Structure
The zebrafish (Danio rerio) (2Z6G) contains residues 126-681 and a central core of and an alpha helix, the , at the ß-catenin C-terminal domain.
The terminal domains sequences mediate some of the protein interactions and are negatively charged (Figure 1). It is observed that the helix-C constitutes the C-terminal domain. The N terminus of the first armadillo repeat has an . Both N- and C-terminal domains do not interact specifically with the armadillo repeat domain. [2]
The armadillo domain is more conserved than the terminal domains. It is made of 12 armadillo repeats each one with (as shown in ARM repeat 5), except for the . Furthermore, it has a particular site which is positively charged (Figure 1), constituting the binding surface for the majority of ß-catenin ligands. Because the armadillo domain is positively while the terminal tails are negatively charged (Figure 1), their interactions are nonspecific. It is proposed that both tails act like chaperones - they might avoid nonspecific protein interactions of the ARM repeat domain and its self-aggregation.[2]
In contrast to the armadillo ligand-binding structural groove, the C-terminal tail is highly negatively charged (Figure 1). The C-helix caps the Hydrophobic . However, the other side of the surface, exposed to solvent, is composed of Polar residues (Figure 2). Thereby, this structure forms part of the superhelical structure core of ß-catenin together with armadillo repeat domain. It is possible that the C-helix is important for the transactivation of Wnt-responsive genes, but not for the cell adhesion through cadherins. Hence, this same β-catenin region is also the binding site of transcriptional inhibitors that compete directly with TCF for β-catenin binding.[2]
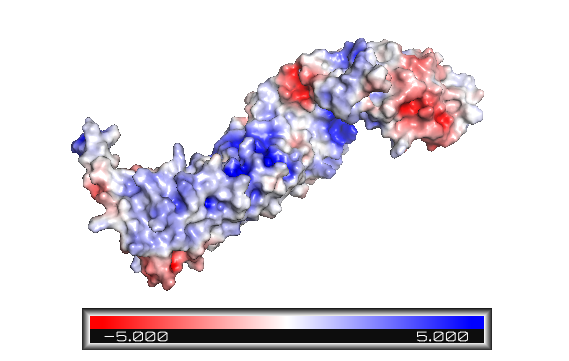
Figure 1: Beta-catenin eletrostatic surface. The color blue indicates positively charged sites, and red, negative. The armadillo repeat domain has various positive sites and a particular one is an important binding area. The terminal tails are predominantly represented in red - and the C-helix is highly negatively charged.
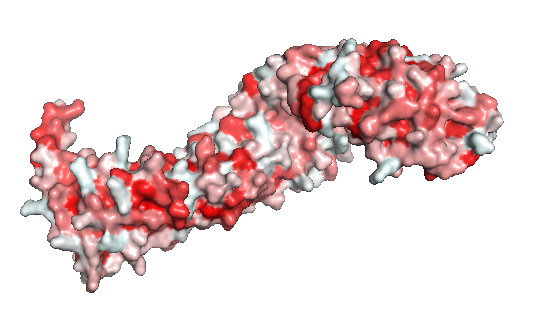
Figure 2: The beta-catenin polarity surface. The red color represents hidrophobic sites, and white, the hidrophilic areas. The protein does not have a partiular polar or apolar area. Polarity is well distributed through the molecule as well as the protein ligands.
Finally, the Danio rerio (2Z6G full length structure, blue), Mus musculus (2BCT armadillo repeat region, green) and Homo sapiens (2Z6H full length structure, pink) beta-catenin alignment (Figure 3) shows that the protein structure is quite similar in these organisms. The three structures have 12 armadillo repeat group and the superposition indicates that the helix C in zebrafish and human beta-catenin conformation and orientation are essentially the same in both crystal structures. This great similarity between these proteins demonstrates that beta-catenin is evolutionary conserved and so are the pathways that it takes part.
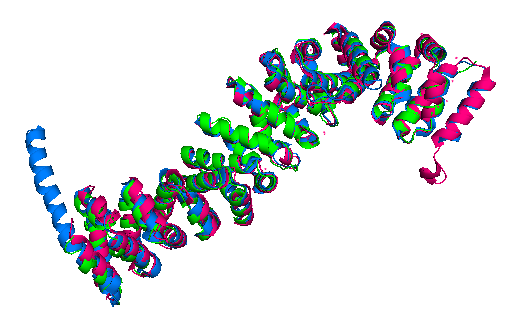
Figure 3: Superposition of a full length zebrafish (shown in blue), full length human (pink) and armadillo repeat region mouse (green) beta-catenin.
