User:Luca Paulino Otvos/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
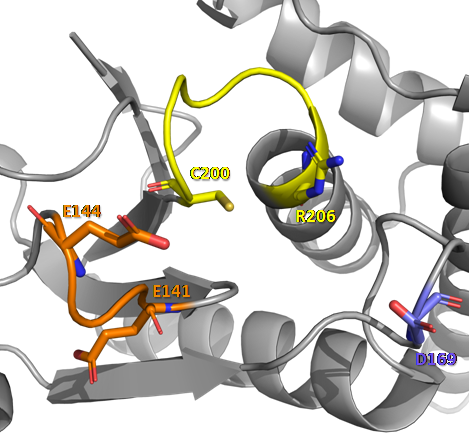
| - | The protein tyrosine phosphatase localized to the Mitochondrion 1 (PTPMT1) is a dual specificity phosphatases (DUSP) that catalyzes the dephosphorylation of phosphothreonine, phosphoserine and/or phosphotyrosine residues in lipid or protein substrates. Its name came from the fact that it was the first phosphatase identified exclusively in mitochondria | + | The protein tyrosine phosphatase localized to the Mitochondrion 1 (PTPMT1) is a dual specificity phosphatases (DUSP) that catalyzes the dephosphorylation of phosphothreonine, phosphoserine and/or phosphotyrosine residues in lipid or protein substrates. Its name came from the fact that it was the first phosphatase identified exclusively in mitochondria <ref>DOI 10.1074/jbc.M404959200</ref>. PTPMT1 is a phosphatase directed to the mitochondria by an N-terminal sequence and is found anchored in the inner mitochondrial membrane with its phosphatase domain facing the matrix [2]. |
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| - | <3 - Pagliarini, D.J., Worby, C.A., Dixon, J.E., 2004. A PTEN-like phosphatase with a novel substrate specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 38590–38596. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M404959200> | ||
| - | <4 - Pagliarini, D.J., Wiley, S.E., Kimple, M.E., Dixon, J.R., Kelly, P., Worby, C.A., Casey, P.J., Dixon, J.E., 2005. Involvement of a mitochondrial phosphatase in the regulation of ATP production and insulin secretion in pancreatic beta cells. Mol. Cell 19, 197–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2005.06.008> | ||
| - | <5 - Zhang, Z.Y., Wang, Y., Wu, L., Fauman, E.B., Stuckey, J.A., Schubert, H.L., Saper, M.A., Dixon, J.E., 1994. The Cys(X)5Arg catalytic motif in phosphoester hydrolysis. Biochemistry 33, 15266–15270. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00255a007> | ||
| - | <6 - Nath, A.K., Ryu, J.H., Jin, Y.N., Roberts, L.D., Dejam, A., Gerszten, R.E., Peterson, R.T., 2015. PTPMT1 Inhibition Lowers Glucose through Succinate Dehydrogenase Phosphorylation. Cell Rep. 10, 694–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.01.010> | ||
| - | <7 - Lu, Y.-W., Claypool, S.M., 2015. Disorders of phospholipid metabolism: an emerging class of mitochondrial disease due to defects in nuclear genes. Front. Genet. 6, 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2015.00003> | ||
Revision as of 13:07, 1 November 2021
This is a default text for your page Luca Paulino Otvos/Sandbox 1. Click above on edit this page to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
|
Contents |
Function
The protein tyrosine phosphatase localized to the Mitochondrion 1 (PTPMT1) is a dual specificity phosphatases (DUSP) that catalyzes the dephosphorylation of phosphothreonine, phosphoserine and/or phosphotyrosine residues in lipid or protein substrates. Its name came from the fact that it was the first phosphatase identified exclusively in mitochondria [3]. PTPMT1 is a phosphatase directed to the mitochondria by an N-terminal sequence and is found anchored in the inner mitochondrial membrane with its phosphatase domain facing the matrix [2].
Biological roles
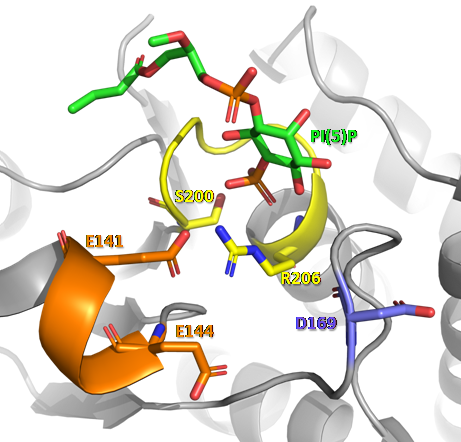
One of the best known functions of this phosphatase is its participation in the biosynthetic pathway of cardiolipin [3], a phospholipid that makes up the inner mitochondrial membrane and is essential for metabolic functions, crest structuring and mitochondrial dynamics [5]. In this process, PTPMT1 is responsible for the dephosphorylation step of phosphatidylglycerolphosphate (PGP) forming phosphatidylglycerol (PG), which is the substrate of cardiolipin synthase. PTPMT1 is also involved in glucose homeostasis and insulin secretion in pancreatic β cells. The silencing of this phosphatase in the INS-1 832/13 cell line results in a significant increase in ATP production and insulin secretion [2]. These results were further explained, based on the discovery that PTPMT1 is able to dephosphorylate and, consequently, inactivate succinate dehydrogenase, an enzyme that participates in the reaction of succinate to fumarate, and is probably important in the regulation of this enzyme in the Krebs cycle [4].
Disease
Relevance
Structural highlights
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Pagliarini DJ, Worby CA, Dixon JE. A PTEN-like phosphatase with a novel substrate specificity. J Biol Chem. 2004 Sep 10;279(37):38590-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M404959200. Epub 2004 , Jul 9. PMID:15247229 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M404959200