We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
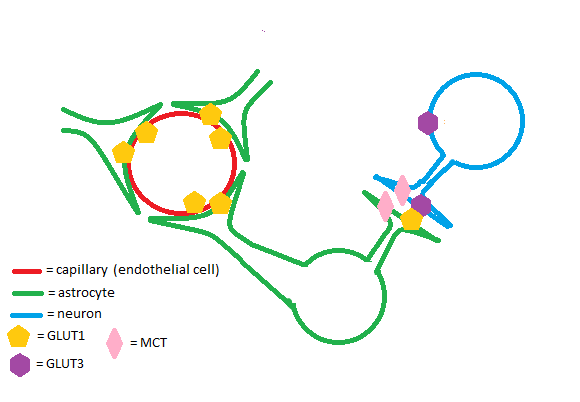
GLUT1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
The GLUT1 transporter is highly expressed in both the placenta and the developing embryo/fetus.<ref>PMID:30593896</ref> During pregnancy, there is no significant fetal gluconeogenesis in humans.<ref>PMID:31175930</ref> High GLUT1 expression in the fetoplacental tissues ensures that the fetus receives a steady supply of glucose. | The GLUT1 transporter is highly expressed in both the placenta and the developing embryo/fetus.<ref>PMID:30593896</ref> During pregnancy, there is no significant fetal gluconeogenesis in humans.<ref>PMID:31175930</ref> High GLUT1 expression in the fetoplacental tissues ensures that the fetus receives a steady supply of glucose. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Retina=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Studies on mice have shown that GLUT1 knockout leads to photoreceptor cell death; cone cells are less affected than rod cells.<ref>PMID:30462537</ref> | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Revision as of 18:52, 28 April 2022
Facilitated Glucose Transporter 1, Solute Carrier Family 2, Homo sapiens
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Pragallapati S, Manyam R. Glucose transporter 1 in health and disease. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2019 Sep-Dec;23(3):443-449. doi:, 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_22_18. PMID:31942129 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_22_18
- ↑ Koepsell H. Glucose transporters in brain in health and disease. Pflugers Arch. 2020 Sep;472(9):1299-1343. doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02441-x. Epub, 2020 Aug 13. PMID:32789766 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00424-020-02441-x
- ↑ Illsley NP, Baumann MU. Human placental glucose transport in fetoplacental growth and metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020 Feb 1;1866(2):165359. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.12.010. Epub 2018 Dec 26. PMID:30593896 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.12.010
- ↑ Borges MH, Pullockaran J, Catalano PM, Baumann MU, Zamudio S, Illsley NP. Human placental GLUT1 glucose transporter expression and the fetal insulin-like growth factor axis in pregnancies complicated by diabetes. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019 Sep 1;1865(9):2411-2419. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.06.002. Epub 2019 Jun 5. PMID:31175930 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.06.002
- ↑ Swarup A, Samuels IS, Bell BA, Han JYS, Du J, Massenzio E, Abel ED, Boesze-Battaglia K, Peachey NS, Philp NJ. Modulating GLUT1 expression in retinal pigment epithelium decreases glucose levels in the retina: impact on photoreceptors and Muller glial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019 Jan 1;316(1):C121-C133. doi:, 10.1152/ajpcell.00410.2018. Epub 2018 Nov 21. PMID:30462537 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00410.2018
- ↑ Macheda ML, Rogers S, Best JD. Molecular and cellular regulation of glucose transporter (GLUT) proteins in cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2005 Mar;202(3):654-62. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20166. PMID:15389572 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcp.20166
- ↑ Oh S, Kim H, Nam K, Shin I. Glut1 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion by regulating epidermal growth factor receptor and integrin signaling in triple-negative breast cancer cells. BMB Rep. 2017 Mar;50(3):132-137. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.3.189. PMID:27931517 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.3.189
- ↑ Asano T, Katagiri H, Takata K, Lin JL, Ishihara H, Inukai K, Tsukuda K, Kikuchi M, Hirano H, Yazaki Y, et al.. The role of N-glycosylation of GLUT1 for glucose transport activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24632-6. PMID:1761560