TEM1-beta-Lactamase/beta-lactamase Inhibitor Protein (BLIP)
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (13 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
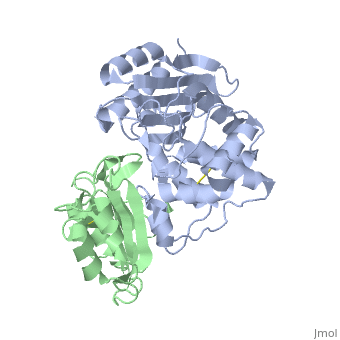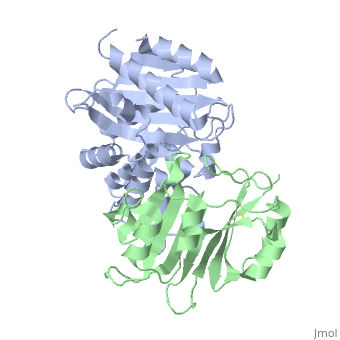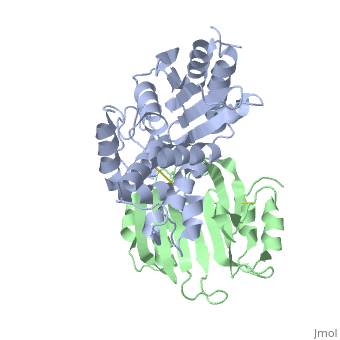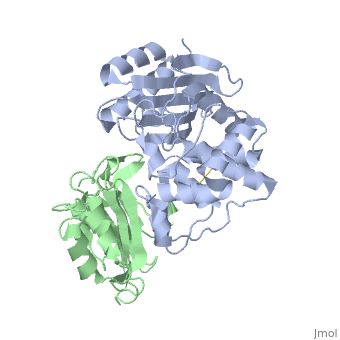
| - | + | <StructureSection load='2g2u' size='350' side='right' caption='TEM1-β-lactamase (grey) complex with BLIP (green) (PDB code [[2g2u]]).' scene=''> | |
| - | The [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme enzyme] TEM1 [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta-lactamase β-lactamase] ([http://www.expasy.org/enzyme/3.5.2.6 EC 3.5.2.6]; <scene name='1s0w/Tem1-blip/11'>TEM1)</scene> and its protein inhibitor, <scene name='1s0w/Tem1-blip1/2'>β-lactamase inhibitor protein (BLIP)</scene> form a <scene name='1s0w/Tem1-blip/9'>complex</scene>. <scene name='1s0w/Tem1-blip1/4'>Overlap </scene> of the residues which participate in TEM1-BLIP interactions between: 1) [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiprotein_complex '''complex'''] of <font color='lime'><b>mutated BLIP (F142A) and wildtype TEM1 (lime; [[1s0w]])</b></font>; 2) '''complex''' of <font color='magenta'><b>the wildtype BLIP/wildtype TEM1 (magenta;</b></font> [[1jtg]]); 3) '''unbound''' [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wild_type wildtype] BLIP | + | The [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme enzyme] TEM1 [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta-lactamase β-lactamase] ([http://www.expasy.org/enzyme/3.5.2.6 EC 3.5.2.6]; <scene name='1s0w/Tem1-blip/11'>TEM1)</scene> and its protein inhibitor, <scene name='1s0w/Tem1-blip1/2'>β-lactamase inhibitor protein (BLIP)</scene> form a <scene name='1s0w/Tem1-blip/9'>complex</scene>. <scene name='1s0w/Tem1-blip1/4'>Overlap </scene> of the residues which participate in TEM1-BLIP interactions between: 1) [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiprotein_complex '''complex'''] of <font color='lime'><b>mutated BLIP (F142A) and wildtype TEM1 (lime; [[1s0w]])</b></font>; 2) '''complex''' of <font color='magenta'><b>the wildtype BLIP/wildtype TEM1 (magenta;</b></font> [[1jtg]]); 3) '''unbound''' [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wild_type wildtype] BLIP<ref name="Nature">PMID:8145854</ref>.and '''unbound''' wildtype TEM1 ([[1btl]]), <font color='orange'><b>these two structures colored orange</b></font>). T marks residues of TEM1 and B of BLIP. The distance between TEM Glu-104 and BLIP Lys-74 is marked for the wildtype ([[1jtg]]) and mutated (F142A, [[1s0w]]) TEM1-BLIP '''complex''' structures<ref name="PNAS">PMID:15618400</ref><ref name="Nature" />. |
| - | + | ||
| - | The TEM1–BLIP in the KFYEY [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mutation mutant] structure ([[1xxm]]) is <scene name='1xxm/Tem1_blip/6'>overlaid</scene> on the wildtype complex ([[1jtg]]) structure. Mutated <font color='red'><b>TEM1</b></font> is shown in red, <font color='lime'><b>BLIP</b></font> (lime) (1xxm) , wildtype <font color='black'><b>TEM1</b></font> (yellow) and <font color='orange'><b>BLIP</b></font> ([[1jtg]]) in <font color='orange'><b>orange</b></font>, respectively. <font color='blueviolet'><b>Mutated BLIP residues ('''K'''74A, '''F'''142A, '''Y'''143A) are colored in blue-violet</b></font>, TEM1 residues <font color='blue'><b>E104</b></font> and <font color='blue'><b>Y105</b></font>, where mutations to alanines were performed (''i.g.'' E104A, Y105A), are colored <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font> and corresponding to them alanines <font color='magenta'><b>A104</b></font> and <font color='magenta'><b>A105</b></font> are colored <font color='magenta'><b>magenta</b></font> in the multiple mutant complex ('''KFYEY'''). These two structures are very similar. All-atom RMS deviation (RMSD) between the structures of the wildtype and the '''KFYEY''' mutant is 0.37 Å | + | The TEM1–BLIP in the KFYEY [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mutation mutant] structure ([[1xxm]]) is <scene name='1xxm/Tem1_blip/6'>overlaid</scene> on the wildtype complex ([[1jtg]]) structure. Mutated <font color='red'><b>TEM1</b></font> is shown in red, <font color='lime'><b>BLIP</b></font> (lime) (1xxm) , wildtype <font color='black'><b>TEM1</b></font> (yellow) and <font color='orange'><b>BLIP</b></font> ([[1jtg]]) in <font color='orange'><b>orange</b></font>, respectively. <font color='blueviolet'><b>Mutated BLIP residues ('''K'''74A, '''F'''142A, '''Y'''143A) are colored in blue-violet</b></font>, TEM1 residues <font color='blue'><b>E104</b></font> and <font color='blue'><b>Y105</b></font>, where mutations to alanines were performed (''i.g.'' E104A, Y105A), are colored <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font> and corresponding to them alanines <font color='magenta'><b>A104</b></font> and <font color='magenta'><b>A105</b></font> are colored <font color='magenta'><b>magenta</b></font> in the multiple mutant complex ('''KFYEY'''). These two structures are very similar. All-atom RMS deviation (RMSD) between the structures of the wildtype and the '''KFYEY''' mutant is 0.37 Å<ref name='PNAS' /> |
| - | + | The <scene name='2b5r/Bound_unbound/3'>TEM1-BLIP</scene> complex where BLIP residues of the <font color='blue'><b>bound</b></font> structure are colored <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font> and of the <font color='cyan'><b>unbound</b></font> are in <font color='cyan'><b>cyan</b></font>. TEM1 residues from the <font color='red'><b>bound complex</b></font> are in <font color='red'><b>red</b></font> and from the <font color='black'><b>unbound structure</b></font> in yellow. <font color='blue'><b>BLIP</b></font> and <font color='red'><b>TEM1</b></font> residues are labeled <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font> and <font color='red'><b>red</b></font>. The <scene name='2b5r/Bound_unbound/4'>interface</scene> between BLIP and TEM1 was divided into six interface clusters (<scene name='2b5r/C1/2'>C1</scene>, <scene name='2b5r/C2/3'>C2</scene>, <scene name='2b5r/C3/2'>C3</scene>, <scene name='2b5r/C4/3'>C4</scene>, <scene name='2b5r/C5/2'>C5</scene>, <scene name='2b5r/C6/2'>C6</scene>). Superpositions of these clusters from TEM1–BLIP (complex-[[1jtg]]), TEM1 (unbound-[[1btl]]) and BLIP (unbound<ref name='Nature' /> structures are shown. <scene name='2b5r/C1mut/2'>Overlap</scene> of cluster C1 from TEM1-BLIP wt, mutant and unbound structures (<font color='red'><b>TEM1<sub>wt</sub></b></font>-<font color='blue'><b>BLIP<sub>wt</sub></b></font> complex, <font color='lime'><b>TEM1<sub>wt</sub>-BLIP<sub>D49A</sub></b></font>, <font color='black'><b>unbound TEM1</b></font> (yellow), and <font color='cyan'><b>unbound BLIP</b></font>). <font color='blue'><b>D49 in BLIP</b></font> is located in the center of C1, surrounded by <font color='red'><b>4 TEM1 residues</b></font>. The <font color='blue'><b>D49A mutation</b></font> (''i.e.'' removal of a side chain) does not cause structural change in the TEM1-BLIP complex. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | The <scene name='2b5r/Bound_unbound/3'>TEM1-BLIP</scene> complex where BLIP residues of the <font color='blue'><b>bound</b></font> structure are colored <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font> and of the <font color='cyan'><b>unbound</b></font> are in <font color='cyan'><b>cyan</b></font>. TEM1 residues from the <font color='red'><b>bound complex</b></font> are in <font color='red'><b>red</b></font> and from the <font color='black'><b>unbound structure</b></font> in yellow. <font color='blue'><b>BLIP</b></font> and <font color='red'><b>TEM1</b></font> residues are labeled <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font> and <font color='red'><b>red</b></font>. The <scene name='2b5r/Bound_unbound/4'>interface</scene> between BLIP and TEM1 was divided into six interface clusters (<scene name='2b5r/C1/2'>C1</scene>, <scene name='2b5r/C2/3'>C2</scene>, <scene name='2b5r/C3/2'>C3</scene>, <scene name='2b5r/C4/3'>C4</scene>, <scene name='2b5r/C5/2'>C5</scene>, <scene name='2b5r/C6/2'>C6</scene>). Superpositions of these clusters from TEM1–BLIP (complex-[[1jtg]]), TEM1 (unbound-[[1btl]]) and BLIP (unbound | + | |
