This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
SN2 reaction
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
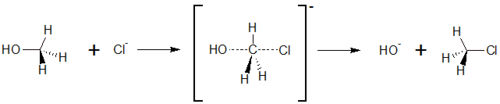
On the other side, SN2 reactions are characterised for exchanging substituents. The substituent that leaves the molecule is called leaving group. | On the other side, SN2 reactions are characterised for exchanging substituents. The substituent that leaves the molecule is called leaving group. | ||
| - | |||
Typically, alkanes with a substituent in primary position undergo S<sub>N</sub>2 reactions. In contrast to a S<sub>N</sub>1 reaction, no stable carbo cation can be formed. Therefore, another way will be taken. | Typically, alkanes with a substituent in primary position undergo S<sub>N</sub>2 reactions. In contrast to a S<sub>N</sub>1 reaction, no stable carbo cation can be formed. Therefore, another way will be taken. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 26: | ||
<jmolButton><script>if(_animating);anim off;else;frame play;endif</script><text>Toggle animation</text></jmolButton> | <jmolButton><script>if(_animating);anim off;else;frame play;endif</script><text>Toggle animation</text></jmolButton> | ||
</jmol> | </jmol> | ||
| - | |||
| - | This demo was adapted from http://www.chemieunterricht-interaktiv.de/en/animations/sn2_substitution/sn2_substitution_3d.html by Dr. V. Pietzner, part of the ChiLe project | ||
===See also=== | ===See also=== | ||
[[SN1_reaction|S<sub>N</sub>1 reaction: Substitution of Cl<sup>−</sup> and ''tert''-Butanol ]] | [[SN1_reaction|S<sub>N</sub>1 reaction: Substitution of Cl<sup>−</sup> and ''tert''-Butanol ]] | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| + | This demo was adapted from http://www.chemieunterricht-interaktiv.de/en/animations/sn2_substitution/sn2_substitution_3d.html by Dr. V. Pietzner, part of the ChiLe project | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 14:17, 8 October 2020
SN2-Substitution of chloride and methanol
| |||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky, Angel Herraez, Verena Pietzner