is a multi-subunit protease complex which cleaves many transmembrane proteins; it is known as an intramembrane protease. γ-secretase is highly studied in its cleavage of amyloid precursor protein (APP) releasing beta-amyloid (Aβ peptides) which further oligomerize to form neurofibrillary tangles and plaques in Alzheimer’s disease.[1]
Background
The family of intramembrane-cleaving proteases (i-CLiPs) contains the presenilin family of aspartyl proteases, zinc metalloprotease, site-2 protease family, rhomboid family of serine proteases, and γ-secretase. All i-CLiPs enzymatically cleave their substrates within the plane of the lipid bilayer in a process termed regulated intramembrane proteolysis. A large function of γ-secretase is its involvement in intramembranous proteolysis of type I membrane proteins. It cleaves numerous functionally important proteins, such as Notch, E-cadherin, ErbB4, CD44, tyrosinase, TREM2 and Alcadein, suggesting the participation of γ-secretase in a vast range of biological activities. The best-studied γ-secretase substrates are APP for its roles in Alzheimer’s Disease, and Notch for its importance in development and cell fate determination.[2]
GS recognizes and catalyzes the cleavage of its substrate into 3 residue segments.[3] Products of initial APP cleavage include the 48-residue peptide Aβ48 or the 49-residue peptide Aβ49. GS then cleaves these peptides into a variety of peptide fragments separated by 3 residues; Aβ48 is cleaved into Aβ45, Aβ42, and Aβ38; Aβ49 is cleaved into Aβ46, Aβ43, and Aβ40. Aβ products are connected to neurological diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), with varying length peptide products showing different disease symptoms. The connection between GS and AD has made GS a popular drug target. Although various inhibitors of GS have been identified, no inhibitors have been clinically approved for treating AD, as GS is also linked to important neurological functions and inhibition of these GS functions leads to dangerous side effects upon inhibition.[4]
Structure of Gamma Secretase Complex
γ-secretase has been identified as an aspartyl protease accountable for cleaving over 90 integral membrane proteins after they have undergone ectodomain shedding. GS has been characterized as a high molecular weight complex that consists of four essential subunits in a 1:1:1:1 heterodimer[5]: , , , and .[6]These subunits are stabilized as functional GS by hydrophobic interactions and 4 phosphatidylcholines.These have interfaces between: PS1 and PEN-2, APH-1 and PS1, APH-1 and NCT.
PSs play a very significant role in AD and is considered a vital catalytic subunit in γ-secretase. PS are multi-transmembrane proteins with nine transmembrane helixes; it is assumed the amino-terminus is located in the cytosol while the carboxyl-terminus is exposed to the luminal/extracellular space. Functional PS requires endoproteolytic cleavage between TM6 and TM7 which generates a 27–28 kDa amino-terminal fragment (NTF) and a 16–17 kDa carboxyl-terminal fragment (CTF). [2] The two in PS1 and PS2 (D257 in TM 6 and at D385 in TM 7) play crucial roles in intramembranous cleavage and AD plaque formation; substitutions of these residues reduces cleavage of APP and Notch1 proteins.[7] PS, NTF, and CTF bind to form stable and active PS heterodimers at a 1:1 stoichiometry. [2]
The remaining (NCT, APH-1, PEN-2) help with stabilizing GS by forming a mature enzyme. NCT contains a large extracellular (or ectodomain) domain, transmembrane helix, and smaller cytoplasmic domain.[5]The ectodomain of NCT recognizes and binds to the amino-terminal stubs of previously cleaved transmembrane proteins. is important to substrate recognition and binding. APH-1 aids the formation of a pre-complex, which interacts with PS1 or PS2[7]; it contains two different isoforms from two paralogous genes on chromosomes 1 (APH-1A) and 15 (APH-1B). also serves as a scaffold for anchoring and supporting the flexible conformational changes of PS1. While PEN-2 works in enzyme maturation[5]; it enters the formed complex to initiate the cleavage of PS1 or PS2 to form an N-terminal 28-kDa fragment and a C-terminal 18-kDa fragment, both APH-1 and PEN-2 are critical to the γ-secretase complex.[7] Activation of the active site is dependent on the binding of . PEN-2 is also important in maturation of the enzyme.[8] The γ-secretase complex has a molecular weight of approximately 170 kDa, with an additional 30–70 kDa derived from NCT glycosylation, reaching a total size of about 230 kDa with 19 TMs.[2]
Function
Once all of the subunits are present, the complex must be correctly assembled for γ-secretase to function properly. The complex is first assembled in the endoplasmic reticulum.