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| - | To analyze the contribution of non-alanine mutations, E104Y and Y105N in the TEM1 protein were constructed. These residues are polar and have a similar size, hence no major structural changes are expected for these mutants. The complex structure of TEM1 E104Y-Y105N (TEM1<sub>YN</sub>) with BLIP<sub>wt</sub> was solved ([[2b5r]]). The YN mutation caused only small reduction of binding energy (4.2 kJ/mol), which is slightly less then that obtained for the alanine substitutions of these residues. The <scene name='2b5r/Superpos/1'>superposition</scene> of <font color='magenta'><b>TEM1<sub>wt</sub></b></font>-<font color='black'><b>BLIP<sub>wt</sub></b></font> (yellow) complex ([[1jtg]]; <font color='magenta'><b>TEM1 colored in magenta;</b></font> <font color='black'><b>BLIP in yellow</b></font>) with <font color='lime'><b>TEM1<sub>YN</sub> (colored in lime)</b></font> - <font color='pink'><b>BLIP<sub>wt</sub> (pink)</b></font> complex ([[2b5r]]). Only a <scene name='2b5r/Superposition/12'>minor change</scene> <font color='orange'><b>(colored orange)</b></font> in <scene name='2b5r/Superpos/2'>TEM1<sub>YN</sub></scene> was observed. But, these small changes in TEM1 sequence lead to a major local <scene name='2b5r/Blip/3'>backbone rearrangement</scene> of the <scene name='2b5r/Blip/4'>hairpin loop</scene> between <font color='blue'><b>residues 46–53</b></font> in <font color='black'><b>BLIP</b></font> (yellow). This rearrangement of the <font color='red'><b>loop</b></font> is not observed in the <font color='pink'><b>unbound BLIP</b></font> structure. This shows that the rearrangement of BLIP was caused by the TEM1 mutations, resulting in a new low energy state. <scene name='2b5r/Superpos/3'>Superposition</scene> of residues in wt and mutant complexes near the BLIP 46-53 loop. TEM1 <font color='cyan'><b>wt E104 and Y105 are colored cyan</b></font>, while <font color='orange'><b>mutant E104Y and Y105N are colored orange</b></font>. BLIP residues colored in <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font> and <font color='red'><b>red</b></font> in the <font color='blue'><b>wt</b></font> and <font color='red'><b>mutant</b></font> complexes | + | To analyze the contribution of non-alanine mutations, E104Y and Y105N in the TEM1 protein were constructed. These residues are polar and have a similar size, hence no major structural changes are expected for these mutants. The complex structure of TEM1 E104Y-Y105N (TEM1<sub>YN</sub>) with BLIP<sub>wt</sub> was solved ([[2b5r]]). The YN mutation caused only small reduction of binding energy (4.2 kJ/mol), which is slightly less then that obtained for the alanine substitutions of these residues. The <scene name='2b5r/Superpos/1'>superposition</scene> of <font color='magenta'><b>TEM1<sub>wt</sub></b></font>-<font color='black'><b>BLIP<sub>wt</sub></b></font> (yellow) complex ([[1jtg]]; <font color='magenta'><b>TEM1 colored in magenta;</b></font> <font color='black'><b>BLIP in yellow</b></font>) with <font color='lime'><b>TEM1<sub>YN</sub> (colored in lime)</b></font> - <font color='pink'><b>BLIP<sub>wt</sub> (pink)</b></font> complex ([[2b5r]]). Only a <scene name='2b5r/Superposition/12'>minor change</scene> <font color='orange'><b>(colored orange)</b></font> in <scene name='2b5r/Superpos/2'>TEM1<sub>YN</sub></scene> was observed. But, these small changes in TEM1 sequence lead to a major local <scene name='2b5r/Blip/3'>backbone rearrangement</scene> of the <scene name='2b5r/Blip/4'>hairpin loop</scene> between <font color='blue'><b>residues 46–53</b></font> in <font color='black'><b>BLIP</b></font> (yellow). This rearrangement of the <font color='red'><b>loop</b></font> is not observed in the <font color='pink'><b>unbound BLIP</b></font> structure. This shows