User:Isabela Fonseca de Oliveira Granha/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
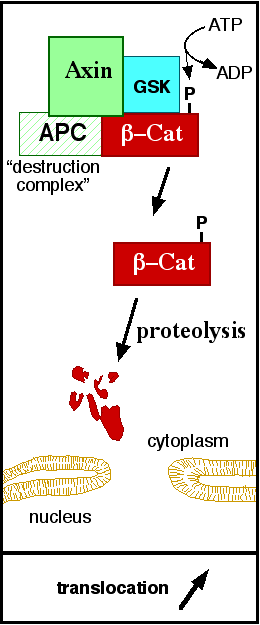
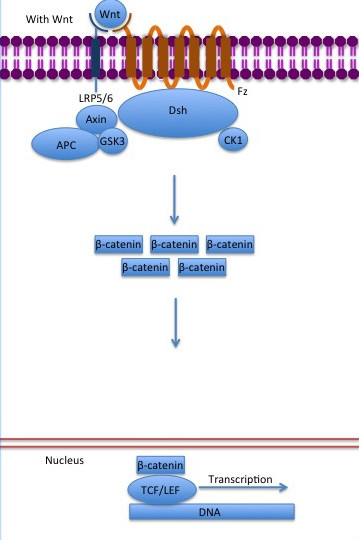
The inhibition of ß-catenin destruction complex through activation of the Wnt pathway (Figure 3) leads to increased levels of the protein in cytoplasm and its translocation into the nucleus. ß-catenin interacts with different nuclear pore complex components and ARM repeats <scene name='84/848919/R10-12/1'>R10-R12</scene> are critical for its import and export. [[Forkhead box protein|FoxM1]] also facilitates its nuclear translocation directly interacting with ARM repeats <scene name='84/848919/R11-12/2'>R11-R12</scene>. [[Forkhead box protein|FoxM1]] forms a complex with ß-catenin/TCF on the promoters of Wnt target genes. Once in the nucleus, ß-catenin and its DNA binding partners can activate transcription of Wnt/ß-catenin target genes. Therefore, ß-catenin can only initiates transcription in a multimeric complex, as its central transcriptional activator. <ref name="valenta2012" /> | The inhibition of ß-catenin destruction complex through activation of the Wnt pathway (Figure 3) leads to increased levels of the protein in cytoplasm and its translocation into the nucleus. ß-catenin interacts with different nuclear pore complex components and ARM repeats <scene name='84/848919/R10-12/1'>R10-R12</scene> are critical for its import and export. [[Forkhead box protein|FoxM1]] also facilitates its nuclear translocation directly interacting with ARM repeats <scene name='84/848919/R11-12/2'>R11-R12</scene>. [[Forkhead box protein|FoxM1]] forms a complex with ß-catenin/TCF on the promoters of Wnt target genes. Once in the nucleus, ß-catenin and its DNA binding partners can activate transcription of Wnt/ß-catenin target genes. Therefore, ß-catenin can only initiates transcription in a multimeric complex, as its central transcriptional activator. <ref name="valenta2012" /> | ||
| - | TCF transcription factors works as the principal nuclear member of ß-catenin multimeric complex. TCFs bind to DNA enhancers and ß-catenin acts as a link in a chain between them and others transcriptional coactivators. This interaction can be modulated to enhance, repress os switch off ß-catenin-mediated transcription. The majority of these transcription coactivators binds to <scene name='84/848919/R12andhelix-c/1'>the last ARM repeat and interacts with Helix-C</scene> and many of them can affect chromatin structure. Indeed, it seems that the C-terminus region of ß-catenin coordinates the recruitment and sequential exchange of these proteins. Binding of ß-catenin to TCF is blocked by some proteins such as <scene name='84/848919/Icat_bcat/3'>ICAT (orange), which interacts with the central ARM repeat of ß-catenin (green).</scene> ([http://www.rcsb.org/structure/1M1E 1M1E, from | + | TCF transcription factors works as the principal nuclear member of ß-catenin multimeric complex. TCFs bind to DNA enhancers and ß-catenin acts as a link in a chain between them and others transcriptional coactivators. This interaction can be modulated to enhance, repress os switch off ß-catenin-mediated transcription. The majority of these transcription coactivators binds to <scene name='84/848919/R12andhelix-c/1'>the last ARM repeat and interacts with Helix-C</scene> and many of them can affect chromatin structure. Indeed, it seems that the C-terminus region of ß-catenin coordinates the recruitment and sequential exchange of these proteins. Binding of ß-catenin to TCF is blocked by some proteins such as <scene name='84/848919/Icat_bcat/3'>ICAT (orange), which interacts with the central ARM repeat of ß-catenin (green).</scene> ([http://www.rcsb.org/structure/1M1E 1M1E, from ''Mus musculus'' and ''Homo sapiens'']) <ref name="valenta2012" /> |
[[Image:Canonical Wnt pathway with Wnt..jpg]] | [[Image:Canonical Wnt pathway with Wnt..jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 12:55, 9 July 2020
ß-catenin
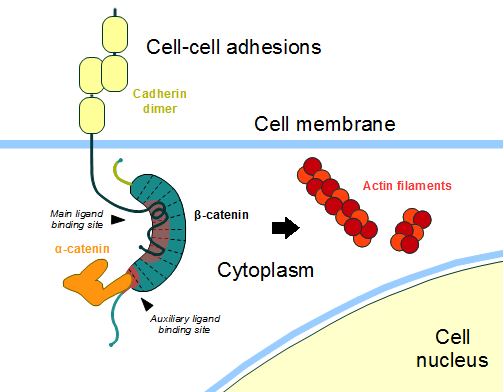
ß-catenin is an important element in cell-cell adherens junctions, called cadherins. Reported in all Eukaryota (Eukaryota) phylum, in humans the gene CTNNB1 (CTNNB1) transcribes a 95kDa protein that allows cadherins to anchor in cytoeskeleton (actin filaments) by connecting cytoplasmic proteins. Besides that, it is an essential regulator of the canonical Wnt pathway [1] (related to embryonic development). Disturbance of this activity is associated with cancer and other diseases. Therefore, ß-catenin is an important target for developing medication for many diseases, with considerable interest in its structure. [2]
| |||||||||||