Cell Adhesion
In the absence of Wnt stimulus, ß-catenin is located at the cytoplasmic side of the membrane as a component of cadherin-based cell-cell connections (Figure 4). Cadherins are transmembrane glycoproteins calcium-dependent that mediate cell-cell adhesion through link specially to ß-catenin by their cytoplasmic tails. The cadherin-catenin complex forms adherens junctions that polarize epithelial tissues and hold the cells together. However, in case of some tumor metastasis, that complex is reported as disrupted: in order to become more migratory, epithelial cells must loose their characteristic polarity, thus the complex might be affected (phenomenon described as 'cadherin switching' in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, EMT).[3]
The most known interaction occurs between , epithelial cadherin (the ß-catenin residues 134–671 are represented in green and the residues 577–728 of the mature E-cadherin sequence are colored in rose. The proteins are from Mus musculus) (1I7X). They are associated while still in the endoplasmic reticulum and interfering with the binding of these proteins results in proteasomal degradation of the cadherin. First, alpha-catenin binds to ß-catenin at the first ARM repeat, amino acids , resulting in an alpha-catenin/ß-catenin heterodimer. This binding stabilizes ß-catenin in the hinged form, and E-cadherin can connect simultaneously. The , covering the entire length of the ß-catenin ARM repeat domain and involving the C-terminal 100 residues of the cadherin cytoplasmic domain. [4] [5]
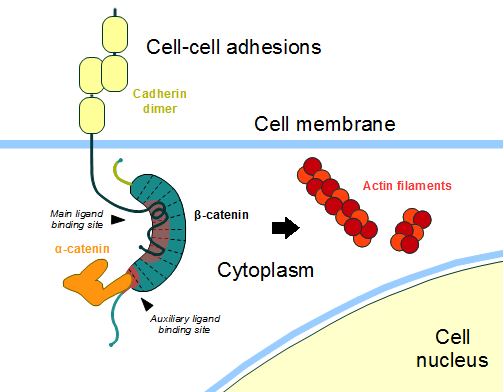
Figure 4: Cadherin-based cell adhesion. Alpha-catenin/ß-catenin forms a heterodimer that can connects to E-cadherin promoting the adherens junctions. As a homodimer, alpha-catenin interacts with actin. Adapted from: Bubus12/CC BY [1]
The ß-catenin destruction complex
In baseline conditions without Wnt signaling, ß-catenin concentrations are low in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Then, the destruction complex (Figure 5), formed by APC, Axin, CK1ɑ and GSK, is active and causes the degradation of the protein through proteasome. Initially it is recognized by APC and Axin that promote the phosphorylation of Ser45 by CK1ɑ. This facilitates the phosphorylation by GSK in the residues of the amino acids Thr41, Ser37 and Ser33. The last two, when phosphorylated, leads to recognition by ß-TrCP and consequently ubiquitination by an E3 ligase and degradation by 26S proteasome. [4] Furthermore, the relation Wnt/ß-catenin pathway usually are reported by 'canonical' and 'non-canonical', whose meaning remotes to the components of the cascate. The first leads to accumulation and stabilization of cytosolic (unphosphorylated) ß-catenin and the second promotes the increase in intracellular calcium or mediate cell polarity, but both are established in embryonic development of normal tissue and organs. [6] [7]
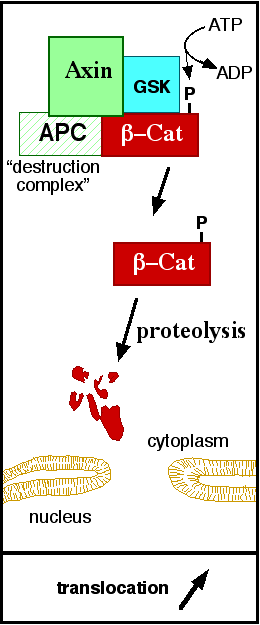
Figure 5: A simplified diagram of the ß-catenin destruction complex. The destruction complex proteins promote the ß-catenin proteolysis in cytoplasm. Source: JWSchmidt at the English language Wikipedia/CC BY-SA [2]
DNA binding and transcription
The inhibition of ß-catenin destruction complex through activation of the Wnt pathway (Figure 6) leads to increased levels of the protein in cytoplasm and its translocation into the nucleus. ß-catenin interacts with different nuclear pore complex components and ARM repeats are critical for its import and export. FoxM1 also facilitates its nuclear translocation directly interacting with ARM repeats . FoxM1 forms a complex with ß-catenin/TCF on the promoters of Wnt target genes. Once in the nucleus, ß-catenin and its DNA binding partners can activate transcription of Wnt/ß-catenin target genes. Therefore, ß-catenin can only initiates transcription in a multimeric complex, as its central transcriptional activator. [4]
