S100 protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (5 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | |||
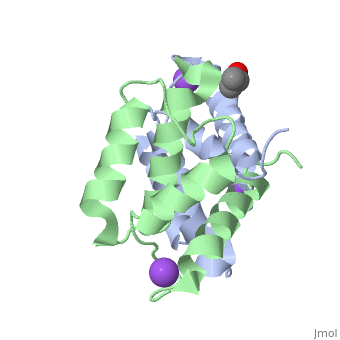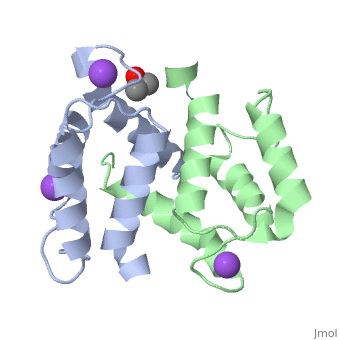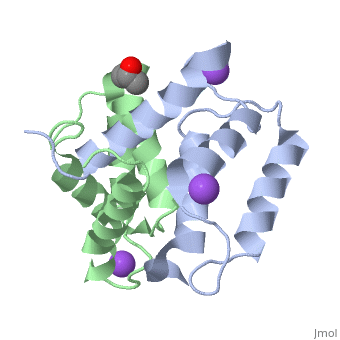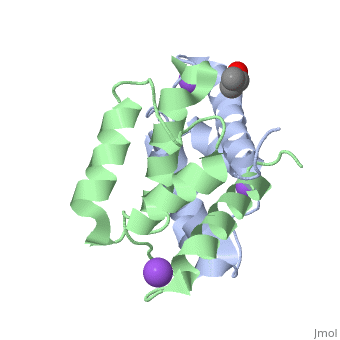
<StructureSection load='2rgi' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Human S-100A2 complex with isopropanol and Na+ ion (PDB code [[2rgi]])'> | <StructureSection load='2rgi' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Human S-100A2 complex with isopropanol and Na+ ion (PDB code [[2rgi]])'> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| Line 30: | Line 29: | ||
S100A16 is a special member of the S100 class of calcium binding proteins, because it <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/As/12'>performs a conformational change upon calcium(II) binding</scene> much smaller than experienced by most S100 proteins. This was observed after determination of the solution structures of apo and <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Dual_binding_calcium/3'>calcium(II)-bound S100A16</scene> and the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Crysal/2'>crystal structure of apo S100A16</scene>. The likely reason for minimal conformational change <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Calcium_binding_start/7'>in S100A16</scene> is the lower calcium binding affinity and stronger <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Hydrophobic_interactions_2/3'>hydrophobic interaction</scene> between <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Please_work/3'>helix III and IV present in this protein </scene> with respect to other S100 proteins. Another characteristic of <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Opening/3'>S100A16</scene> is that the helix IV has the same length in <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/25_residue_long_apo/3'>both apo</scene> and <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/25_residue_calclium_bound/3'>calcium(II) forms</scene> because of <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Motif_good/5'>the presence of a Gly-Gly-Ile-Thr-Gly-Pro sequence motif</scene> in helix IV. Based on the available structures of S100 members, we analyzed and summarized all their conformational changes due to calcium(II) binding by a principal component analysis. <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Calcium_binding_start/7'>Calcium binding</scene> was proved by both NMR titration and Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC) experiments. Even if the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Binding_calcium_glu/2'>important Glu residue</scene> in the last position of first EF-hand calcium binding loop <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Binding_calcium/13'>is missing</scene>, these experimental data indicated that S100A16 can still bind one calcium(II) ion in such loop. NMR relaxation <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Flexible_broadwide/4'>studies showed that the first calcium binding loop and the beginning of the second helix</scene> are the most <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Flexible_broad/3'>flexible regions in both the apo and calcium(II)-bound S100A16</scene>. Although the biological function of S100A16 is still unclear yet, these structural and dynamic properties can provide useful information for further functional studies. | S100A16 is a special member of the S100 class of calcium binding proteins, because it <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/As/12'>performs a conformational change upon calcium(II) binding</scene> much smaller than experienced by most S100 proteins. This was observed after determination of the solution structures of apo and <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Dual_binding_calcium/3'>calcium(II)-bound S100A16</scene> and the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Crysal/2'>crystal structure of apo S100A16</scene>. The likely