 - 229 + antibody<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1cu4]] - ShPrP peptide epitope + anti-PrP antibody<br /> | ||
*HET-S from ''Podospora anserine'' | *HET-S from ''Podospora anserine'' | ||
| Line 110: | Line 112: | ||
}} | }} | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Revision as of 09:45, 27 November 2019
| |||||||||||
3D structures of prion
Updated on 27-November-2019
- ↑ Cong X, Bongarzone S, Giachin G, Rossetti G, Carloni P, Legname G. Dominant-negative effects in prion diseases: insights from molecular dynamics simulations on mouse prion protein chimeras. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2012 Aug 30. PMID:22934595 doi:10.1080/07391102.2012.712477