The events leading to the formation of a mature γ-secretase complex start from the formation of an initial scaffolding complex composed of APH-1 and NCT. Once the scaffold is created, the full-length PS can attach itself.[1]The proximal C-terminus of the PS holoprotein binds to the APH-1-NCT subcomplex by interacting with the TM domain of NCT. Following PS binding, PEN-2 is incorporated into the complex by interacting with TM4 of PS. At the final step, the loop domain between TM6 and TM7 of PS is cleaved by endoproteolysis. Alternatively, the APH-1-NCT subcomplex may bind directly to a cognate PS1-PEN-2 structure to generate the mature γ-secretase complex.[2]The active complex is then shuttled to the Golgi where it is glycosylated. Only after the assembly of all and the glycosylation will GS become active.[5]
Alzheimer's Pathway
On the cell surface, amyloid precursor protein (APP) can be proteolyzed directly by α-secretase followed by γ-secretase, a process that does not generate Aβ, or APP can be reinternalized in clathrin-coated pits into another endosomal compartment containing the proteases BACE1 and γ-secretase resulting in the production of Aβ. FRET analysis indicates that γ-secretase activity is present on the cell surface, where it complements α-secretase activity, and in endosomal compartments, where it complements BACE1 activity.[7] The cleavage of various substrates appears to be dependent on the subcellular compartment; APP is mainly cleaved in the TGN and early endosomal domains thus, a disturbance in the localization of the γ-secretase complex may play some role in abnormal Aβ generation and AD pathogenesis.[6]
The initial cleavage of APP by α- or β-secretase, results in membrane-bound C-terminal fragments of APP (APP αCTF and βCTF). If γ-secretase cleaves αCTF then p83 is formed, however, if γ-secretase cleaves βCTF Aβ is generated. The p83 fragment is rapidly degraded and widely believed to have a negligible function, whereas is neurotoxic.[2] γ-secretase-mediated cleavage is unique in that the cleavage takes place within the transmembrane domain, though the exact site can vary. γ-cleavage yields Aβ40 and Aβ42 which is the more amyloidogenic species; in addition, it may release intracellular domain of APP (AICD). Recent data has shown that PS/γ-secretase also mediates ζ-site cleavage (Aβ46) and ε-site cleavage (Aβ49)[6]; the existence of different Aβ species, including the shorter Aβ38 fragments suggests that γ-secretase cleaves APP in a sequential manner, first at the ε-site, followed by the ζ-site, and the γ-site.2 Upon Aβ formation, Aβ is then dumped into the extracellular space following vesicle recycling or degraded in lysosomes.[7]
Alzheimer's Disease
Although the majority of Aβ is secreted out of the cell, Aβ can be generated in several subcellular compartments within the cell, such as the ER, Golgi/TGN, and endosome/lysosome. The extracellular Aβ is degraded while the intracellular Aβ may accumulate within neurons and contribute to the Alzheimer's Disease. Patients that exhibit mild cognitive impairment are more prone to developing Alzheimer's Disease if they are found to contain intraneuronal Aβ immunoreactivity in the hippocampal and entorhinal cortical regions. Another effect of Aβ aggregation within the cell is disruption of the vesicular membrane leading to its pathological effect. Studies done on familial AD (FAD) mutations consistently show increases in the ratio of Aβ42/40, suggesting that elevated levels of Aβ42 relative to Aβ40 is critical for AD pathogenesis, probably by providing the core for Aβ assembly into oligomers, fibrils, and amyloidogenic plaques.[6] In addition to generating Aβ, γ-secretase cleavage of APP also generates an APP intracellular domain (AICD) within the cell which can induce apoptosis. AICD has been found to possess transcriptional transactivation activity and can regulate the transcription of multiple genes including APP, GSK-3b, KAI1, neprilysin, BACE1, p53, EGFR, and LRP1, additionally, ACID can sensitize neurons to toxic stimuli. [2] However, as the intracellular domain of APP, one important function of AICD is to facilitate the interaction of APP with various cytosolic factors that regulate APP's intracellular trafficking and/or signal transduction function. Interestingly, it seems that AICD-mediated APP interaction with different factors is controlled by the phosphorylation state of AICD.[6]
Relevance