that the rearrangement of BLIP was caused by the TEM1 mutations, resulting in a new low energy state. <scene name='2b5r/Superpos/3'>Superposition</scene> of residues in wt and mutant complexes near the BLIP 46-53 loop. TEM1 <font color='cyan'><b>wt E104 and Y105 are colored cyan</b></font>, while <font color='orange'><b>mutant E104Y and Y105N are colored orange</b></font>. BLIP residues colored in <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font> and <font color='red'><b>red</b></font> in the <font color='blue'><b>wt</b></font> and <font color='red'><b>mutant</b></font> complexes<ref name="JMB">PMID:17070843</ref>. |
| + | See also [[Journal:Structure:1|Promiscuous Protein Binding as a Function of Protein Stability]] | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | ==3D structures of β-lactamase inhibitor protein== | ||
| + | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| + | *β-lactamase inhibitor protein | ||
| - | + | **[[3gmu]], [[3gmx]], [[3gmy]] - ScBLIP – ''Streptomyces clavuligerus''<br /> | |
| + | **[[3gmv]] - SeBLIP I – ''Streptomyces exfoliates''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3qi0]] - SeBLIP II | ||
| - | + | *β-lactamase inhibitor protein complex with β-lactamase | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | **[[1jtd]] – SeBLIP II + TEM-1 β-lactamase<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3gmw]] - SeBLIP I + TEM-1 β-lactamase<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1jtg]], [[2b5r]] - SeBLIP + TEM-1 β-lactamase (mutant)<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1s0w]] - ScBLIP (mutant) + TEM-1 β-lactamase<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1xxm]] - ScBLIP (mutant) + TEM-1 β-lactamase (mutant) <br /> | ||
| + | **[[2g2u]] - ScBLIP + SHV-1 β-lactamase<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2g2w]], [[3n4i]] - ScBLIP + SHV-1 β-lactamase (mutant) <br /> | ||
| + | **[[3c4o]], [[3c4p]] - ScBLIP (mutant) + SHV-1 β-lactamase<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3c7u]], [[3c7v]] - ScBLIP + TEM-1 β-lactamase (mutant) <br /> | ||
| + | **[[3e2k]] - ScBLIP + KPC-2 β-lactamase<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3e2l]] - ScBLIP + KPC-2 β-lactamase (mutant) <br /> | ||
| + | **[[7s5s]] - ScBLIP + Ec β-lactamase<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3qhy]] - SeBLIP II + BLA-1 β-lactamase<br /> | ||
| + | }} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| - | + | <references /> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of β-lactamase inhibitor protein
Updated on 14-December-2023
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Strynadka NC, Jensen SE, Johns K, Blanchard H, Page M, Matagne A, Frere JM, James MN. Structural and kinetic characterization of a beta-lactamase-inhibitor protein. Nature. 1994 Apr 14;368(6472):657-60. PMID:8145854 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/368657a0
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Reichmann D, Rahat O, Albeck S, Meged R, Dym O, Schreiber G. The modular architecture of protein-protein binding interfaces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Jan 4;102(1):57-62. Epub 2004 Dec 23. PMID:15618400
- ↑ Reichmann D, Cohen M, Abramovich R, Dym O, Lim D, Strynadka NC, Schreiber G. Binding hot spots in the TEM1-BLIP interface in light of its modular architecture. J Mol Biol. 2007 Jan 19;365(3):663-79. Epub 2006 Oct 3. PMID:17070843 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.09.076
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Categories: Topic Page | Escherichia coli | Protein complex | Streptomyces clavuligerus | ISPC, Israel Structural Proteomics Center. | Reichman, D. | Schreiber, G. | Beta-lactamase inhibitor protein | Blip | ISPC | Israel Structural Proteomics Center | Protein-protein complex | Structural genomic | Tem-1 beta-lactamase | Beta-lactamase | Albeck, S. | Dym, O. | Meged, R. | Rahat, O. | Beta-2 lactamase inhibitor protein | Jelsch, C. | Masson, J M. | Mourey, L. | Samama, J P. | Hydrolase