Staphylococcal nuclease
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (5 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
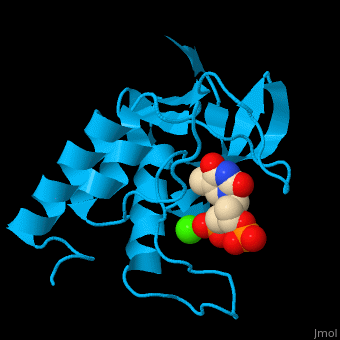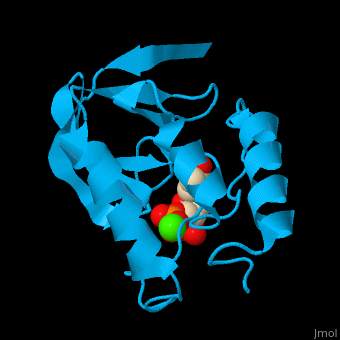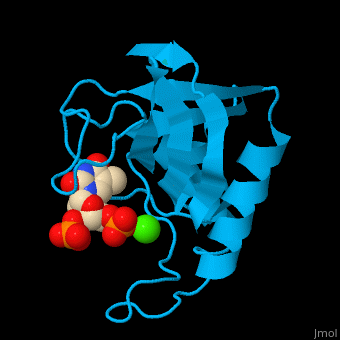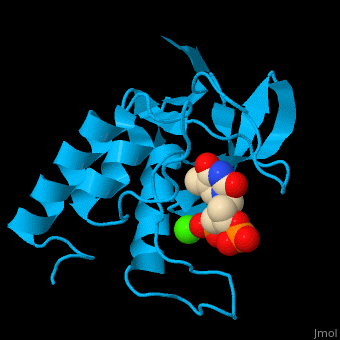
| - | <StructureSection load='' size=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='49/497241/Cv/1' caption='Stapphylococcal nuclease complex with inhibitor thymidine diphosphate and Ca+2 ion (green) [[1snc]]' pspeed='8'> |
| - | '''Micrococcal nuclease''', or '''Staphylococcal nuclease''', is a monomeric Ca++ dependent enzyme of 149 amino acids that cleaves either DNA or RNA substrates. It is used for relatively non-specific cleavage of nucleic acids in molecular biology, and has been an important model system for the study of protein folding. | + | '''Micrococcal nuclease''', or '''Staphylococcal nuclease''' or '''Nuclease A''' or '''thermonuclease''', is a monomeric Ca++ dependent enzyme of 149 amino acids that cleaves either DNA or RNA substrates. It is used for relatively non-specific cleavage of nucleic acids in molecular biology, and has been an important model system for the study of protein folding. |
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
| - | The first structure was solved in 1969 in the Cotton lab at MIT, published in 1971<ref>Arnone AA, Bier CJ, Cotton FA, Day VW, Hazen EE Jr, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Yonath A (1971) "A High Resolution Structure of an Inhibitor Complex of the Extracellular Nuclease of Staphylococcus aureus: I. Experimental Procedures and Chain Tracing," J. Biol. Chem. 246, 2303-2316</ref>, and deposited in the PDB as now-obsoleted 1sns in April 1974. The highest resolution wildtype structure in the PDB with deposited data is 2snc at 1.65A[http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=1SNC]. As seen in the ribbon diagram above, the nuclease molecule has 3 long alpha helices and a 5-stranded, barrel-shaped beta sheet, in an arrangement known as the OB-fold (for oligonucleotide-binding fold) as classified in the SCOP database. There are about | + | The first structure was solved in 1969 in the Cotton lab at MIT, published in 1971<ref>Arnone AA, Bier CJ, Cotton FA, Day VW, Hazen EE Jr, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Yonath A (1971) "A High Resolution Structure of an Inhibitor Complex of the Extracellular Nuclease of Staphylococcus aureus: I. Experimental Procedures and Chain Tracing," J. Biol. Chem. 246, 2303-2316</ref>, and deposited in the PDB as now-obsoleted 1sns in April 1974. The highest resolution wildtype structure in the PDB with deposited data is 2snc at 1.65A[http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=1SNC]. As seen in the ribbon diagram above, the nuclease molecule has 3 long alpha helices and a 5-stranded, barrel-shaped beta sheet, in an arrangement known as the OB-fold (for oligonucleotide-binding fold) as classified in the SCOP database. There are about 300 PDB entries for Staph. nuclease, including extremely extensive mutational studies from many labs focused on understanding aspects of protein folding<ref>PMID:22496593</ref><ref>PMID: 15228960</ref><ref>PMID: 8762134</ref>. |
| + | |||
| + | *<scene name='49/497241/Cv/7'>Stapphylococcal nuclease interactons with inhibitor thymidine diphosphate (TDP) and Ca+2 ion</scene>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. | ||
| + | *<scene name='49/497241/Cv/8'>Ca coordination site</scene>. | ||
| - | *<scene name='49/497241/Cv/5'>Stapphylococcal nuclease interactons with inhibitor thymidine diphosphate and Ca+2 ion</scene>. Water molecules shown as red spheres. | ||
| - | *<scene name='49/497241/Cv/6'>Ca coordination site</scene>. | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of Staphylococcal nuclease== | ==3D structures of Staphylococcal nuclease== | ||
| + | [[Staphylococcal nuclease 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Arnone AA, Bier CJ, Cotton FA, Day VW, Hazen EE Jr, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Yonath A (1971) "A High Resolution Structure of an Inhibitor Complex of the Extracellular Nuclease of Staphylococcus aureus: I. Experimental Procedures and Chain Tracing," J. Biol. Chem. 246, 2303-2316
- ↑ Roche J, Caro JA, Norberto DR, Barthe P, Roumestand C, Schlessman JL, Garcia AE, Garcia-Moreno E B, Royer CA. Cavities determine the pressure unfolding of proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Apr 10. PMID:22496593 doi:10.1073/pnas.1200915109
- ↑ Chen J, Lu Z, Sakon J, Stites WE. Proteins with simplified hydrophobic cores compared to other packing mutants. Biophys Chem. 2004 Aug 1;110(3):239-48. PMID:15228960 doi:10.1016/j.bpc.2004.02.007
- ↑ Wynn R, Harkins PC, Richards FM, Fox RO. Mobile unnatural amino acid side chains in the core of staphylococcal nuclease. Protein Sci. 1996 Jun;5(6):1026-31. PMID:8762134 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/pro.5560050605
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky, Jane S. Richardson