Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (19 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
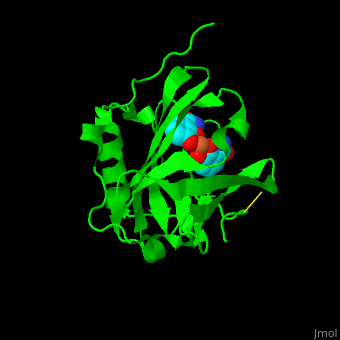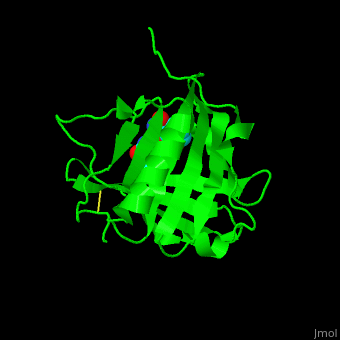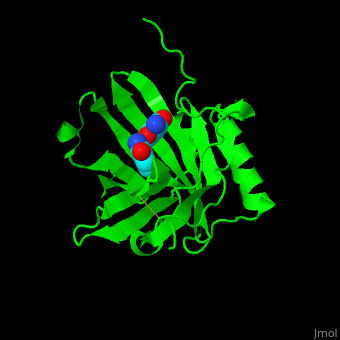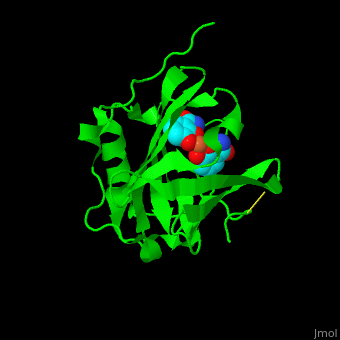
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of human neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin complex with Fe+3 ion and Siderophores (PDB code [[1x71]]).' scene='59/596433/Cv/1'> |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin''' (NGAL) or '''lipocalin-2''' is involved in innate immunity by sequestering bacterial iron and thus preventing bacterial growth. | + | '''Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin''' (NGAL) or '''lipocalin-2''' is involved in innate immunity by sequestering bacterial iron and thus preventing bacterial growth<ref>PMID:10475571</ref>. '''Lipocalin-1''' (Lcn1) or '''Tear lipocalin''' is a major protein in tears which binds diverse set of lipophilic molecules <ref>PMID:21791187</ref>. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| - | NGAL is secreted in high levels into the blood following acute kidney injury and thus can be used as a biomarker for it. | + | NGAL is secreted in high levels into the blood following acute kidney injury and thus can be used as a biomarker for it<ref>PMID:20921623</ref>. Lcn1 functions in tears includes their viscosity and it serves as biomarker for dry eyes. |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| + | <scene name='59/596433/Cv/4'>NGAL binds siderophores with cation-π interactions and an Fe+3 ion</scene> like carboxymycobactin or enterobactin<ref>PMID:15642259</ref>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin== | ==3D structures of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin== | ||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[1dfv]], [[1qqs]], [[3bx8]], [[6gqz]], [[6z6z]] – hNGAL – human <br /> | ||
| + | **[[3dtq]], [[5jr8]], [[5mhh]], [[6o5d]], [[6qmu]] – hNGAL (mutant)<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1ngl]] – hNGAL - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2k23]] – NGAL – rat - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3s26]] – mNGAL – mouse<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin complex | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[1l6m]] – hNGAL (mutant) + Fe+3<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5khp]], [[5kic]], [[5kid]] – hNGAL + actinide<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3pec]], [[3ped]] – hNGAL + Fe+3 + carboxymycobactin<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1x71]], [[1x89]], [[1x8u]] – hNGAL (mutant) + Fe+3 + carboxymycobactin<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3by0]], [[3cbc]], [[3cmp]], [[3hwd]], [[3hwf]], [[3hwg]], [[3i0a]], [[3k3l]], [[3t1d]], [[3u0d]], [6o5d]] – hNGAL (mutant) + Fe+3 + enterobactin<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4zfx]] – hNGAL + actinide + enterobactin<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4k19]] – hNGAL (mutant) + Fe+3 + fluvibactin<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3tf6]] – hNGAL (mutant) + Eu+2+ enterobactin<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6gr0]] – hNGAL + Ga+3 + oxidanyl derivative<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3fw4]], [[3fw5]] – hNGAL (mutant) + Fe+3 + catechol