There are 32 APP, 179 PSEN1 (presenilin 1 gene locus), and 14 PSEN2 gene mutations that result in early-onset, autosomal dominant, fully penetrant AD. In APP, mutations cluster around the γ-secretase cleavage site, although the most famous APP mutation (APP-swe) causes a change in amino acids adjacent to the BACE1 cleavage site.[7] AD-related loci are found on chromosome 1 and chromosome 14; two homologous genes, PSEN1(encoding PS1) on chromosome 14 and PSEN2 (encoding PS2) on chromosome 1.[2] PSEN gene mutations (which gives rise to proteins presenilin, PS1 and PS2) predominantly alter the amino acids in their nine transmembrane domains. The common thread to all these mutations is that they increase production of the less soluble and more toxic Aβ42 relative to Aβ40.[7] Familial Alzheimer’s disease (FAD) is commonly caused by mutations in the PSEN1 gene. [9] These familial mutations lead to the heritable form of Alzheimer’s disease.[5]
Structural highlights
The structural information of the γ-secretase complex has been primarily obtained by electron microscopy analysis with a maximum resolution of 12 Å, revealing a with several extracellular domains, three cavities, and a potential substrate-binding surface groove in the TM region. The most recent sturcutre of the γ-secretase complex was visualized by a cryo-electron microscopy with a resolution of 4.5 Å. γ-secretase exhibits a horseshoe-shaped structure with 19 TMs and a bilobed ectodomain which is Nicastrin, "the extracellular domain of Nicastrin contains a large lobe and a small lobe." The large lobe of Nicastrin thought to be responsible for substrate recognition, associates with the small lobe through a at the center. The horseshoe shape is described as having a "thick" end, where PS1 and PEN-2 are located, and "thin" end, where APH-1 and Nicastrin are located. At the thick end, PEN-2 spans the membrane twice as its N- and C-terminal domains face the lumen of the ER. However, at the thin end, APH-1 contains seven TM domains with the N-terminal domain facing the extracellular space and the C-terminal domain facing the cytosol. Further work is required to elucidate structural details of other γ-secretase components at the atomic level.[2] However, strong evidence suggests that the γ-secretase complex resides primarily in the ER, Golgi/TGN, endocytic and intermediate compartments, most of which (except the TGN) are not major subcellular localizations for APP.[6]
Substrate Structure
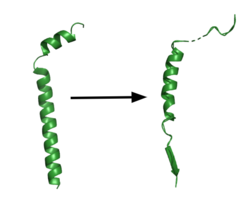
Figure 1. APP fragment conformational change in gamma secretase. APP bound to GS undergoes a conformational change. The free state consists of 2 helices. Once bound to GS, the N-terminal helix unfolds into a coil and the C-terminal helix unwinds into a β-strand. The β-strand of APP forms a β-sheet with PS1. Cleavage by the protease occurs between the helix and the β-strand.
[4] GS has been structurally characterized in the presence of both APP and Notch substrates. In each of these structures, the substrate bound in a similar location and underwent a similar structural transition upon binding to the active site of GS. Each substrate is composed of an N-terminal loop and a TM helix. The peptide substrate enters the enzyme by via the lid complex, and once in place, the TM helix of the substrate is anchored by . Upon binding to GS, the C-terminal extracellular helix of the substrate unwinds. The substrate's N-terminal end of the TM helix unwinds into a β-strand (Fig. 1). To differentiate substrates, the β-strand is often the main point of identification for the enzyme. Substrate binding induces a structural change in GS, creating two β-strands that form a β-sheet with the one β-strand of the substrate. This β-sheet is in close proximity with the active site, and guides the process of catalysis.[4]
Lid Complex
The is the first point of entry and recognition for the substrate. is located within the NCT subunit between Asn55 and Asn435. This lobe of NCT is divided into two separate subunits; the large and small lobes with Phe287 from the large lobe acting as a pivot between them. Phe287 is surrounded by of the small subunit. The congregation of hydrophobic residues in the small subunit composes a greasy pocket which provides an environment for easy structural movement. The lid consists of 5 aromatic residues, which are highly involved with stabilizing the closed conformation. This conformation is stabilized by . Once the substrate binds and the lid is opened, a charged, hydrophilic binding pocket is revealed. The pocket contains . The pocket is further involved with substrate binding and recognition once the lid is removed. The lid complex is relatively far away from the catalytic site of the enzyme in PS1 when inactive. Once a substrate binds, the enzyme undergoes a conformational change in which the rotation of the large lobe in relation to the small lobe reorients the substrate for cleavage, by aligning the pocket in NCT to the active site in PS1.[10]
Active Site
