Rhodopsin Structure and Function
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (10 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
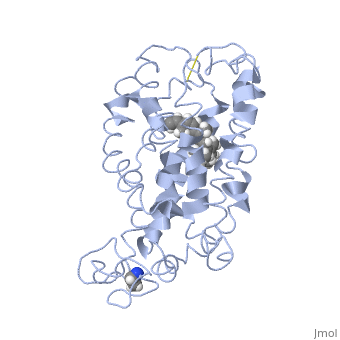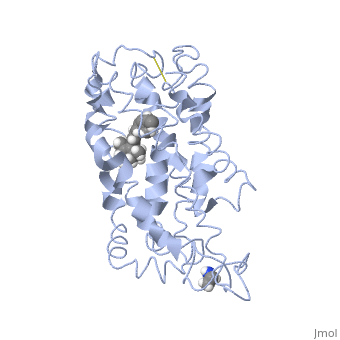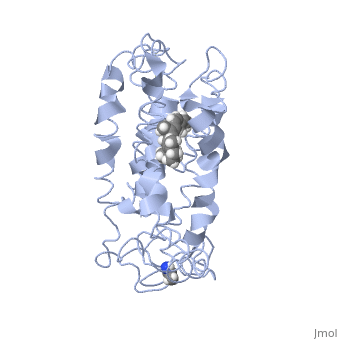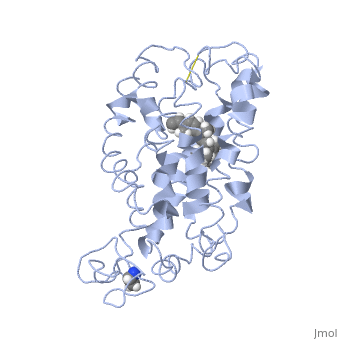
| - | + | <StructureSection load='1jfp' size='340' side='right' caption='Bovine rhodopsin complex with retinal (PDB code [[1jfp]])' scene=''> | |
| - | <StructureSection load='1jfp' size='340' side='right' caption='Bovine rhodopsin complex with retinal (PDB code [[1jfp]])' | + | |
| - | + | ||
==Rhodopsin== | ==Rhodopsin== | ||
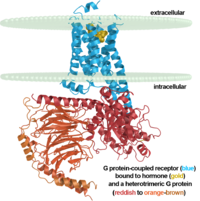
| - | Rhodopsin is a member of the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) family. Rhodopsin is the | + | '''Rhodopsin''' is a member of the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) family. Rhodopsin is the |
common GPCR structure used to understand functionality of G-protein coupled receptors. | common GPCR structure used to understand functionality of G-protein coupled receptors. | ||
Rhodopsin is commonly found in the photoreceptors in the retina, specifically in the rod | Rhodopsin is commonly found in the photoreceptors in the retina, specifically in the rod | ||
| Line 36: | Line 35: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='1jfp' size='340' side='right' caption='Bovine rhodopsin complex with retinal (PDB code [[1jfp]])'/> | ||
<scene name='77/778331/Rhodopsin_no_ligand/1'>Rhodopsin protein</scene> Fully functional rhodopsin has the typical GPCR structure of a seven transmembrane helical bundle with the N-terminus on the interior of the rods and the C-terminus in the cytoplasm. The N-terminus is located near the extracellular loops and ends of the transmembrane protein. There are hydrogen bonding between the transmembrane sections and the extracellular loops that are involved in the activation of rhodopsin when a photon is received. The N-terminus is thought to play a role in orientation of the extracellular loops<ref name="Article4">PMID:29042326</ref>. Transmembrane domain 1 and 2 play a role in stabilizing the protein and giving the protein functionality<ref name="Article3">PMID:21352497</ref>. Rhodopsin has two components: opsin (a membrane-bound polypeptide) and 11-cis-retinal (a chromophore that is bound to opsin via a protonated Schiff-base)<ref name="Article5">PMID:12402507</ref>. | <scene name='77/778331/Rhodopsin_no_ligand/1'>Rhodopsin protein</scene> Fully functional rhodopsin has the typical GPCR structure of a seven transmembrane helical bundle with the N-terminus on the interior of the rods and the C-terminus in the cytoplasm. The N-terminus is located near the extracellular loops and ends of the transmembrane protein. There are hydrogen bonding between the transmembrane sections and the extracellular loops that are involved in the activation of rhodopsin when a photon is received. The N-terminus is thought to play a role in orientation of the extracellular loops<ref name="Article4">PMID:29042326</ref>. Transmembrane domain 1 and 2 play a role in stabilizing the protein and giving the protein functionality<ref name="Article3">PMID:21352497</ref>. Rhodopsin has two components: opsin (a membrane-bound polypeptide) and 11-cis-retinal (a chromophore that is bound to opsin via a protonated Schiff-base)<ref name="Article5">PMID:12402507</ref>. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 40: | ||
<scene name='77/778331/Rhodopsin_and_ligand/1'>Rhodopsin and Ligand</scene> This is rhodopsin with 11-cis retinal bound. After 11-cis retinal becomes activated and becomes all-trans, rhodopsin undergoes the conformational change to become metarhodopsin I and then metarhodopsin II which is the fully active form of rhodopsin. Metarhodopsin II then associates with the G protein transducin and the signal cascade can continue. | <scene name='77/778331/Rhodopsin_and_ligand/1'>Rhodopsin and Ligand</scene> This is rhodopsin with 11-cis retinal bound. After 11-cis retinal becomes activated and becomes all-trans, rhodopsin undergoes the conformational change to become metarhodopsin I and then metarhodopsin II which is the fully active form of rhodopsin. Metarhodopsin II then associates with the G protein transducin and the signal cascade can continue. | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also: | ||
| + | *[[Receptor]] | ||
| + | *[[Transmembrane (cell surface) receptors]] | ||
| + | *[[G protein-coupled receptors]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Jason Telford, Abbey Lynn Lauer, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Karsten Theis