derivative<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5nkn]] – hNGAL + colchicine<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4zhc]] – hNGAL + actinide + pyridine derivative<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4zhd]] – hNGAL (mutant) + actinide + benzoyl derivative<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4zhf]], [[4zhg]], [[4zhh]] – hNGAL (mutant) + actinide +pyridine derivative<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3cmp]], [[3hwe]] – hNGAL (mutant) + Fe+3 + bishacam<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3dsz]] – hNGAL + Yt+3 + DTPA<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4iaw]], [[4iax]] – hNGAL (mutant) + Yt+3 + DTPA<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3tzs]] – hNGAL (mutant) + phenylurea<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4gh7]], [[5n47]], [[5n48]] – hNGAL (mutant) + fibronectin<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4qae]] – hNGAL (mutant) + hepcidin<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3bx7]] – hNGAL + CTLA-4<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6z2c]] – hNGAL + transition state analog<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4mvi]], [[4mvk]], [[4mvl]] – hNGAL (mutant) + beta-APP40<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6s8v]] – hNGAL + h4F2HC<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6sua]] – hNGAL (mutant) + m4F2HC<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3u9p]] – mNGAL + antibody<br /> | ||
| - | + | *Lipocalin-1 (Lcn1) | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | **[[4qaf]] – hLcn1 + VEGF-A<br /> | |
| + | **[[1xki]] – hLcn1 (mutant) + Zn<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3eyc]] – hLcn1 (mutant) + butanediol<br /> | ||
| - | [[1l6m]] – hNGAL (mutant) + Fe+3<br /> | ||
| - | [[3pec]] – hNGAL + Fe+3 + carboxymycobactin<br /> | ||
| - | [[1x71]], [[1x89]], [[1x8u]] – hNGAL (mutant) + Fe+3 + carboxymycobactin<br /> | ||
| - | [[3by0]], [[3cbc]], [[3cmp]], [[3hwd]], [[3hwf]], [[3hwg]], [[3i0a]], [[3k3l]], [[3t1d]] – hNGAL (mutant) + Fe+3 + enterobactin<br /> | ||
| - | [[3tf6]] – hNGAL (mutant) + Eu+2+ enterobactin<br /> | ||
| - | [[3fw4]], [[3fw5]] – hNGAL (mutant) + Fe+3 + catechol derivative<br /> | ||
| - | [[3cmp]], [[3hwe]] – hNGAL (mutant) + Fe+3 + bishacam<br /> | ||
| - | [[3dsz]] – hNGAL + Yt+3 + DTPA<br /> | ||
| + | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin
Updated on 16-July-2023
References
- ↑ Friedl A, Stoesz SP, Buckley P, Gould MN. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in normal and neoplastic human tissues. Cell type-specific pattern of expression. Histochem J. 1999 Jul;31(7):433-41. PMID:10475571
- ↑ Dartt DA. Tear lipocalin: structure and function. Ocul Surf. 2011 Jul;9(3):126-38. PMID:21791187
- ↑ Viau A, El Karoui K, Laouari D, Burtin M, Nguyen C, Mori K, Pillebout E, Berger T, Mak TW, Knebelmann B, Friedlander G, Barasch J, Terzi F. Lipocalin 2 is essential for chronic kidney disease progression in mice and humans. J Clin Invest. 2010 Nov;120(11):4065-76. doi: 10.1172/JCI42004. PMID:20921623 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/JCI42004
- ↑ Holmes MA, Paulsene W, Jide X, Ratledge C, Strong RK. Siderocalin (Lcn 2) also binds carboxymycobactins, potentially defending against mycobacterial infections through iron sequestration. Structure. 2005 Jan;13(1):29-41. PMID:15642259 doi:10.1016/j.str.2004.10.009