WWP2
From Proteopedia
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='5TJ8' size='350' side='right' caption='WWP2 Ubiquitin Ligase Full-length Structure (PDB entry [[5TJ8]])' scene=''> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
WWP2 is a family member of Homologous to the E6-AP Carboxyl Terminus (HECT) E3 Ligases which accept a ubiquitin molecule from an enzyme upstream in the ubiquitination pathway and transfer the ubiquitin to a target signaling molecule or transcription factor. The thioester bond formation between an active site Cystine on HECT E3 Ligases and ubiquitin differentiates this family of enzymes from the more abundant RING family of ubiquitin ligases which do not covalently bond to the ubiquitin ligand. | WWP2 is a family member of Homologous to the E6-AP Carboxyl Terminus (HECT) E3 Ligases which accept a ubiquitin molecule from an enzyme upstream in the ubiquitination pathway and transfer the ubiquitin to a target signaling molecule or transcription factor. The thioester bond formation between an active site Cystine on HECT E3 Ligases and ubiquitin differentiates this family of enzymes from the more abundant RING family of ubiquitin ligases which do not covalently bond to the ubiquitin ligand. | ||
| + | --- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Structure== | ||
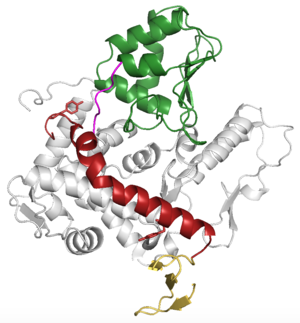
| + | <StructureSection load='5TJ8' size='350' side='right' caption='WWP2 Ubiquitin Ligase Full-length Structure (PDB entry [[5TJ8]])' scene=''> | ||
Green link for <scene name='84/848928/Linker/1'>Scene F2</scene> | Green link for <scene name='84/848928/Linker/1'>Scene F2</scene> | ||
Green link for Scene F1 | Green link for Scene F1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 17-142 is C2 Domain | ||
| + | 302-361 is WW1 and WW2 | ||
| + | 361-407 is 2,3 Linker | ||
| + | 407-477 is WW3 and WW4 | ||
| + | 489-870 is HECT | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 18:44, 15 June 2020
Contents |
Introduction
WWP2 is a family member of Homologous to the E6-AP Carboxyl Terminus (HECT) E3 Ligases which accept a ubiquitin molecule from an enzyme upstream in the ubiquitination pathway and transfer the ubiquitin to a target signaling molecule or transcription factor. The thioester bond formation between an active site Cystine on HECT E3 Ligases and ubiquitin differentiates this family of enzymes from the more abundant RING family of ubiquitin ligases which do not covalently bond to the ubiquitin ligand. ---
Structure
| |||||||||||
This is a default text for your page WWP2. Click above on edit this page to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs.
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
Function
Disease
Relevance
Structural highlights
</StructureSection>
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Tihitina Y Aytenfisu, Hannah Campbell, Sandra B. Gabelli, Michal Harel