The is located between TM6 and TM7 of the PS1 subunit, which is mainly hydrophilic and disordered. Both TM6 and TM7 contribute an aspartate residue to the active site. These two aspartates, Asp257 and Asp385 are located approximately 10.6 A˚ apart when inactive.[10] Substrate recognition is controlled by the closely spaced PAL sequence of . GS becomes active upon substrate binding, when TM2 and TM6 each rotate about 15 degrees to more closely associate. Two β-strands are induced in PS1, creating an with the β-strand of the substrate.[4] The β-strand of the substrate interacts via main chain H-bonds , stabilizing the active site. hydrogen bond to each other and are located 6–7 Å away from the scissile peptide bond of the substrate, allowing catalysis to occur.[8] GS cleaves in 3 residue segments which is driven by the presence of three amino acid binding pockets in the active site.[3]
In APP, the cleavage site is between the helix and the N-terminal β-strand.[4] GS can cleave via different pathways, depending on its starting point, but the 2 most commonly used pathways produce Aβ48 and Aβ49.[3]. Tripeptide cleavage starting between results in Aβ48. Cleavage between yields Aβ49. The accumulation of these Aβ peptides has strong implications in Alzheimer's disease.[4]
3D structures of γ secretase
Updated on 12-March-2023
4r12 – hGS nicastrin component
2n7q, 2n7r – hGS nicastrin component transmembrane domain - NMR
5a63, 5fn5 – hGS APH-1A+PEN-2 subunits + nicastrin + presenilin – human – Cryo EM
4uis – hGS + lysozyme – Cryo EM
6iyc – hGS APH-1A+PEN-2 subunits + nicastrin + presenilin + amyloid-beta A4 protein – Cryo EM
5fn3, 5fn4 – hGS APH-1A+PEN-2 subunits + nicastrin + presenilin + poly-Ala – Cryo EM
6idf – hGS APH-1A+PEN-2 subunits + nicastrin + presenilin + notch 1 – Cryo EM
5fn2 – hGS APH-1A+PEN-2 subunits + nicastrin + presenilin + drug – Cryo EM
6lqg, 6lr4, 7c9i, 7d8x, 7y5t, 7y5x, 7y5z – hGS APH-1A+PEN-2 subunits + nicastrin + presenilin + inhibitor – Cryo EM
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-012351830-9/50024-X
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 Zhang X, Li Y, Xu H, Zhang YW. The gamma-secretase complex: from structure to function. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Dec 11;8:427. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00427., eCollection 2014. PMID:25565961 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2014.00427
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Bolduc DM, Montagna DR, Seghers MC, Wolfe MS, Selkoe DJ. The amyloid-beta forming tripeptide cleavage mechanism of gamma-secretase. Elife. 2016 Aug 31;5. doi: 10.7554/eLife.17578. PMID:27580372 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.17578
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 Zhou R, Yang G, Guo X, Zhou Q, Lei J, Shi Y. Recognition of the amyloid precursor protein by human gamma-secretase. Science. 2019 Feb 15;363(6428). pii: science.aaw0930. doi:, 10.1126/science.aaw0930. Epub 2019 Jan 10. PMID:30630874 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.aaw0930
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Carroll CM, Li YM. Physiological and pathological roles of the gamma-secretase complex. Brain Res Bull. 2016 Sep;126(Pt 2):199-206. doi:, 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.04.019. Epub 2016 Apr 28. PMID:27133790 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.04.019
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 Zhang YW, Thompson R, Zhang H, Xu H. APP processing in Alzheimer's disease. Mol Brain. 2011 Jan 7;4:3. doi: 10.1186/1756-6606-4-3. PMID:21214928 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1756-6606-4-3
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 O'Brien RJ, Wong PC. Amyloid precursor protein processing and Alzheimer's disease. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2011;34:185-204. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-061010-113613. PMID:21456963 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-061010-113613
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Yang G, Zhou R, Shi Y. Cryo-EM structures of human gamma-secretase. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2017 Oct;46:55-64. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2017.05.013. Epub, 2017 Jul 17. PMID:28628788 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2017.05.013
- ↑ Kelleher RJ 3rd, Shen J. Presenilin-1 mutations and Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jan 24;114(4):629-631. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1619574114. Epub 2017 Jan 12. PMID:28082723 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1619574114
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Bai XC, Yan C, Yang G, Lu P, Ma D, Sun L, Zhou R, Scheres SH, Shi Y. An atomic structure of human gamma-secretase. Nature. 2015 Aug 17. doi: 10.1038/nature14892. PMID:26280335 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature14892

