S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (21 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
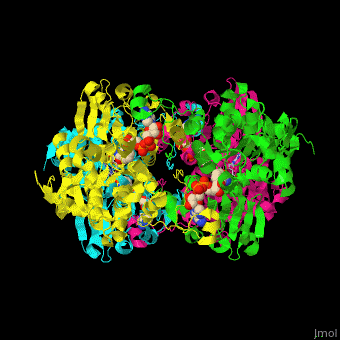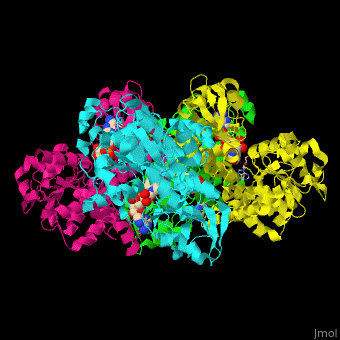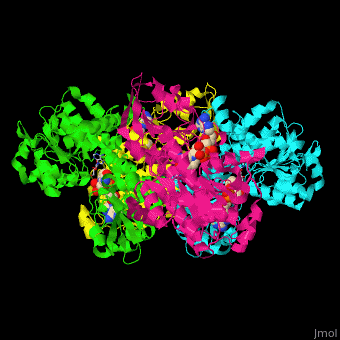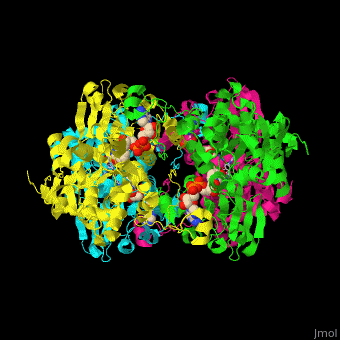
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of rat S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase tetramer complex with NAD and adenine (PDB entry [[1xwf]])' scene='55/552186/Cv/1'> |
| - | + | == Function == | |
| - | '''S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase''' (AHCH) converts S-adenosylhomocysteine (AdoHcy) to L-homocysteine and adenosine. AHCH uses NAD+ as cofactor. AHCH is an essential enzyme in processes like transmethylation, trans-sulfuration and purine metabolism. | + | '''S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase''' (AHCH) converts S-adenosylhomocysteine (AdoHcy) to L-homocysteine and adenosine. AHCH uses NAD+ as cofactor. AHCH is an essential enzyme in processes like transmethylation, trans-sulfuration and purine metabolism<ref>PMID:15488656</ref>. |
| + | |||
| + | == Disease == | ||
| + | AHCH deficiency causes a genetic disorder of methionine metabolism<ref>PMID:15024124</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Structural highlights == | ||
| + | The biological assembly of rat S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase is <scene name='55/552186/Cv/6'>homotetramer</scene>. AHCH structure contains <scene name='55/552186/Cv/7'>3 domains: catalytic, NAD-binding and C-terminal domain</scene>. The <scene name='55/552186/Cv/8'>active site is located in a cleft between the catalytic domain and the NAD-binding domain and it contains the cofactor NAD and the product adenine</scene><ref>PMID:16061414</ref>. | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase== | ==3D structures of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase== | ||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| + | |||
| + | *S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[1ky4]] – rAHCH + NAD - rat<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[1ky5]] – rAHCH (mutant) + NAD <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[1b3r]] – rAHCH catalytic domain + NAD <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[1a7a]] – hAHCH + NAD – human<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3gvp]] – hAHCH SAHH-like domain + NAD <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3d64]] – BpAHCH + NAD – ''Burkholderia pseudmallei''<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3x2f]] – AHCH + NADH – ''Thermotoga maritima''<BR /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase complex with adenosine derivatives | ||
| - | [[ | + | **[[1d4f]], [[1xwf]] – rAHCH (mutant) + NAD + adenosine<BR /> |
| - | [[ | + | **[[1k0u]], [[2h5l]] – rAHCH + NAD + adenosine analog<BR /> |
| - | [[ | + | **[[1li4]], [[3nj4]] – hAHCH + NAD + adenosine derivative<BR /> |
| - | [[ | + | **[[1v8b]] – AHCH + NAD + adenosine – ''Plasmodium falciparum''<BR /> |
| - | [[ | + | **[[3dhy]], [[2ziz]], [[2zj0]], [[2zj1]] – MtAHCH + NAD + adenosine derivative – ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''<BR /> |
| + | **[[3ce6]] – MtAHCH + NAD + adenosine<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3glq]] – BpAHCH + NAD + adenosine derivative <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3n58]] – AHCH + NAD + adenosine – ''Brucella melitensis''<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3ond]] – lAHCH + NAD + adenosine – lupin<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3one]] – lAHCH + NAD + adenine <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3onf]] – lAHCH + NAD + adenosine derivative <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[5m66]] – BeAHCH + NAD + adenosine – ''Bradyrhizobium elkanii''<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[5m5k]] – BeAHCH + NAD + adenosine + cordycepin<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[5m67]] – BeAHCH + NAD + adenosine + deoxyadenine<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3g1u]] – AHCH + NAD + adenosine – ''Leishmania major''<BR /> | ||
| - | + | *S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase other complexes | |
| - | [[ | + | **[[5w49]], [[5w4b]] – hAHCH + NAD + inhibitor<BR /> |
| - | + | }} | |
| - | + | == References == | |
| - | + | <references/> | |
| - | + | [[Category:Topic Page]] | |
| - | + | [[Category:One-carbon metabolism]] | |
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase
Updated on 14-November-2023
References
- ↑ Altintas E, Sezgin O. S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase, S-adenosylmethionine, S-adenosylhomocysteine: correlations with ribavirin induced anemia. Med Hypotheses. 2004;63(5):834-7. PMID:15488656 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2004.03.031
- ↑ Baric I, Fumic K, Glenn B, Cuk M, Schulze A, Finkelstein JD, James SJ, Mejaski-Bosnjak V, Pazanin L, Pogribny IP, Rados M, Sarnavka V, Scukanec-Spoljar M, Allen RH, Stabler S, Uzelac L, Vugrek O, Wagner C, Zeisel S, Mudd SH. S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase deficiency in a human: a genetic disorder of methionine metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Mar 23;101(12):4234-9. Epub 2004 Mar 15. PMID:15024124 doi:10.1073/pnas.0400658101
- ↑ Yamada T, Takata Y, Komoto J, Gomi T, Ogawa H, Fujioka M, Takusagawa F. Catalytic mechanism of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase: roles of His 54, Asp130, Glu155, Lys185, and Aspl89. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005 Nov;37(11):2417-35. PMID:16061414 doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2005.06.009
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Karsten Theis, Joel L. Sussman