TCF transcription factors works as the principal nuclear member of ß-catenin multimeric complex. TCFs bind to DNA enhancers and ß-catenin acts as a link in a chain between them and others transcriptional coactivators. This interaction can be modulated to enhance, repress os switch off ß-catenin-mediated transcription. The majority of these transcription coactivators binds to and many of them can affect chromatin structure. Indeed, it seems that the C-terminus region of ß-catenin coordinates the recruitment and sequential exchange of these proteins. Binding of ß-catenin to TCF is blocked by some proteins such as (here ICAT is represented in orange and is a full length structure from Homo sapiens; ß-catenin is shown in green and is from Mus musculus). (1M1E) [4]
This interaction can be divided in two regions: the and the . The first one overlaps with others ß-catenin ligands and is known for its several (for example, Val68, Met69, and Phe71 interact with hydrophobic sites on the surface of ß-catenin) and - Asp66 and Glu75 form salt bridges with ß-catenin residues Lys435 (repeat 8) and Lys312 (repeat 5). There are other polar contacts to stabilize the protein-protein binding. Finally, the interaction between the ICAT helical domain and the two last ARM repeat is water-mediated contact (with ARM 11) and hydrophobic interactions (ARM 12). The hydrophobic interactions are stabilized by the connections between (shown in pink). Lys19 also forms a with ß-catenin Glu664 (repeat 12). Another polar interaction occurs between 1. [8]
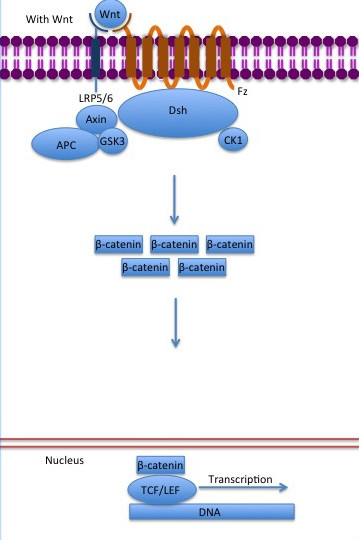
Figure 6: The canonical Wnt pathway when Wnt is present. The inhibition of the destruction complex allows ß-catenin translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus. Source: Gpruett2/CC BY-SA [3]
References
- ↑ Logan CY, Nusse R. The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:781-810. doi:, 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.20.010403.113126. PMID:15473860 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.20.010403.113126
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Xing Y, Takemaru K, Liu J, Berndt JD, Zheng JJ, Moon RT, Xu W. Crystal structure of a full-length beta-catenin. Structure. 2008 Mar;16(3):478-87. PMID:18334222 doi:10.1016/j.str.2007.12.021
- ↑ Developmental Biology . Eleventh Edition. By Scott F. Gilbert and Michael J. F. Barresi. Sunderland (Massachusetts): Sinauer Associates. ISBN: 978-1-60535-470-5. 2016.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Valenta T, Hausmann G, Basler K. The many faces and functions of beta-catenin. EMBO J. 2012 Jun 13;31(12):2714-36. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.150. Epub 2012 May, 22. PMID:22617422 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2012.150
- ↑ Huber, A. H., & Weis, W. I. (2001). The structure of the β-catenin/E-cadherin complex and the molecular basis of diverse ligand recognition by β-catenin. Cell, 105(3), 391-402.
- ↑ Arend et al,2013. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway in ovarian cancer: A review. Gynecologic Oncology. Volume 131, Issue 3, December 2013, Pages 772-779.
- ↑ Takayama et al, 1996. ß-Catenin Expression in Human Cancers. American journal of Pathology, Vol. 148, No. 1, January.
- ↑ Daniels, D. L., & Weis, W. I. (2002). ICAT inhibits beta-catenin binding to Tcf/Lef-family transcription factors and the general coactivator p300 using independent structural modules. Molecular cell, 10(3), 573–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00631-7.






