Acetylcholinesterase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[Image:small_wh_ray0001.gif|left|150px]]<br /> | [[Image:small_wh_ray0001.gif|left|150px]]<br /> | ||
'''Acetylcholinesterase''' (AChE) is key enzyme in the nervous system of animals. By rapid hydrolysis of the neurotransmitter, [[Acetylcholine|acetylcholine]] (ACh), AChE terminates neurotransmission at cholinergic synapses. It is a very fast enzyme, especially for a serine hydrolase, functioning at a rate approaching that of a diffusion-controlled reaction. AChE inhibitors are among the key drugs approved by the FDA for management of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The powerful toxicity of organophosphorus (OP) poisons is attributed primarily to their potent AChE inhibitors. | '''Acetylcholinesterase''' (AChE) is key enzyme in the nervous system of animals. By rapid hydrolysis of the neurotransmitter, [[Acetylcholine|acetylcholine]] (ACh), AChE terminates neurotransmission at cholinergic synapses. It is a very fast enzyme, especially for a serine hydrolase, functioning at a rate approaching that of a diffusion-controlled reaction. AChE inhibitors are among the key drugs approved by the FDA for management of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The powerful toxicity of organophosphorus (OP) poisons is attributed primarily to their potent AChE inhibitors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also [[Acetylcholinesterase (Hebrew)]] | ||
== Key Enzyme in the Nervous System == | == Key Enzyme in the Nervous System == | ||
| Line 9: | Line 11: | ||
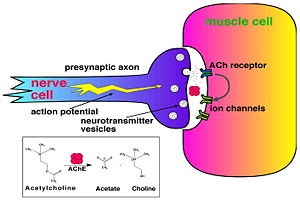
[[Image:Synapse_Schematic.jpg|thumb|Cholinergic Synapse|300px|left]] | [[Image:Synapse_Schematic.jpg|thumb|Cholinergic Synapse|300px|left]] | ||
| - | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acetylcholinesterase Acetylcholinesterase] [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrolysis hydrolysizes] the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neurotransmitter neurotransmitter] [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acetylcholine acetylcholine] <scene name='2ace/Cv/2'>(ACh)</scene>, producing <scene name='2ace/Cv/3'>choline and an acetate</scene> group. ACh directly binds <scene name='22/22/Cv/1'>Ser200</scene> (via its [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nucleophile nucleophilic] Oγ atom) within the <scene name='2ace/Cv/5'>catalytic triad (Ser200, His440, and Glu327)</scene> (ACh/''Tc''AChE structure [[2ace]]). The residues <scene name='2ace/Cv/6'>Trp84 and Phe330</scene> are also important in the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ligand ligand] recognition <ref name="Raves">PMID:8989325</ref>. After this binding acetylcholinesterase <scene name='2ace/Cv/7'>hydrolysizes</scene> ACh. | + | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acetylcholinesterase Acetylcholinesterase] [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrolysis hydrolysizes] the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neurotransmitter neurotransmitter] [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acetylcholine acetylcholine] <scene name='2ace/Cv/2'>(ACh)</scene>, producing <scene name='2ace/Cv/3'>choline and an acetate</scene> group. ACh directly binds <scene name='22/22/Cv/1'>Ser200</scene> (via its [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nucleophile nucleophilic] Oγ atom) within the <scene name='2ace/Cv/5'>catalytic triad (Ser200, His440, and Glu327)</scene> (ACh/''Tc''AChE structure [[2ace]]). The residues <scene name='2ace/Cv/6'>Trp84 and Phe330</scene> are also important in the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ligand ligand] recognition <ref name="Raves">PMID:8989325</ref>. After this binding acetylcholinesterase <scene name='2ace/Cv/7'>hydrolysizes</scene> ACh. <br /> |
| + | See also [[Acetylcholinesterase with acetylcholine]]. | ||
== Treatment of Alzheimer's disease == | == Treatment of Alzheimer's disease == | ||
| - | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer's_disease Alzheimer's disease] (AD) is a disorder that attacks the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Central_nervous_system central nervous system] through progressive degeneration of its neurons. AD occurs in around 10% of the elderly and, as yet, there is no known cure. Patients with this disease develop [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dementia dementia] which becomes more severe as the disease progresses. It was suggested that symptoms of AD are caused by decrease of activity of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholinergic cholinergic] [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neocortex neocortical] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hippocampus hippocampal] neurons. Treatment of AD by ACh precursors and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholinergic cholinergic] [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Agonist agonists] was ineffective or caused severe side effects. ACh hydrolysis by AChE causes termination of cholinergic neurotransmission. Therefore, compounds which inhibit AChE might significantly increase the levels of ACh depleted in AD. Indeed, it was shown that [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acetylcholinesterase_inhibitor AChE inhibitors] improve the cognitive abilities of AD patients at early stages of the disease development. The way in which the various cholinesterase inhibitors interact with AChE can be see at [[Acetylcholinesterase: Treatment of Alzheimer's disease]].<br /> | + | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer's_disease Alzheimer's disease] (AD) is a disorder that attacks the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Central_nervous_system central nervous system] through progressive degeneration of its neurons. AD occurs in around 10% of the elderly and, as yet, there is no known cure. Patients with this disease develop [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dementia dementia] which becomes more severe as the disease progresses. It was suggested that symptoms of AD are caused by decrease of activity of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholinergic cholinergic] [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neocortex neocortical] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hippocampus hippocampal] neurons. Treatment of AD by ACh precursors and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholinergic cholinergic] [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Agonist agonists] was ineffective or caused severe side effects. ACh hydrolysis by AChE causes termination of cholinergic neurotransmission. Therefore, compounds which inhibit AChE might significantly increase the levels of ACh depleted in AD. Indeed, it was shown that [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acetylcholinesterase_inhibitor AChE inhibitors] improve the cognitive abilities of AD patients at early stages of the disease development. The way in which the various cholinesterase inhibitors interact with AChE can be see at:<br /> |
| + | *[[Acetylcholinesterase: Treatment of Alzheimer's disease]].<br /> | ||
| + | *[[Acetylcholinesterase complexed with N-9-(1',2',3',4'-tetrahydroacridinyl)-1,8-diaminooctane]].<br /> | ||
== Organophosphorus acid anhydride nerve agents == | == Organophosphorus acid anhydride nerve agents == | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Eran Hodis, Clifford Felder, Jaime Prilusky, Harry Greenblatt, Yechun Xu