We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
GLUT1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| + | |||
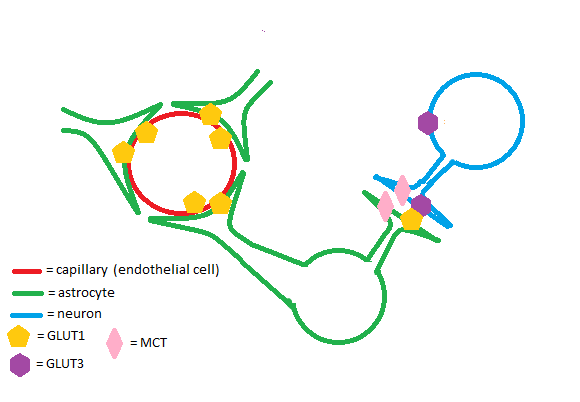
The GLUT1 is an insulin-independent glucose transporter expressed by all cells in the body to maintain adequate baseline glucose uptake. Tissues that express GLUT1 at high concentrations include (but are not limited to): the placenta and fetal tissues, epithelial cells of the retina and mammary gland, and the brain.<ref>PMID:31942129L</ref> The GLUT1 transporter works synergistically with the GLUT3 transporter in the brain. Astrocytes and endothelial cells of brain capillaries primarily express GLUT1; neurons primarily express GLUT3. GLUT1 has a relatively high Km and is upregulated in times of hypoglycemia in the brain to ensure adequate glucose uptake. GLUT3 has a low Km to ensure a steady supply of glucose for neurons even when extracellular glucose concentrations are low.<ref>PMID:32789766</ref> | The GLUT1 is an insulin-independent glucose transporter expressed by all cells in the body to maintain adequate baseline glucose uptake. Tissues that express GLUT1 at high concentrations include (but are not limited to): the placenta and fetal tissues, epithelial cells of the retina and mammary gland, and the brain.<ref>PMID:31942129L</ref> The GLUT1 transporter works synergistically with the GLUT3 transporter in the brain. Astrocytes and endothelial cells of brain capillaries primarily express GLUT1; neurons primarily express GLUT3. GLUT1 has a relatively high Km and is upregulated in times of hypoglycemia in the brain to ensure adequate glucose uptake. GLUT3 has a low Km to ensure a steady supply of glucose for neurons even when extracellular glucose concentrations are low.<ref>PMID:32789766</ref> | ||
| + | [[Image:Blood-brain_barrier.png]] | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Revision as of 20:31, 25 April 2022
Structure
| |||||||||||
References
Pragallapati S, Manyam R. Glucose transporter 1 in health and disease. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2019 Sep-Dec;23(3):443-449. doi: 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_22_18. PMID: 31942129; PMCID: PMC6948067.
Koepsell H. Glucose transporters in brain in health and disease. Pflugers Arch. 2020 Sep;472(9):1299-1343. doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02441-x. Epub 2020 Aug 13. PMID: 32789766; PMCID: PMC7462931.
Asano T, Katagiri H, Takata K, Lin JL, Ishihara H, Inukai K, Tsukuda K, Kikuchi M, Hirano H, Yazaki Y, et al. The role of N-glycosylation of GLUT1 for glucose transport activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24632-6. PMID: 1761560.