Structure
The (2Z6G) contains residues 126-681 and a central core of and an alpha helix, the , at the beginning of the ß-catenin C-terminal domain. The armadillo domain is made of three helices in each repeat and has a particular site which is positively charged, constituting the for the majority of ß-catenin ligands. [1]
The terminal domains sequences are less conserved than the armadillo repeat domain, mediate some of the protein interactions and are both negatively charged. It is observed that the , and the N terminus of the first armadillo repeat has an . Both N- and C-terminal domains do not interact with the armadillo repeat domain. [1]
In contrast to the armadillo ligand-binding structural groove, the C-terminal tail is highly negatively charged. The helix-C caps the Hydrophobic . However, the other side of the surface, exposed to solvent, is composed of Polar residues. Thereby, this structure forms part of the superhelical structure core of ß-catenin together with armadillo repeat domain. [1]
It is possible that the helix-C is important for the transactivation of Wnt-responsive genes, but not for the cell adhesion through cadherins. Hence, this same β-catenin region is also the binding site of transcriptional inhibitors that compete directly with TCF for β-catenin binding.[1]
Cell Adhesion
In the absence of Wnt stimulus, the ß-catenin is located at the cytoplasmic side of the membrane as a component of cadherin-based cell-cell connections. Cadherins are transmembrane glycoproteins calcium-dependent adhesion that can link to ß-catenin through their cytoplasmic tails. The cadherin-catenin complex forms adherens junctions that polarize epithelial tissues and hold the cells together. [2]
The most known interaction occurs between (1I7X) (epithelial cadherin). They are associated while still in the endoplasmic reticulum and interfering with the binding of these proteins results in proteasomal degradation of the cadherin. First, alpha-catenin binds to ß-catenin at the first ARM repeat, amino acids , resulting in an alpha-catenin/ß-catenin heterodimer. This binding stabilizes ß-catenin in the hinged form, and E-cadherin can connect simultaneously. The is extensive, covering the entire length of the ß-catenin ARM repeat domain and involving the C-terminal 100 residues of the cadherin cytoplasmic domain. [3] [4]
The ß-catenin destruction complex
In baseline conditions without Wnt signaling, ß-catenin concentrations are low in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Then, the destruction complex (Figure 1), formed by APC, Axin, CK1ɑ and GSK, is active and causes the degradation of the protein through proteasome. Initially it is recognized by APC and Axin that promote the phosphorylation of Ser45 by CK1ɑ. This facilitates the phosphorylation by GSK in the residues of the amino acids Thr41, Ser37 and Ser33. The last two, when phosphorylated, leads to recognition by ß-TrCP and consequently ubiquitination by an E3 ligase and degradation by 26S proteasome. [3]
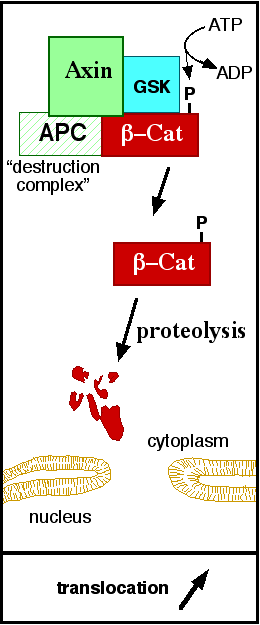
Figure 1: A simplified diagram of the ß-catenin destruction complex. The destruction complex proteins promote the ß-catenin proteolysis in cytoplasm.
DNA binding and transcription
The inhibition of ß-catenin destruction complex through activation of the Wnt pathway (Figure 2) leads to increased levels of the protein in cytoplasm and its translocation into the nucleus. ß-catenin interacts with different nuclear pore complex components and ARM repeats are critical for its import and export. FoxM1 also facilitates its nuclear translocation directly interacting with ARM repeats . FoxM1 forms a complex with ß-catenin/TCF on the promoters of Wnt target genes. Once in the nucleus, ß-catenin and its DNA binding partners can activate transcription of Wnt/ß-catenin target genes. Therefore, ß-catenin can only initiates transcription in a multimeric complex, as its central transcriptional activator. [3]
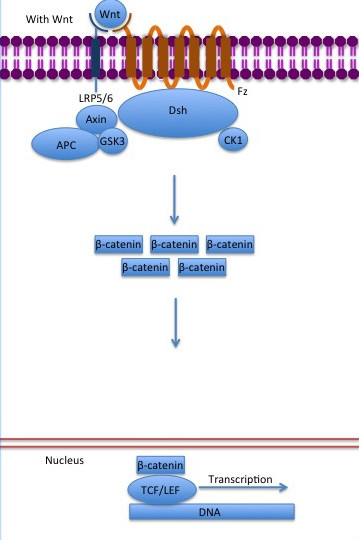 Figure 2: The canonical Wnt pathway when Wnt is present. The inhibition of the destruction complex allows ß-catenin translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus.
Figure 2: The canonical Wnt pathway when Wnt is present. The inhibition of the destruction complex allows ß-catenin translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus.
TCF transcription factors works as the principal nuclear member of ß-catenin multimeric complex. TCFs bind to DNA enhancers and ß-catenin acts as a link in a chain between them and others transcriptional coactivators. This interaction can be modulated to enhance, repress os switch off ß-catenin-mediated transcription. The majority of these transcription coactivators binds to and many of them can affect chromatin structure. Indeed, it seems that the C-terminus region of ß-catenin coordinates the recruitment and sequential exchange of these proteins. Binding of ß-catenin to TCF is blocked by some proteins such as (1M1E) [3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Xing Y, Takemaru K, Liu J, Berndt JD, Zheng JJ, Moon RT, Xu W. Crystal structure of a full-length beta-catenin. Structure. 2008 Mar;16(3):478-87. PMID:18334222 doi:10.1016/j.str.2007.12.021
- ↑ Developmental Biology . Eleventh Edition. By Scott F. Gilbert and Michael J. F. Barresi. Sunderland (Massachusetts): Sinauer Associates. ISBN: 978-1-60535-470-5. 2016.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Valenta T, Hausmann G, Basler K. The many faces and functions of beta-catenin. EMBO J. 2012 Jun 13;31(12):2714-36. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.150. Epub 2012 May, 22. PMID:22617422 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2012.150
- ↑ Huber, A. H., & Weis, W. I. (2001). The structure of the β-catenin/E-cadherin complex and the molecular basis of diverse ligand recognition by β-catenin. Cell, 105(3), 391-402.


