SAGA-associated factor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: <StructureSection load='3mhs' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of SGF11 in the SAGA complex with Sus1, SGF73 and UB8P (PDB entry 3mhs)' scene=''> '''SAGA-associated fact...) |
|||
| (14 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
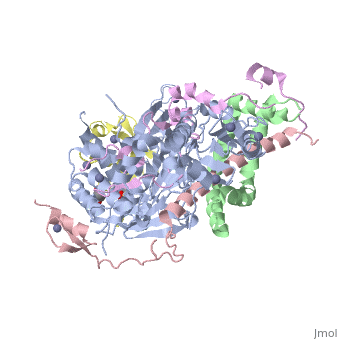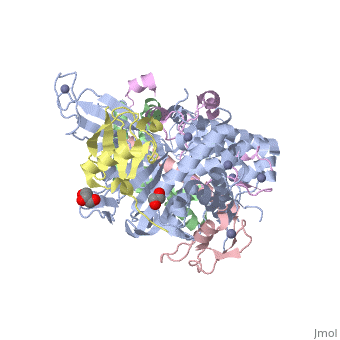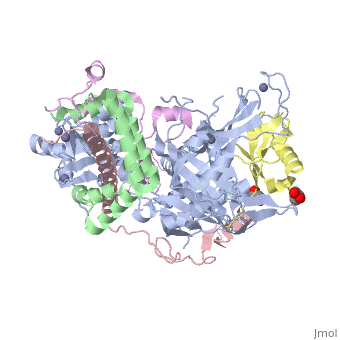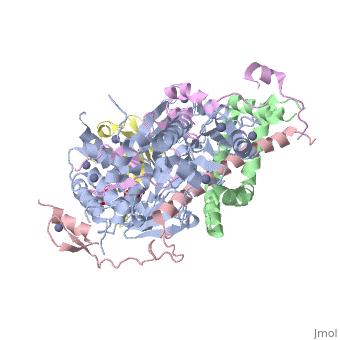
| - | + | <StructureSection load='3mhs' size='340' side='right' caption='Structure of SGF11 (pink) in the SAGA complex with Sus1 (green) , SGF73 (magenta), ubiquitin (yellow), UB8P (grey), glycerol and Zn+2 ions (grey) (PDB entry [[3mhs]])' scene=''> | |
| - | <StructureSection load='3mhs' size=' | + | |
| - | '''SAGA-associated factor''' (SGF) is part of the coactivator complex SAGA ( | + | '''SAGA-associated factor''' (SGF) is part of the coactivator complex SAGA ('''S'''pt-'''A'''da-'''G'''cn5-'''A'''cetyl transferase) which facilitates transcription of stress-activated genes<ref>PMID:19731963</ref>.<br /> |
| + | * '''SGF11''' is required for the deubiuqitination of histone H2B and for the maintenance of steady-state H3 methylation level.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''SGF29''' binds methylated lysine of histone H3 and is involved in transcriptional regulation<ref>PMID:23894581</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''SGF73''' is required for the assembly of RITS complex in yeast<ref>PMID:26443059</ref>.<br />. | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of SAGA-associated factor== | ==3D structures of SAGA-associated factor== | ||
| - | == | + | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} |
| + | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| + | |||
| + | *SGF11 | ||
| - | [[2lo2]] – ySGF zinc finger domain – yeast – NMR<br /> | + | **[[2lo2]] – ySGF zinc finger domain – yeast – NMR<br /> |
| - | [3kik]], [[3kjl]] – ySGF Sus1-binding domain + Sus1 <br /> | + | **[[3kik]], [[3kjl]] – ySGF Sus1-binding domain + Sus1 <br /> |
| - | [[3mhh]], [[3m99]], [[4fip]], [[4fjc]], [[4fk5]] – | + | **[[3mhh]], [[3m99]], [[4fip]], [[4fjc]], [[4fk5]], [[4wa6]] – ySGF11 + SGF73 + yUBP8 + SUS1 <br /> |
| - | [[3mhs]] – yUBP8 + | + | **[[3mhs]], [[6aqr]] – ySGF11 + SGF73 + yUBP8 + SUS1 + ubiquitin<br /> |
| + | **[[4w4u]], [[6aqr]] – ySGF11 + ySGF73 + SUS1 + ubiquitin carboxyl terminal hydrolase<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4zux]] – SGF11 + SGF73 + yUBP8 + SUS1 + ubiquitin + histone H3.2, H4, H2A, H2B + DNA<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6tbm]] – KpSGF + TBP + SPT20 + SPT8 + transcription coactivator HFI1 + TFIID + polyubiquitin + SUS1 + transcription-associated protein – ''Komagataela phaffii'' - Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| - | + | *SGF29 | |
| - | [[3me9]], [[3mea]], [[3met]], [[3meu]], [[3mev]], [[3mew]], [[3mp1]], [[3mp6]] – hSGF tudor domain + histone H3 peptide – human<br /> | + | **[[3me9]], [[3mea]], [[3met]], [[3meu]], [[3mev]], [[3mew]], [[3mp1]], [[3mp6]], [[5c0m]] – hSGF tudor domain + histone H3 peptide – human<br /> |
| - | [[3lx7]], [[3mp8]] - hSGF tudor domain <br /> | + | **[[3lx7]], [[3mp8]] - hSGF tudor domain <br /> |
| + | **[[5c0m]] - hSGF tudor domain + CABRA containing peptide <br /> | ||
| - | + | *SGF73 | |
| - | [[2lo3]] – ySGF zinc finger domain – NMR<br /> | + | **[[6t9i]], [[6t9k]], [[6t9l]] – ySGF in transcription coactivator SAGA – Cryo EM<br /> |
| + | **[[2lo3]] – ySGF zinc finger domain – NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3mhh]], [[3m99]], [[4fip]], [[4fjc]], [[4fk5]], [[4wa6]] – ySGF73 + yUBP8 + Sus1 <br /> | ||
| + | **[[3mhs]] – ySGF73 + yUBP8 + Sus1 + ubiquitin<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6tb4]] – KpSGF + TBP + SPT20 + transcription coactivator HFI1 + TFIID + ADA3 + transcription-associated protein - Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | [[Category: Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of SAGA-associated factor
Updated on 09-March-2022
References
- ↑ Mischerikow N, Spedale G, Altelaar AF, Timmers HT, Pijnappel WW, Heck AJ. In-depth profiling of post-translational modifications on the related transcription factor complexes TFIID and SAGA. J Proteome Res. 2009 Nov;8(11):5020-30. doi: 10.1021/pr900449e. PMID:19731963 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/pr900449e
- ↑ Schram AW, Baas R, Jansen PW, Riss A, Tora L, Vermeulen M, Timmers HT. A dual role for SAGA-associated factor 29 (SGF29) in ER stress survival by coordination of both histone H3 acetylation and histone H3 lysine-4 trimethylation. PLoS One. 2013 Jul 23;8(7):e70035. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070035. Print 2013. PMID:23894581 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070035
- ↑ Deng X, Zhou H, Zhang G, Wang W, Mao L, Zhou X, Yu Y, Lu H. Sgf73, a subunit of SAGA complex, is required for the assembly of RITS complex in fission yeast. Sci Rep. 2015 Oct 7;5:14707. doi: 10.1038/srep14707. PMID:26443059 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/srep14707