reason for minimal conformational change <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Calcium_binding_start/7'>in S100A16</scene> is the lower calcium binding affinity and stronger <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Hydrophobic_interactions_2/3'>hydrophobic interaction</scene> between <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Please_work/3'>helix III and IV present in this protein </scene> with respect to other S100 proteins. Another characteristic of <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Opening/3'>S100A16</scene> is that the helix IV has the same length in <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/25_residue_long_apo/3'>both apo</scene> and <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/25_residue_calclium_bound/3'>calcium(II) forms</scene> because of <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Motif_good/5'>the presence of a Gly-Gly-Ile-Thr-Gly-Pro sequence motif</scene> in helix IV. Based on the available structures of S100 members, we analyzed and summarized all their conformational changes due to calcium(II) binding by a principal component analysis. <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Calcium_binding_start/7'>Calcium binding</scene> was proved by both NMR titration and Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC) experiments. Even if the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Binding_calcium_glu/2'>important Glu residue</scene> in the last position of first EF-hand calcium binding loop <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Binding_calcium/13'>is missing</scene>, these experimental data indicated that S100A16 can still bind one calcium(II) ion in such loop. NMR relaxation <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Flexible_broadwide/4'>studies showed that the first calcium binding loop and the beginning of the second helix</scene> are the most <scene name='Journal:JBIC:3/Flexible_broad/3'>flexible regions in both the apo and calcium(II)-bound S100A16</scene>. Although the biological function of S100A16 is still unclear yet, these structural and dynamic properties can provide useful information for further functional studies. | ||
| - | + | ||
== 3D Structures of S100 proteins == | == 3D Structures of S100 proteins == | ||
| + | [[S100 proteins 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | **[[2y5i]] – CBP + Ca - zebrafish <br /> | ||
| - | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Donato R, Cannon BR, Sorci G, Riuzzi F, Hsu K, Weber DJ, Geczy CL. Functions of S100 proteins. Curr Mol Med. 2013 Jan;13(1):24-57. PMID:22834835
- ↑ Yao R, Lopez-Beltran A, Maclennan GT, Montironi R, Eble JN, Cheng L. Expression of S100 protein family members in the pathogenesis of bladder tumors. Anticancer Res. 2007 Sep-Oct;27(5A):3051-8. PMID:17970044
- ↑ Wilsmann-Theis D, Wagenpfeil J, Holzinger D, Roth J, Koch S, Schnautz S, Bieber T, Wenzel J. Among the S100 proteins, S100A12 is the most significant marker for psoriasis disease activity. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016 Jul;30(7):1165-70. doi: 10.1111/jdv.13269., Epub 2015 Sep 2. PMID:26333514 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jdv.13269
- ↑ Zhu L, Okano S, Takahara M, Chiba T, Tu Y, Oda Y, Furue M. Expression of S100 protein family members in normal skin and sweat gland tumors. J Dermatol Sci. 2013 Jun;70(3):211-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2013.03.002. Epub, 2013 Mar 16. PMID:23623205 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2013.03.002
- ↑ Bertini I, Borsi V, Cerofolini L, Das Gupta S, Fragai M, Luchinat C. Solution structure and dynamics of human S100A14. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2012 Nov 30. PMID:23197251 doi:10.1007/s00775-012-0963-3
- ↑ Babini E, Bertini I, Borsi V, Calderone V, Hu X, Luchinat C, Parigi G. Structural characterization of human S100A16, a low-affinity calcium binder. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2010 Nov 3. PMID:21046186 doi:10.1007/s00775-010-0721-3